Question: answer without explanation asap thanks Question 1 1 pts Please use the chart below - which plots the indirect quote for Japanese yen (the number



 answer without explanation asap thanks
answer without explanation asap thanks
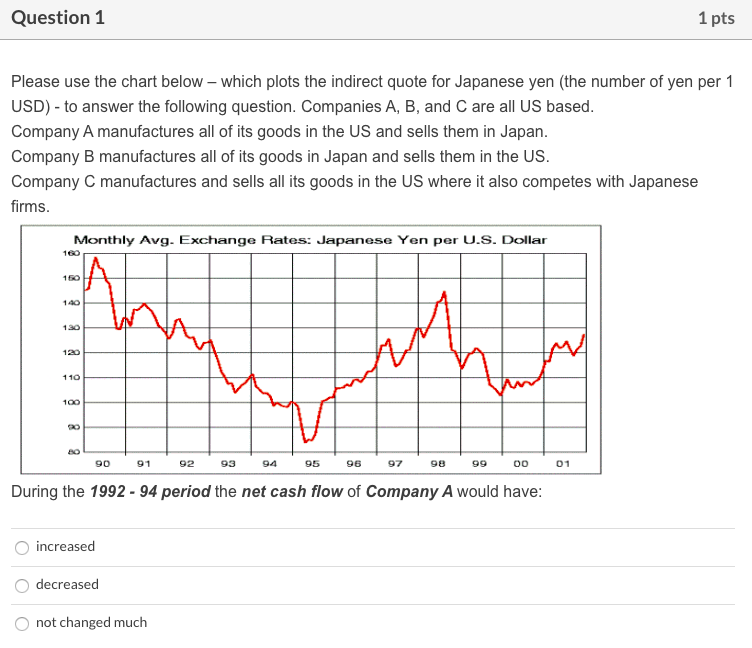
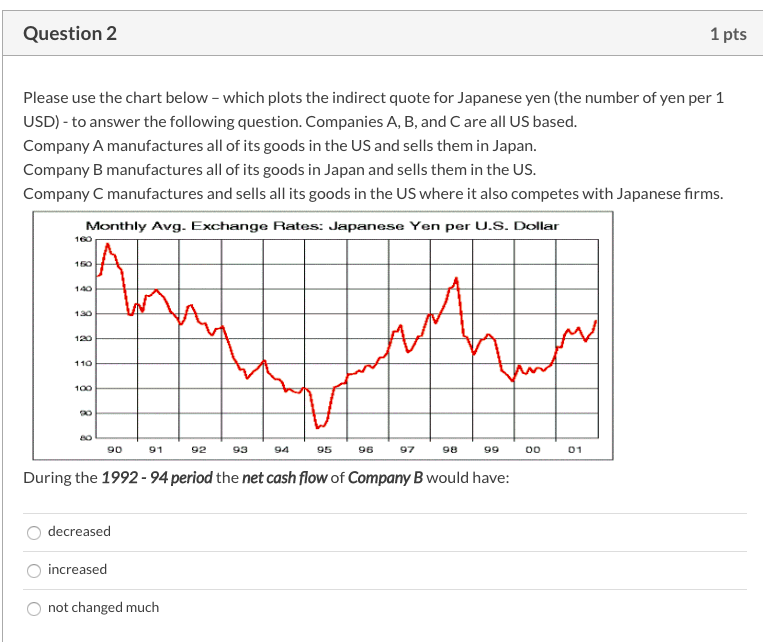
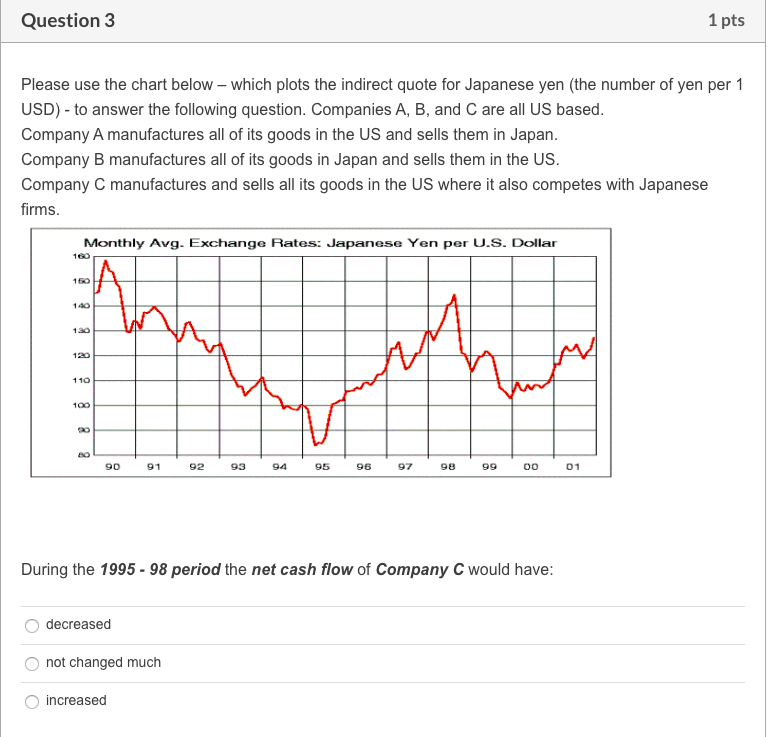
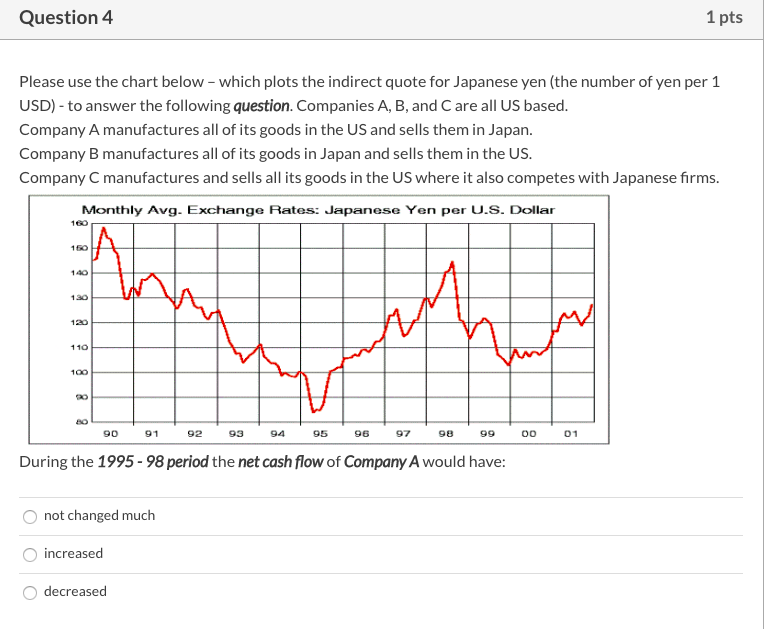
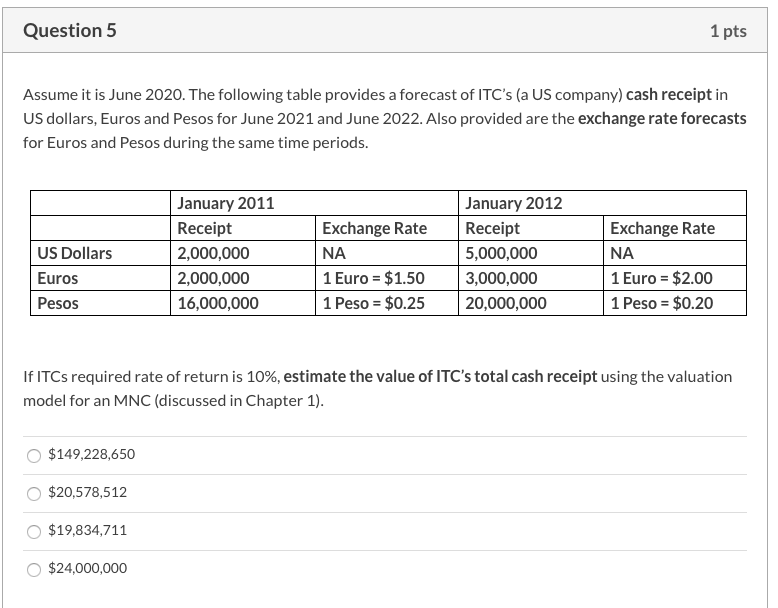
Question 1 1 pts Please use the chart below - which plots the indirect quote for Japanese yen (the number of yen per 1 USD) - to answer the following question. Companies A, B, and C are all US based. Company A manufactures all of its goods in the US and sells them in Japan. Company B manufactures all of its goods in Japan and sells them in the US. Company C manufactures and sells all its goods in the US where it also competes with Japanese firms. Monthly Avg. Exchange Rates: Japanese Yen per U.S. Dollar 160 140 130 120 110 100 20 90 91 92 93 94 95 96 97 98 99 00 01 During the 1992 - 94 period the net cash flow of Company A would have: increased decreased not changed much Question 2 1 pts Please use the chart below - which plots the indirect quote for Japanese yen (the number of yen per 1 USD) - to answer the following question. Companies A, B, and C are all US based. Company A manufactures all of its goods in the US and sells them in Japan. Company B manufactures all of its goods in Japan and sells them in the US. Company C manufactures and sells all its goods in the US where it also competes with Japanese firms. Monthly Avg. Exchange Rates: Japanese Yen per U.S. Dollar 160 140 120 110 100 20 8 90 91 92 93 94 95 96 97 98 99 00 01 During the 1992-94 period the net cash flow of Company B would have: decreased increased not changed much Question 3 1 pts Please use the chart below which plots the indirect quote for Japanese