Question: Apply Spreadsheet Design Principles (show formulas, color code, label, isolate variables, add comments, etc.) as you complete each template! Use analytic solver to complete each
Apply Spreadsheet Design Principles (show formulas, color code, label, isolate variables, add comments, etc.) as you complete each template! Use analytic solver to complete each spreadsheet in Microsoft excel.
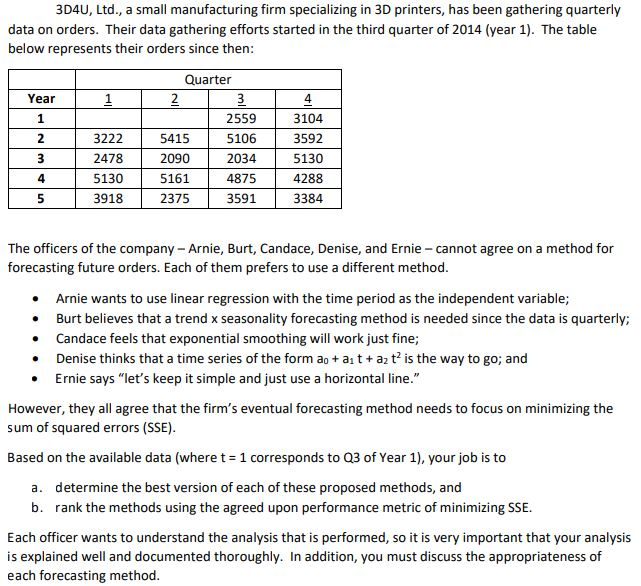
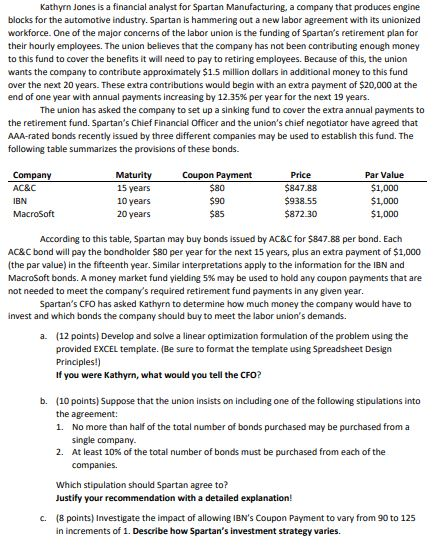

3D4U, Ltd., a small manufacturing firm specializing in 3D printers, has been gathering quarterly data on orders. Their data gathering efforts started in the third quarter of 2014 (year 1). The table below represents their orders since then: Quarter 2 Year 1 4 2559 3104 1 2 3222 5106 3592 5415 3 2478 2090 5130 2034 5130 4875 4 5161 4288 3918 2375 3591 3384 5 The officers of the company Arnie, Burt, Candace, Denise, and Ernie cannot agree on a method for forecasting future orders. Each of them prefers to use a different method. Arnie wants to use linear regression with the time period as the independent variable; Burt believes that a trend x seasonality forecasting method is needed since the data is quarterly; Candace feels that exponential smoothing will work just fine; Denise thinks that a time series of the form ao a t+ a2 t? is the way to go; and Ernie says "let's keep it simple and just use a horizontal line." However, they all agree that the firm's eventual forecasting method needs to focus on minimizing the sum of squared errors (SSE) Based on the available data (where t 1 corresponds to Q3 of Year 1), your job is to determine the best version of each of these proposed methods, and a. b. rank the methods using the agreed upon performance metric of minimizing SSE Each officer wants to understand the analysis that is performed, so it is very important that your analysis is explained well and documented thoroughly. In addition, you must discuss the appropriateness of each forecasting method. Kathyrn Jones is a financial analyst for Spartan Manufacturing, a company that produces engine blocks for the automotive industry. Spartan is hammering out a new labor agreement with its unionized workforce. One of the major concerns of the labor union is the funding of Spartan's retirement plan for their hourly employees. The union believes that the company has not been contributing enough money to this fund to cover the benefits it will need to pay to retiring employees. Because of this, the union wants the company to contribute approximately $15 million dollars in additional money to this fund over the next 20 years. These extra contributions would begin with an extra payment of $20,000 at the end of one year with annual payments increasing by 12.35 % per year for the next 19 years. The union has asked the company to set up a sinking fund to cover the extra annual payments to the retirement fund. Spartan's Chief Financial Officer and the union's chief negotiator have agreed that AAA-rated bonds recently issued by three different companies may be used to establish this fund. The following table summarizes the provisions of these bonds. Maturity 15 years 10 years 20 years Price Par Value Company Coupon Payment $80 AC&C $847.88 $1,000 $90 $938.55 $1,000 IBN MacroSoft $85 $872.30 $1,000 According to this table, Spartan may buy bonds issued by AC&C for $847.88 per bond. Each AC&C bond will pay the bondholder $80 per year for the next 15 years, plus an extra payment of $1,000 (the par value) in the fifteenth year. Similar interpretations apply to the information for the IBN and MacroSoft bonds. A money market fund yielding 5 % may be used to hold any coupon payments that are not needed to meet the company's required retirement fund payments in any given year. Spartan's CFO has asked Kathyrn to determine how much money the company would have to invest and which bonds the company should buy to meet the labor union's demands. (12 points) Develop and solve a linear optimization formulation of the problem using the provided EXCEL template. (Be sure to format the template using Spreadsheet Design Principles!) a. If you were Kathyrn, what would you tell the CFO? b. (10 points) Suppose that the union insists on including one of the following stipulations into the agreement: 1. No more than half of the total number of bonds purchased may be purchased from a single company 2. At least 10 % of the total number of bonds must be purchased from each of the companies Which stipulation should Spartan agree to? Justify