Question: anser questions 9 and 10 Below, I give you multiple problems all based on a single probabilistic graphical model. P(N=Yes) P(N=No) 0.8 0.2 P(S=Yes) P(S=No)
anser questions 9 and 10
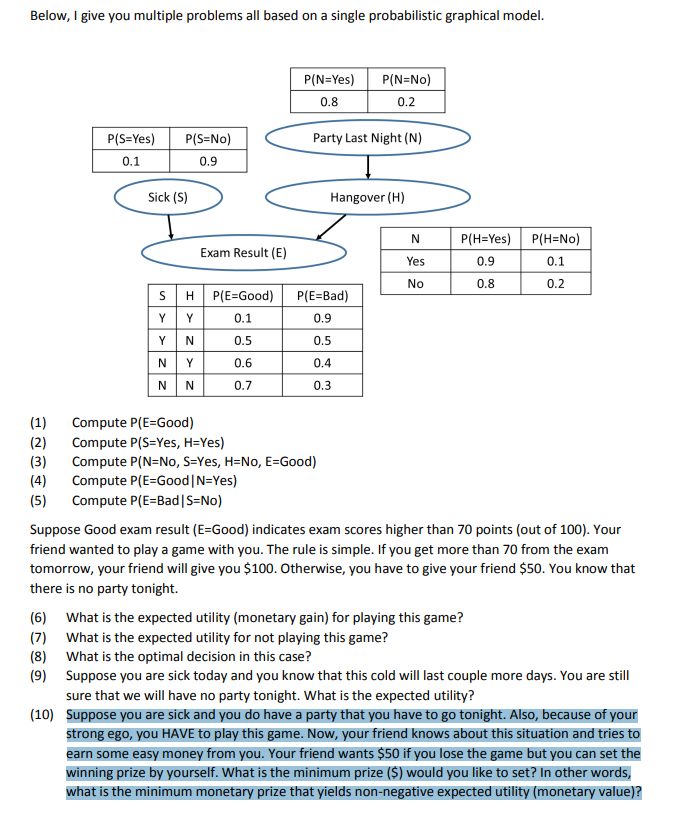
Below, I give you multiple problems all based on a single probabilistic graphical model. P(N=Yes) P(N=No) 0.8 0.2 P(S=Yes) P(S=No) Party Last Night (N) 0.1 0.9 Sick (S) Hangover (H) N P(H=Yes) P(H=No) Exam Result (E) Yes 0.9 0.1 No 0.8 0.2 S H P(E=Good) P(E=Bad) 0.1 0.9 N 0.5 0.5 0.6 0.4 N N 0.7 0.3 (1) Compute P(E=Good) (2) Compute P(S=Yes, H=Yes) (3 ) Compute P(N=No, S=Yes, H=No, E=Good) (4) Compute P(E=Good | N=Yes) (5) Compute P(E=Bad | S=No) Suppose Good exam result (E=Good) indicates exam scores higher than 70 points (out of 100). Your friend wanted to play a game with you. The rule is simple. If you get more than 70 from the exam tomorrow, your friend will give you $100. Otherwise, you have to give your friend $50. You know that there is no party tonight. (6) What is the expected utility (monetary gain) for playing this game? (7) What is the expected utility for not playing this game? (8) What is the optimal decision in this case? (9) Suppose you are sick today and you know that this cold will last couple more days. You are still sure that we will have no party tonight. What is the expected utility? (10) Suppose you are sick and you do have a party that you have to go tonight. Also, because of your strong ego, you HAVE to play this game. Now, your friend knows about this situation and tries to earn some easy money from you. Your friend wants $50 if you lose the game but you can set the winning prize by yourself. What is the minimum prize ($) would you like to set? In other words, what is the minimum monetary prize that yields non-negative expected utility (monetary value)
Step by Step Solution
There are 3 Steps involved in it

Get step-by-step solutions from verified subject matter experts


