Question: answer these questions, thanks. Question 2 10 points Save Ans' Globe Industries manufactures a product used In the Telecom Industry. Ted Dawson, the company's purchasing
answer these questions, thanks.
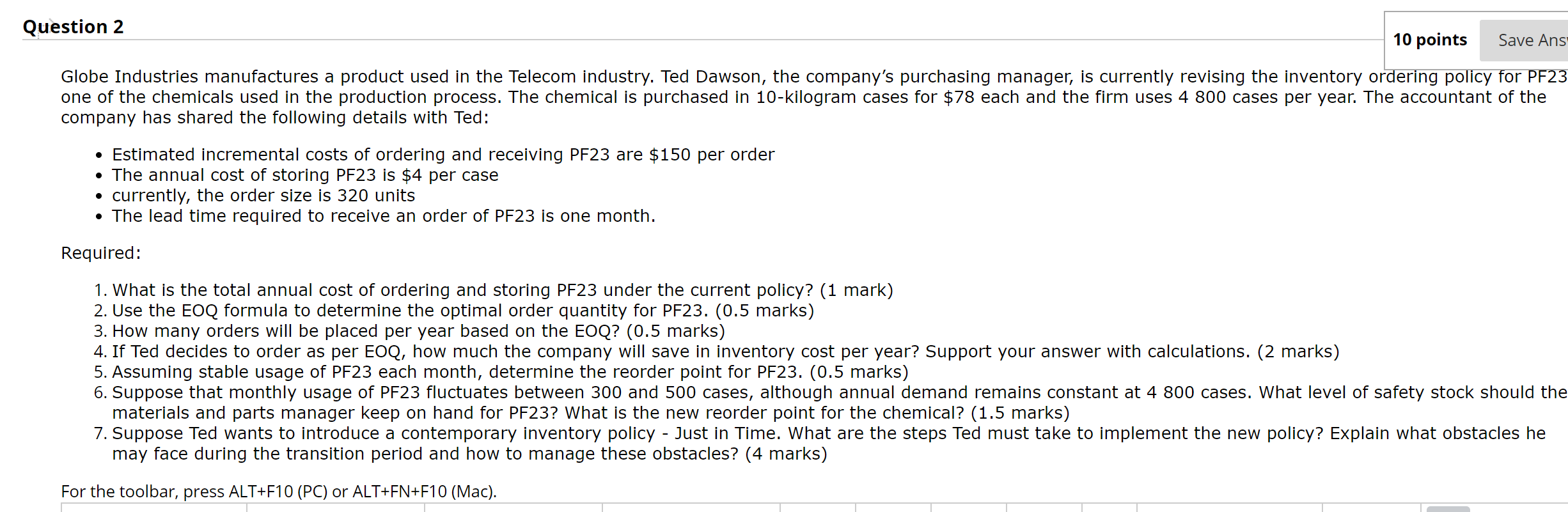

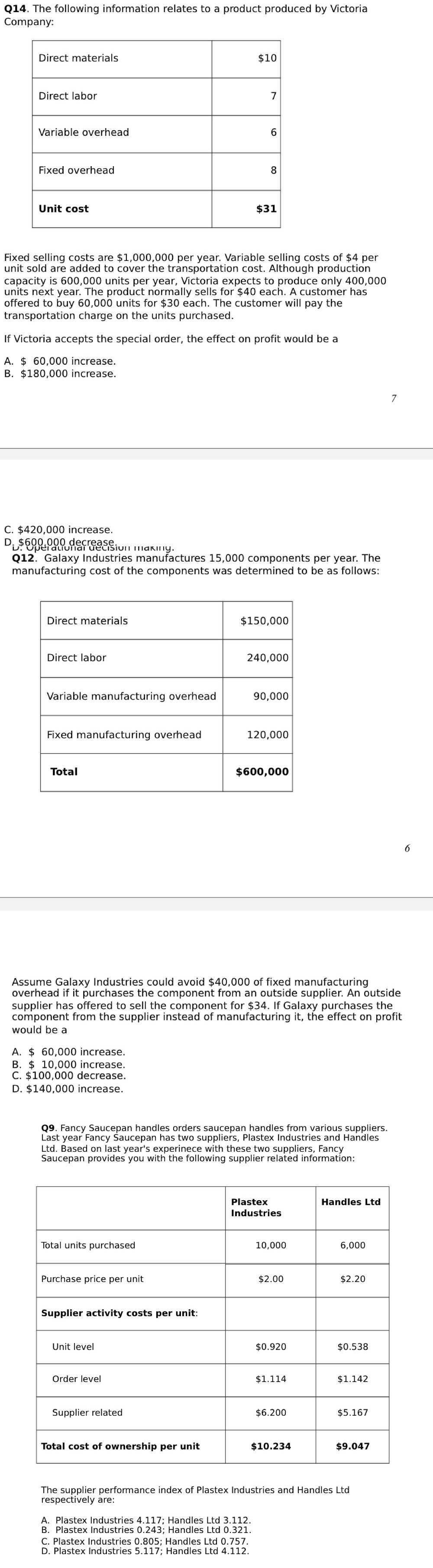
Question 2 10 points Save Ans' Globe Industries manufactures a product used In the Telecom Industry. Ted Dawson, the company's purchasing manager, Is currently revlslng the Inventory orderlng po Icy for PF23 one of the chemicals used In the production process. The chemical Is purchased In 10kilogram cases for $78 each and the firm uses 4 800 cases per year. The accountant of the company has shared the following details with Ted: Estimated Incremental costs of ordering and receiving PF23 are $150 per order The annual cost of storing PF23 Is $4 per case currently, the order size is 320 units The lead time required to receive an order of PF23 is one month. Required: .What Is the total annual cost of ordering and storing PF23 under the current policy? (1 mark) . Use the EOQ formula to determine the optimal order quantity for PF23. (0.5 marks) . How many orders will be placed per year based on the EOQ? (0.5 marks) . If Ted decides to order as per EOQ, how much the company will save in inventory cost per year? Support your answer with calculations. (2 marks) .Assuming stable usage of PF23 each month, determine the reorder point for PF23. (0.5 marks) . Suppose that monthly usage of PF23 fluctuates between 300 and 500 cases, although annual demand remains constant at 4 800 cases. What level of safety stock should the materials and parts manager keep on hand for PF23? What Is the new reorder point for the chemical? (1.5 marks) 7. Suppose Ted wants to Introduce a contemporary Inventory policy Just In Time. What are the steps Ted must take to Implement the new policy? Explain what obstacles he may face during the transition period and how to manage these obstacles? (4 marks) C'IU'IbWN'I For the toolbar, press ALT+F10 (PC) or ALT+FN+F10 (Mac). I l 65. The managing director of H Limited is setting the production plan for the next financial year. H has a short andhas a shortage of skilled labour and wishes to maximise the profitability of the company. H manufactures three products X, Y and Z. There is 200 000 hours of skilled labour available in the year at a cost of $10 per hour. The following information relates to each product. X Z Selling price $50 $54 $84 Materials cost $10 $12 $20 Labour hours 2 2 Maximum demand 40 000 20 000 40 000 Assuming all relevant information is provided, in what order should H manufacture its products to maximise profit in the current year? A. Z then X B. X then Z C. X, Y then Z D. None of the given answers 66. A firm produces products X, Y and Z with contribution margins of $4, $5 and $10 respectively. The firm has only 5000 machine hours available for a particular period. Machine hours required for each of the products are 1, 1 and 5 hours respectively. Demand for the products is 1000 for X, 3000 for Y and 2000 for Z. How many units of each product will the firm produce? A. 2000 Z B. 1000 X, 3000 Y, 2000 Z C. 3000 Y, 1000 X, 200 Z D. 2000 Z, 3000 Y 67. C Limited manufactures specialist medical