Question: Answer the deliverables after reading the information below. Deliverables 1. Use the 10-Strike Software to draw a map of your home network or some other


Answer the deliverables after reading the information below.
Deliverables 1. Use the 10-Strike Software to draw a map of your home network or some other network. Describe two to five components on your map just like the example in the textbook shows. 2. Use the System Information and provide additional information (e.g., MAC address and card manufacturer) about at least two devices on your network.
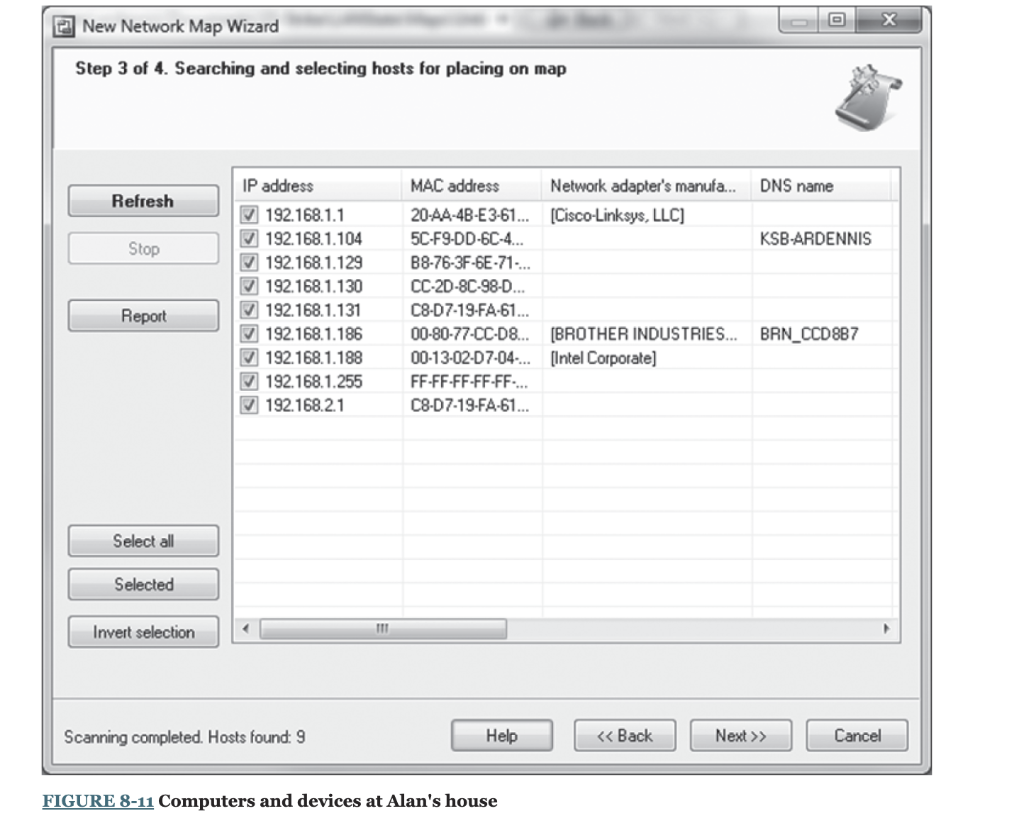
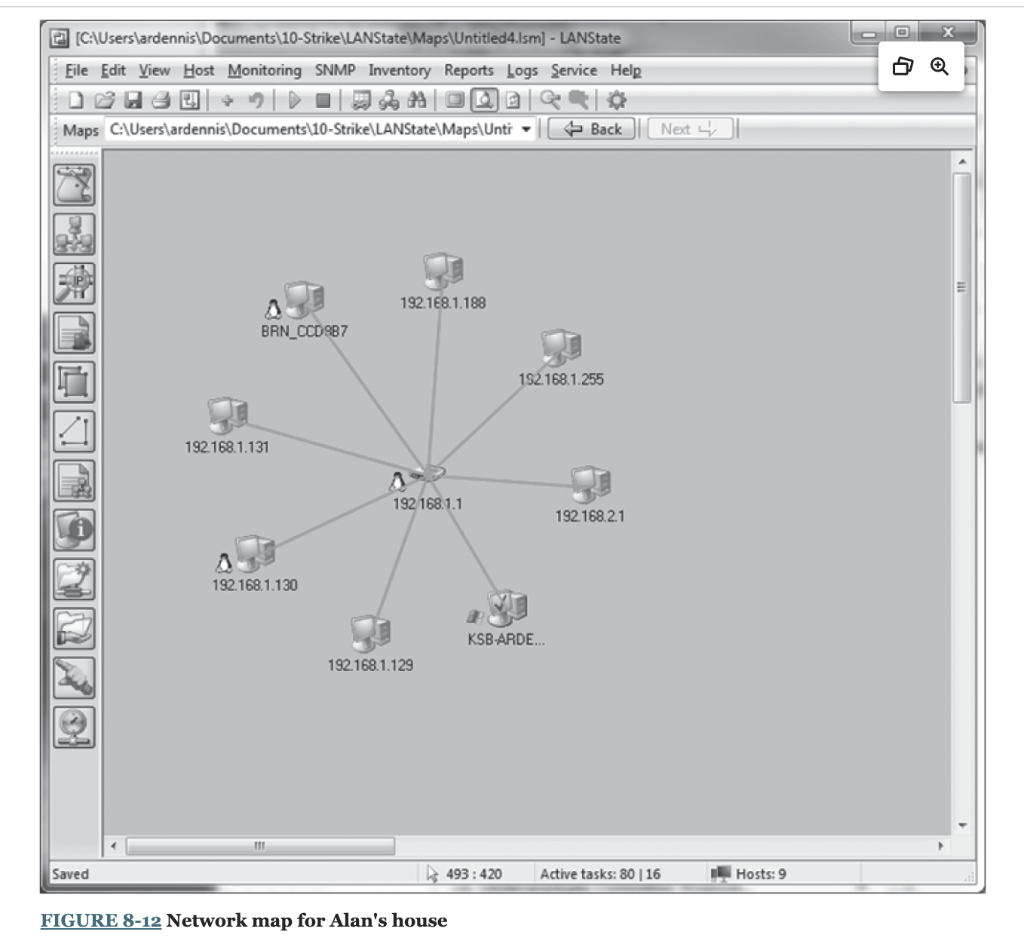
Network mapping software enables you to generate a map of the computers on all the LANs connected to a backbone. There are many good network mapping packages. Two of my favorites are LANState and Network Topology Mapper (www.solarwinds.cometwork-topologymapper.aspx). LANState is simpler to use but works best for small networks. Network Topology Mapper is more complex but can map large networks. This activity will focus on LANState. Mapping a Small Network The first step is to download and install LANState. A demo version of the software is available free of charge from 10-Strike Software (www.10-strike.com/lanstate). You begin by creating a new network map; choose File and then select the Map Creation Wizard. Then choose Scan IP address range and click Next. You will be asked to enter an address range. Choose some range, ideally the address range of a small network. I choose to use my home network range (192.168.1.1 through 192.168.2.254), which has two wireless routers (192.168.1.1 and 192.168.2.1). After you have added the address range to scan, click Next. Step 2 is to select how you will detect the devices on your network. The most common approach is to use an ICMP ping, which was discussed in Chapter 5. This approach sends an ICMP to each possible address in the range you specified. Not all computers are configured to respond to pings for security reasons, so this approach may not reveal all the computers and devices in your network. Make sure that the box in front of ICMP Ping is checked. The second approach is to send an ARP request for every computer in