Question: Architectural simulation is widely used in computer architecture studies because it allows us to estimate the performance impact of new designs. In this part of
Architectural simulation is widely used in computer architecture studies because it allows us to estimate the performance impact of new designs. In this part of the project, you are asked to add a new branch predictor implementation to SimpleScalar. It has already implemented bit branch history table called bimod in the simulator correlating predictor called lev and several others. The bit branch history table uses the bit saturating counter that we have discussed in the class. You are asked to implement another bit branch history table that uses the bit counter as shown in the textbook, Figure C You need to make changes to bpred.h and bpred.c of SimpleScalar to implement the new bit counter and also a small change to simoutorder.c to add a new choice of branch predictor types. Next, you can run the simulation and report the observed results. What is the impact on both the overall performance and branch prediction accuracy when using the two different implementations of bit counters? Compared with the perfect branch predictor that is implemented by SimpleScalar, how much is the performance loss due to branch mispredictions for these two bit branch predictors? Similar to the experiments in Project Part please use the option fastfwd to fastforward the first million instructions and collect statistics on the next million instructions using the option max:inst for the program sjeng sjeng reduced.txt Please include your experimental results and source code the parts that have been modified in your report including the screenshots of timestamps, statistics and the changes to bpred.c in your report
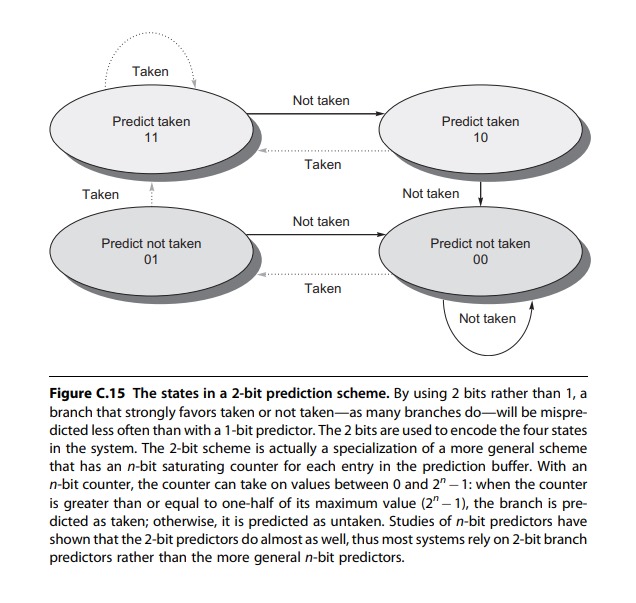
Figure C The states in a bit prediction scheme. By using bits rather than a branch that strongly favors taken or not takenas many branches dowill be mispredicted less often than with a bit predictor. The bits are used to encode the four states in the system. The bit scheme is actually a specialization of a more general scheme that has an n bit saturating counter for each entry in the prediction buffer. With an n bit counter, the counter can take on values between and n : when the counter is greater than or equal to onehalf of its maximum value leftnright the branch is predicted as taken; otherwise, it is predicted as untaken. Studies of n bit predictors have shown that the bit predictors do almost as well, thus most systems rely on bit branch predictors rather than the more general n bit predictors.
Step by Step Solution
There are 3 Steps involved in it
1 Expert Approved Answer
Step: 1 Unlock


Question Has Been Solved by an Expert!
Get step-by-step solutions from verified subject matter experts
Step: 2 Unlock
Step: 3 Unlock


