Question: Answer true or false for each statement and explain why A. LDA is almost never used when we have more than two response classes B.
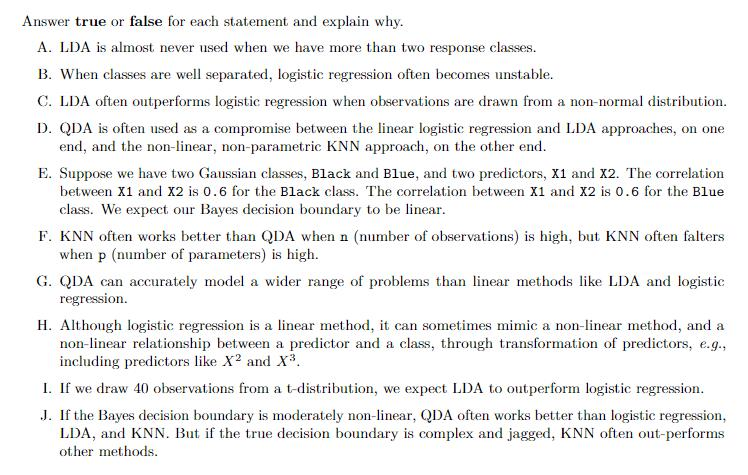
Answer true or false for each statement and explain why A. LDA is almost never used when we have more than two response classes B. When classes are well separated, logistic regression often becomes unstable. C. LDA often outperforms logistic regression when observations are drawn from a non-normal distribution D. QDA is often used as a compromise between the linear logistic regression and LDA approaches, on one end, and the non-linear, non-parametric KNN approach, on the other end. E. Suppose we have two Gaussian classes, Black and Blue, and two predictors, X1 and X2. The correlation between X1 and X2 is 0.6 for the Black class. The correlation between X1 and X2 is 0.6 for the Blue class. We expect our Bayes decision boundary to be linear F. KNN often works better than QDA when n (number of observations) is high, but KNN often falters when p (number of parameters) is high. QDA can accurately model a wider range of problems than linear methods like LDA and logistic regression H. Although logistic regression is a lnear method, it can sometimes mimic a non-linear method, and a non-linear relationship between a predictor and a class, through transformation of predictors, e.g., including predictors like X2 and X3 I. If we draw 40 observations from a t-distribution, we expect LDA to outperform logistic regression. J. If the Bayes decision boundary is moderately non-linear, QDA often works better than logistic regression LDA, and KNN. But if the true decision boundary is complex and jagged, KNN often out-performs other methods Answer true or false for each statement and explain why A. LDA is almost never used when we have more than two response classes B. When classes are well separated, logistic regression often becomes unstable. C. LDA often outperforms logistic regression when observations are drawn from a non-normal distribution D. QDA is often used as a compromise between the linear logistic regression and LDA approaches, on one end, and the non-linear, non-parametric KNN approach, on the other end. E. Suppose we have two Gaussian classes, Black and Blue, and two predictors, X1 and X2. The correlation between X1 and X2 is 0.6 for the Black class. The correlation between X1 and X2 is 0.6 for the Blue class. We expect our Bayes decision boundary to be linear F. KNN often works better than QDA when n (number of observations) is high, but KNN often falters when p (number of parameters) is high. QDA can accurately model a wider range of problems than linear methods like LDA and logistic regression H. Although logistic regression is a lnear method, it can sometimes mimic a non-linear method, and a non-linear relationship between a predictor and a class, through transformation of predictors, e.g., including predictors like X2 and X3 I. If we draw 40 observations from a t-distribution, we expect LDA to outperform logistic regression. J. If the Bayes decision boundary is moderately non-linear, QDA often works better than logistic regression LDA, and KNN. But if the true decision boundary is complex and jagged, KNN often out-performs other methods
Step by Step Solution
There are 3 Steps involved in it

Get step-by-step solutions from verified subject matter experts