equipment. Recruitment and training of manufacturing staff is difficult and C's operations management estimates that only 160 000 hours of labour at a rate of $50 per hour will be available in the next financial year. The following details relate to C's planned production of three products X, Y and Z for the next 12 months. X Y Z Selling price $65 $315 $200 Materials cost $10 $50 $40 Labour hours Maximum demand 100 000 20 000 25 000 To maximise profits the products C should manufacture are: A. Y then Z. B. Y then Z, then X. C. X then Z. D. X then Z, then Y. 68. Karl's Kitchens is experimenting with different vinegars for sale on the domestic market. The contribution margins per carton for three types V1, V2 and V3 are $120, $100 and $150 respectively. The firm is constrained in terms of labour hours, and the labour hours required per carton of each type of vinegar is 2 hours, 1.5 hours and 3 hours respectively. Assume the firm has 2240 available labour hours per month, and the monthly demand is 1200 cartons of V1, 800 cartons of V2 and 300 cartons of V3. What is the product mix that will maximise profit? A. 800 V2, 520 V1 B. 300 V3, 670 V2 C. 1 200 V1, 800 V2, 300 V3 D. 1 120 V1 71. A firm has excess capacity, and has received an order for 50 000 units at $20 each over and above its normal production activity of 600 000 units. To meet this order, new equipment at a cost of $200 000 would have to be bought, and this equipment would have to be scrapped after the order had been filled. The firm currently sells for $50 per unit, has variable costs of $15.80, and fixed costs of $600 000. What is the additional profit (loss) for the firm if it accepts the order? A. Loss of $10 000 B. Profit of $40 000 C. Loss of $40 000 D. Profit of $10 000 72. A firm has excess capacity, and has received an order for 50 000 units at $20 each over and above its normal production activity of 600 000 units. To meet this order, new equipment at a cost of $200 000 would have to be bought, and this equipment would have to be scrapped after the order had been filled. The firm currently sells for $50 per unit, has variable costs of $15.80, and fixed costs of $600 000. Assuming the firm had been aggressively seeking the business of the customer who requested the special order, what would be the minimum price that the firm would be prepared to charge? A. $15.80 B. $50 C. $27.80 D. $19.80 76. Waverly Lid produces commercial grade washing machines. The Karewasher is currently selling for $2000 per unit. The company wants to introduce a new model, Supawasher, which uses less water per load. The comparative life-time costs of the two models are as follow: Karewasher Supawasher (S) (S) Estimated lifetime water usage cost 1400 1000 Estimated lifetime electricity cost 1200 1500 Estimated lifetime maintenance cost 600 400 The economic value of a Supawasher (ignore time value of money) is: $300. B $2300. C. $2900 . D. $4900. 77. Avocado Lid produces small electronic components for kitchen appliances. This year it expects to produce 10 000 units of component X. The variable manufacturing cost of component X is $2 per unit and the variable selling and administrative cost of component X is $3 per unit. In addition, to produce component X Avocado Lid incurs annual fixed manufacturing cost of $50 000 and annual fixed selling and administrative cost of $60 000. If the target profit is $2 per unit, and using cost plus pricing approach, the mark up percentage based on total variable costs is: A. 260%. B. 80%. C. C.63.6%. D. 12.5%. 