your recommendation with a detailed explanation! (8 points) Investigate the impact of allowing IBN's Coupon Payment to vary from 90 to 125 c. in increments of 1. Describe how Spartan's investment strategy varies. The Colonel Motors Corporation is trying to decide whether to introduce a new midsize car. The directors of the company only want to produce the car if it has at least an 80 % chance of generating a positive net present value over the next ten years. If the company decides to produce the car, it will have to pay an uncertain initial startup cost that is estimated to follow a triangular distribution with a minimum value of $2 billion, maximum value of $2.4 billion, and a most likely value of $2.1 billion. In the first year, the company would produce 100,000 units. Demand during the first year is uncertain but expected to be normally distributed with a mean of 95,000 and standard deviation of 7,000. For any year in which the demand exceeds production, production will be increased by 5% in the following year. For any year in which the production exceeds demand, production will be decreased by 5 % in the next year, and the excess cars will be sold to a rental company at a 20 % discount. After the first year, the demand in any year will be modeled as a normally distributed random variable with a mean equal to the actual demand in the previous year and standard deviation of 7,000. In the first year, the sales price of the car will be $13,000 and the total variable cost per car is expected to be $9,500. Both the selling price and variable cost are expected to increase each year at the rate of inflation, which is assumed to be uniformly distributed between 2 % and 7%. The company uses a discount rate of 9% to discount future C cash flows. (15 points) Create a spreadsheet model for this problem using the EXCEL template provided. (Be sure to format the template using Spreadsheet Design Principles!) a. For parts (b) and (c), you must provide an appropriate screen capture image within your file to substantiate your responses. b. (10 points) Replicate the model at least 1000 times. What is the minimum, average, and maximum NPV Colonel Motors can expect if the company decides to produce this car? (Hint: Consider using the NPV() function to discount the profits Colonel Motors would earn each year.) (5 points) Should Colonel Motors produce this car? Justify your recommendation with a detailed c. explanation! 3D4U, Ltd., a small manufacturing firm specializing in 3D printers, has been gathering quarterly data on orders. Their data gathering efforts started in the third quarter of 2014 (year 1). The table below represents their orders since then: Quarter 2 Year 1 4 2559 3104 1 2 3222 5106 3592 5415 3 2478 2090 5130 2034 5130 4875 4 5161 4288 3918 2375 3591 3384 5 The officers of the company Arnie, Burt, Candace, Denise, and Ernie cannot agree on a method for forecasting future orders. Each of them prefers to use a different method. Arnie wants to use linear regression with the time period as the independent variable; Burt believes that a trend x seasonality forecasting method is needed since the data is quarterly; Candace feels that exponential smoothing will work just fine; Denise thinks that a time series of the form ao a t+ a2 t? is the way to go; and Ernie says "let's keep it simple and just use a horizontal line." However, they all agree that the firm's eventual forecasting method needs to focus on minimizing the sum of squared errors (SSE) Based on the available data (where t 1 corresponds to Q3 of Year 1), your job is to determine the best version of each of these proposed methods, and a. b. rank the methods using the agreed upon performance metric of minimizing SSE Each officer wants to understand the analysis that is performed, so it is very important that your analysis is explained well and documented thoroughly. In addition, you must discuss the appropriateness of each forecasting method. Kathyrn Jones is a financial analyst for Spartan Manufacturing, a company that produces engine blocks for the automotive industry. Spartan is hammering out a new labor agreement with its unionized workforce. One of the major concerns of the labor union is the funding of Spartan's retirement plan for their hourly employees. The union believes that the company has not been contributing enough money to this fund to cover the benefits it will need to pay to retiring employees. Because of this, the union wants the company to contribute approximately $15 million dollars