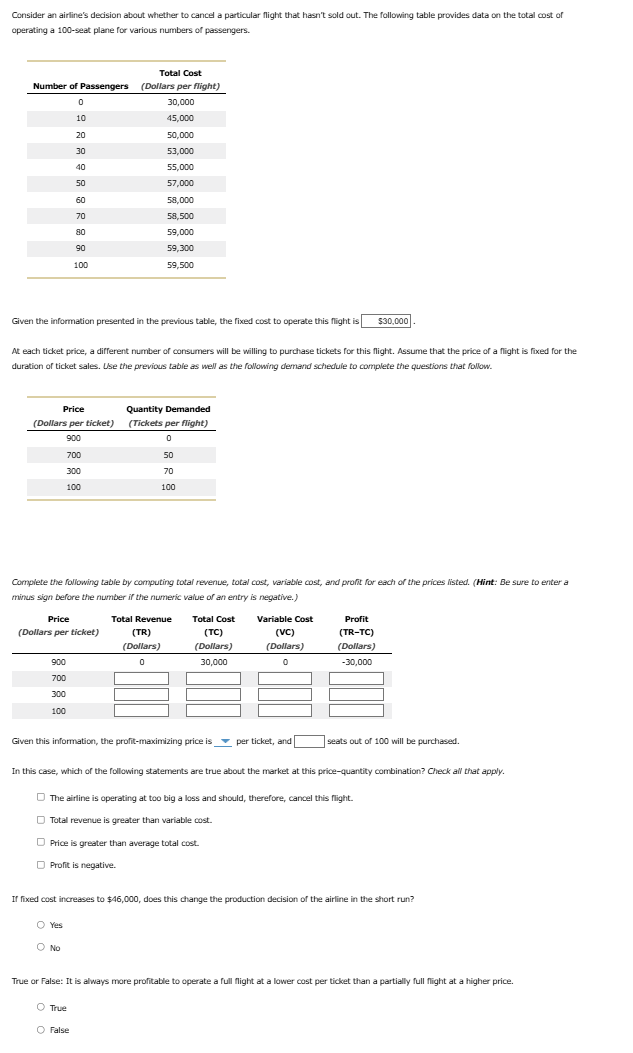
Question: Answer the question. Consider an airline's decision about whether to cancel a particular flight that hasn't sold out. The following table provides data on the
Answer the question.
Consider an airline's decision about whether to cancel a particular flight that hasn't sold out. The following table provides data on the total cost of operating a 100-seat plane for various numbers of passengers. Total Cost Number of Passengers (Dollars per flight) 30,000 10 45,000 20 50,000 30 53,000 40 55,000 50 57,000 60 58,000 70 58,500 59,000 90 59,300 100 59,500 Given the information presented in the previous table, the fixed cost to operate this flight is $30,000 At each ticket price, a different number of consumers will be willing to purchase tickets for this flight. Assume that the price of a flight is fixed for the duration of ticket sales. Use the previous table as well as the following demand schedule to complete the questions that follow. Price Quantity Demanded (Dollars per ticket) "Tickets per flight) 900 0 700 50 300 70 100 100 Complete the following table by computing total revenue, total cost, variable cost, and profit for each of the prices listed. (Hint: Be sure to enter a minus sign before the number if the numeric value of an entry is negative.) Price Total Revenue Total Cost Variable Cost Profit (Dollars per ticket) (TR) (TC) (VC) (TR-TC) "Dollars) "Dollars) Dollars) (Dollars) 900 0 30,000 0 30,000 700 300 100 Given this information, the profit-maximizing price is _ per ticket, and seats out of 100 will be purchased. In this case, which of the following statements are true about the market at this price-quantity combination? Check all that apply. The airline is operating at too big a loss and should, therefore, cancel this flight. D Total revenue is greater than variable cost. Price is greater than average total cost. O Profit is negative. If fixed cost increases to $46,000, does this change the production decision of the airline in the short run? Yes O No True or False: It is always more profitable to operate a full flight at a lower cost per ticket than a partially full flight at a higher price. O True O False