the address range you specified (see Chapter 5 ). The advantage of this approach is that every device will respond to an ARP request. The disadvantage is that you can only use ARPs for devices and computers in your same subnet. Make sure that the box in front of ARP ping is checked. To speed up your network, make sure the box in front of Search SNMP hosts is not checked. SNMP is a network management protocol that we will discuss in Chapter 12. If you're using a small network, it probably does not have SNMP. If you're using a large network that uses SNMP, you probably don't have the password required (unless you're the network manager). Click Next, and after 10-20 seconds, you should see a list of devices and computers that were discovered. Figure 8-11 shows the small network in Alan's house. I have a router (192.168.1.1) that connects a number of computers to the Internet. I also have a second wireless access router (192.168.2.1) and a printer (192.168.1.186). When I did this map, four computers and my networked TV were turned on and responded to LANState's pings (192.168.1.104, 192.168.1.129, 192.168.1.130, 192.168.131, and 192.168.1.188). You will also see that the broadcast address of 192.168.1.255 showed up, although there is no device on this address. Computers and devices that are not turned on do not respond to the pings and therefore are not mapped. Because I use dynamic addressing, the addresses of my computers will change every time I turn them on. Click Next and the network map will be shown. See Figure 8-12. You can also left-click on any device and choose System Information and General to learn more about that device. Figure 8-13 also shows the information about one computer (192.168.1.188). It shows the MAC address (i.e., the Ethernet address), the card manufacturer, and the DNS name (i.e., application layer address) for this computer. Step 3 of 4. Searching and selecting hosts for placing on map Scanning completed. Hosts found: 9 FIGURE 8-11 Computers and devices at Alan's house FIGURE 8-12 Network map for Alan's house FIGURE 8-13 System information for 192.168.1.188
Step by Step Solution
There are 3 Steps involved in it

Get step-by-step solutions from verified subject matter experts