yen (the number of yen per 1 USD) - to answer the following question. Companies A, B, and C are all US based. Company A manufactures all of its goods in the US and sells them in Japan. Company B manufactures all of its goods in Japan and sells them in the US. Company C manufactures and sells all its goods in the US where it also competes with Japanese firms. Monthly Avg. Exchange Rates: Japanese Yen per U.S. Dollar 160 130 WA 120 110 100 20 90 91 92 93 94 95 96 97 98 00 01 During the 1995 - 98 period the net cash flow of Company C would have: decreased not changed much increased Question 4 1 pts Please use the chart below - which plots the indirect quote for Japanese yen (the number of yen per 1 USD) - to answer the following question. Companies A, B, and Care all US based. Company A manufactures all of its goods in the US and sells them in Japan. Company B manufactures all of its goods in Japan and sells them in the US. Company C manufactures and sells all its goods in the US where it also competes with Japanese firms. Monthly Avg. Exchange Rates: Japanese Yen per U.S. Dollar 140 130 120 110 100 8 90 91 92 93 94 95 96 97 98 99 00 01 During the 1995-98 period the net cash flow of Company A would have: not changed much increased decreased Question 5 1 pts Assume it is June 2020. The following table provides a forecast of ITC's (a US company) cash receipt in US dollars, Euros and Pesos for June 2021 and June 2022. Also provided are the exchange rate forecasts for Euros and Pesos during the same time periods. US Dollars Euros Pesos January 2011 Receipt 2,000,000 2,000,000 16,000,000 Exchange Rate NA 1 Euro = $1.50 1 Peso = $0.25 January 2012 Receipt 5,000,000 3,000,000 20,000,000 Exchange Rate NA 1 Euro = $2.00 1 Peso = $0.20 If ITCs required rate of return is 10%, estimate the value of ITC's total cash receipt using the valuation model for an MNC (discussed