 answer what you can this is related to system dynamics.
answer what you can this is related to system dynamics.
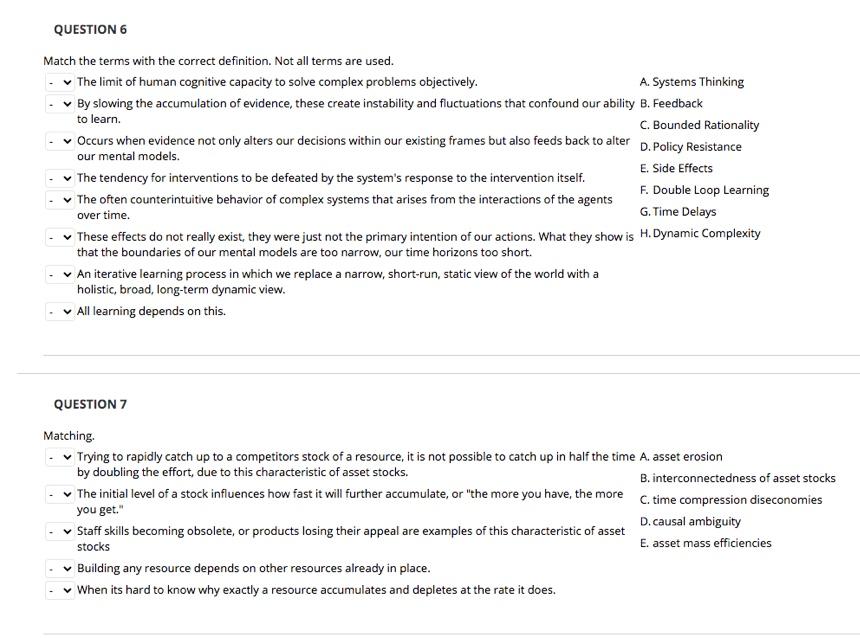
QUESTION 6 Match the terms with the correct definition. Not all terms are used. The limit of human cognitive capacity to solve complex problems objectively. A. Systems Thinking By slowing the accumulation of evidence, these create instability and fluctuations that confound our ability B. Feedback to learn. C. Bounded Rationality Occurs when evidence not only alters our decisions within our existing frames but also feeds back to alter D. Policy Resistance our mental models. E. Side Effects The tendency for interventions to be defeated by the system's response to the intervention itself. F. Double Loop Learning The often counterintuitive behavior of complex systems that arises from the interactions of the agents over time. G. Time Delays These effects do not really exist, they were just not the primary intention of our actions. What they show is H. Dynamic Complexity that the boundaries of our mental models are too narrow, our time horizons too short. An iterative learning process in which we replace a narrow, short-run, static view of the world with a holistic, broad, long-term dynamic view. All learning depends on this. QUESTION 7 Matching, Trying to rapidly catch up to a competitors stock of a resource, it is not possible to catch up in half the time A. asset erosion by doubling the effort, due to this characteristic of asset stocks. B. interconnectedness of asset stocks The initial level of a stock influences how fast it will further accumulate, or "the more you have, the more c.time compression diseconomies you get." D. causal ambiguity Staff skills becoming obsolete, or products losing their appeal are examples of this characteristic of asset stocks E. asset mass efficiencies Building any resource depends on other resources already in place. When its hard to know why exactly a resource accumulates and depletes at the rate it does. QUESTION 6 Match the terms with the correct definition. Not all terms are used. The limit of human cognitive capacity to solve complex problems objectively. A. Systems Thinking By slowing the accumulation of evidence, these create instability and fluctuations that confound our ability B. Feedback to learn. C. Bounded Rationality Occurs when evidence not only alters our decisions within our existing frames but also feeds back to alter D. Policy Resistance our mental models. E. Side Effects The tendency for interventions to be defeated by the system's response to the intervention itself. F. Double Loop Learning The often counterintuitive behavior of complex systems that arises from the interactions of the agents over time. G. Time Delays These effects do not really exist, they were just not the primary intention of our actions. What they show is H. Dynamic Complexity that the boundaries of our mental models are too narrow, our time horizons too short. An iterative learning process in which we replace a narrow, short-run, static view of the world with a holistic, broad, long-term dynamic view. All learning depends on this. QUESTION 7 Matching, Trying to rapidly catch up to a competitors stock of a resource, it is not possible to catch up in half the time A. asset erosion by doubling the effort, due to this characteristic of asset stocks. B. interconnectedness of asset stocks The initial level of a stock influences how fast it will further accumulate, or "the more you have, the more c.time compression diseconomies you get." D. causal ambiguity Staff skills becoming obsolete, or products losing their appeal are examples of this characteristic of asset stocks E. asset mass efficiencies Building any resource depends on other resources already in place. When its hard to know why exactly a resource accumulates and depletes at the rate it does
 answer what you can this is related to system dynamics.
answer what you can this is related to system dynamics. 



