Question: Answer the following problem. Show step-by-step solution and detailed graph are important. Note: Use Equilateral Triangle (Hunter-Nash Method) 1. Ternary acetic acid-benzene-water mixture. The liquid-liquid
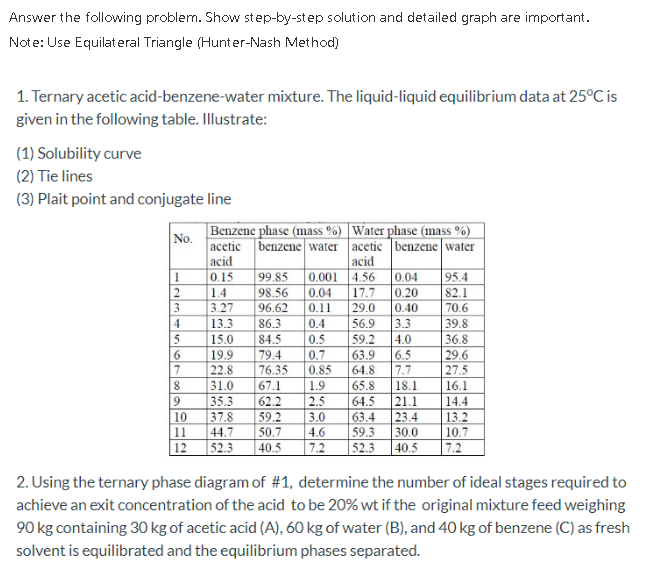
Answer the following problem. Show step-by-step solution and detailed graph are important. Note: Use Equilateral Triangle (Hunter-Nash Method) 1. Ternary acetic acid-benzene-water mixture. The liquid-liquid equilibrium data at 25C is given in the following table. Illustrate: (1) Solubility curve (2) Tie lines (3) Plait point and conjugate line No. Benzene phase (mass %) Water phase (mass %) acetic benzene water acetic benzene water acid acid 1 0.15 99.85 0.001 4.56 0.04 95.4 2 1.4 98.56 0.04 17.7 0.20 82.1 3 3.27 96.62 0.11 29.0 0.40 70.6 4 13.3 86.3 0.4 56.9 3.3 39.8 5 15.0 84.5 0.5 59.2 4.0 36.8 6 19.9 79.4 0.7 63.9 29.6 7 22.8 76.35 0.85 64.8 7.7 27.5 8 31.0 67.1 1.9 65.8 18.1 16.1 9 35.3 62.2 2.5 64.5 21.1 14.4 10 37.8 59.2 3.0 63.4 23.4 13.2 11 44.7 50.7 4.6 59.3 30.0 10.7 12 52.3 40.5 52.3 40.5 22 Polololo 6.5 OK 72 7.2 2. Using the ternary phase diagram of #1, determine the number of ideal stages required to achieve an exit concentration of the acid to be 20% wt if the original mixture feed weighing 90 kg containing 30 kg of acetic acid (A), 60 kg of water (B), and 40 kg of benzene (C) as fresh solvent is equilibrated and the equilibrium phases separated
Step by Step Solution
There are 3 Steps involved in it

Get step-by-step solutions from verified subject matter experts