in Chapter 1). $149,228,650 $20,578,512 $19,834,711 $24,000,000 Question 6 1 pts If the price of Euro goes from $1.45 to $1.60 in one year, then during this time the exports of an US firm which primarily sells its products in Europe will: not change much decrease increase Question 7 1 pts If the price of the British Pounds goes from $1.85 to $1.35 in one year, then during this time the imports of an US firm which manufactures its goods in UK will: not change much decrease increase Question 8 1 pts Which one of the following is NOT a characteristic of the product cycle theory of international trade: Afirm expands overseas because land or/and labor cannot be moved A firm expands overseas because it wants to minimize costs A firm expands overseas because it wants to seek new markets A firm expands overseas because it wants to find raw material Question 9 1 pts Which theory proposes that the world economy will have more goods available at a reduced cost if each country specializes in producing a limited number of goods and trade them with one another? Imperfect market theory Contestable market theory Comparative advantage theory Product cycle theory Question 10 1 pts Please use this information to answer the following question. A typical Brazilian farmer can produce 15000 lbs of wheat or 750 lbs of potatoes per year. A typical Argentina farmer can produce 9000 lbs of wheat or 600 lbs of potatoes per year. Based on the information given, the theory of comparative advantage suggests that: Brazil will be a net importer of both wheat and potatoes from Argentina Brazil will be a net exporter of both wheat and potatoes to Argentina Brazil will be a net importer of potatoes from Argentina Brazil will be a net exporter of potatoes to Argentina
Step by Step Solution
There are 3 Steps involved in it

Get step-by-step solutions from verified subject matter experts