78. Avocado Lid produces small electronic components for kitchen appliances. This year it expects to produce 10 000 units of component X. The variable manufacturing cost of component X represents 50% of its total costs. The target profit is $2 per unit. Using the cost-plus pricing approach based on total costs, the selling price per unit of component X is $20. If Avocado Lid decides to change its cost-plus pricing approach to base the mark up percentage on variable manufacturing costs, the selling price for each unit of component X will be: A. $10 B. $2 D. Not enough information is provided.014. The following information relates to a product produced by Victoria Company: Direct materials $10 Direct labor 7 Variable overhead 6 xed overhead 8 Unit cost $31 leed selling costs are $1,000,000 per year. Variable selling costs of $4 per unit sold are added to cover the transportation cost. Although production capacity is 600,000 units per year, Victoria expects to produce only 400,000 units next year. The product normally sells for $40 each A customer has offered to buy 60,000 units for $30 each. The customer will pay the transportation charge on the units purchased. If Victoria accepts the special order. the effect on prot would be a A. 3 60,000 increase. B. $130,000 increase. C. $420,000 increase. Dio ODD decrease. uplauullul ucLl>lulr \"mung. Q12. Galaxy Industries manufactures 15,000 components per year. The manufacturing cost of the components was determined to be as follows: Direct materials $150,000 Direct labor 240,000 Variable manufacturing overhead 90,000 Fixed manufacturing overhead 120,000 Total $600,000 Assume Galaxy Industries could avoid 540.000 affixed manufacturing overhead if it purchases the component from an outside supplier. An outside supplier has offered to sell the component for 534. If Galaxy purchases the component from the supplier instead of manufacturing it, the effect on profit would be a A. $ 60.000 increase. E. $ 10.000 increase. C. $100,000 decrease. D. $140,000 increase. Q9. Fancy Saucepan handles orders saucepan handles from various suppliers. Last year Fancy saucepan has two suppliers, Plastex Industrles and Handles Ltd. Based on last year's experinere with these two suppliers. Fancy Saucepan provides you With the following supplier related information: Plaster Handles Ltd Industries Total units purchased 10,000 6,000 Purchase price per unit $2.00 $2.20 Supplier activity costs per unit: Unlt level $0.920 $0.538 Order level $1.114 $1.142 Supplier related $6.200 $5.167 Total cost of ownership per unit $10.21! $9.047 The supplier performance index of Plastex Industries and Handles Ltd respectively are. A. Flastex Industries 4.117: Handles Ltd 3.112. E. Flastex Industries 0.243, Handles Ltd 0.321. C. Plastex Industries 0.805. Handles Ltd 0.757. D. Plaslex Industries 5.117; Handles Ltd 4.112
Step by Step Solution
There are 3 Steps involved in it

Get step-by-step solutions from verified subject matter experts