in additional money to this fund over the next 20 years. These extra contributions would begin with an extra payment of $20,000 at the end of one year with annual payments increasing by 12.35 % per year for the next 19 years. The union has asked the company to set up a sinking fund to cover the extra annual payments to the retirement fund. Spartan's Chief Financial Officer and the union's chief negotiator have agreed that AAA-rated bonds recently issued by three different companies may be used to establish this fund. The following table summarizes the provisions of these bonds. Maturity 15 years 10 years 20 years Price Par Value Company Coupon Payment $80 AC&C $847.88 $1,000 $90 $938.55 $1,000 IBN MacroSoft $85 $872.30 $1,000 According to this table, Spartan may buy bonds issued by AC&C for $847.88 per bond. Each AC&C bond will pay the bondholder $80 per year for the next 15 years, plus an extra payment of $1,000 (the par value) in the fifteenth year. Similar interpretations apply to the information for the IBN and MacroSoft bonds. A money market fund yielding 5 % may be used to hold any coupon payments that are not needed to meet the company's required retirement fund payments in any given year. Spartan's CFO has asked Kathyrn to determine how much money the company would have to invest and which bonds the company should buy to meet the labor union's demands. (12 points) Develop and solve a linear optimization formulation of the problem using the provided EXCEL template. (Be sure to format the template using Spreadsheet Design Principles!) a. If you were Kathyrn, what would you tell the CFO? b. (10 points) Suppose that the union insists on including one of the following stipulations into the agreement: 1. No more than half of the total number of bonds purchased may be purchased from a single company 2. At least 10 % of the total number of bonds must be purchased from each of the companies Which stipulation should Spartan agree to? Justify your recommendation with a detailed explanation! (8 points) Investigate the impact of allowing IBN's Coupon Payment to vary from 90 to 125 c. in increments of 1. Describe how Spartan's investment strategy varies. The Colonel Motors Corporation is trying to decide whether to introduce a new midsize car. The directors of the company only want to produce the car if it has at least an 80 % chance of generating a positive net present value over the next ten years. If the company decides to produce the car, it will have to pay an uncertain initial startup cost that is estimated to follow a triangular distribution with a minimum value of $2 billion, maximum value of $2.4 billion, and a most likely value of $2.1 billion. In the first year, the company would produce 100,000 units. Demand during the first year is uncertain but expected to be normally distributed with a mean of 95,000 and standard deviation of 7,000. For any year in which the demand exceeds production, production will be increased by 5% in the following year. For any year in which the production exceeds demand, production will be decreased by 5 % in the next year, and the excess cars will be sold to a rental company at a 20 % discount. After the first year, the demand in any year will be modeled as a normally distributed random variable with a mean equal to the actual demand in the previous year and standard deviation of 7,000. In the first year, the sales price of the car will be $13,000 and the total variable cost per car is expected to be $9,500. Both the selling price and variable cost are expected to increase each year at the rate of inflation, which is assumed to be uniformly distributed between 2 % and 7%. The company uses a discount rate of 9% to discount future C cash flows. (15 points) Create a spreadsheet model for this problem using the EXCEL template provided. (Be sure to format the template using Spreadsheet Design Principles!) a. For parts (b) and (c), you must provide an appropriate screen capture image within your file to substantiate your responses. b. (10 points) Replicate the model at least 1000 times. What is the minimum, average, and maximum NPV Colonel Motors can expect if the company decides to produce this car? (Hint: Consider using the NPV() function to discount the profits Colonel Motors would earn each year.) (5 points) Should Colonel Motors produce this car? Justify your recommendation with a detailed c. explanation
Step by Step Solution
There are 3 Steps involved in it

Get step-by-step solutions from verified subject matter experts


