Question: Artificial Intelligence Assignment Question) MDP and RL The Cliff Walking environment is a gridworld with a discrete state space and discrete action space. The agent
Artificial Intelligence Assignment
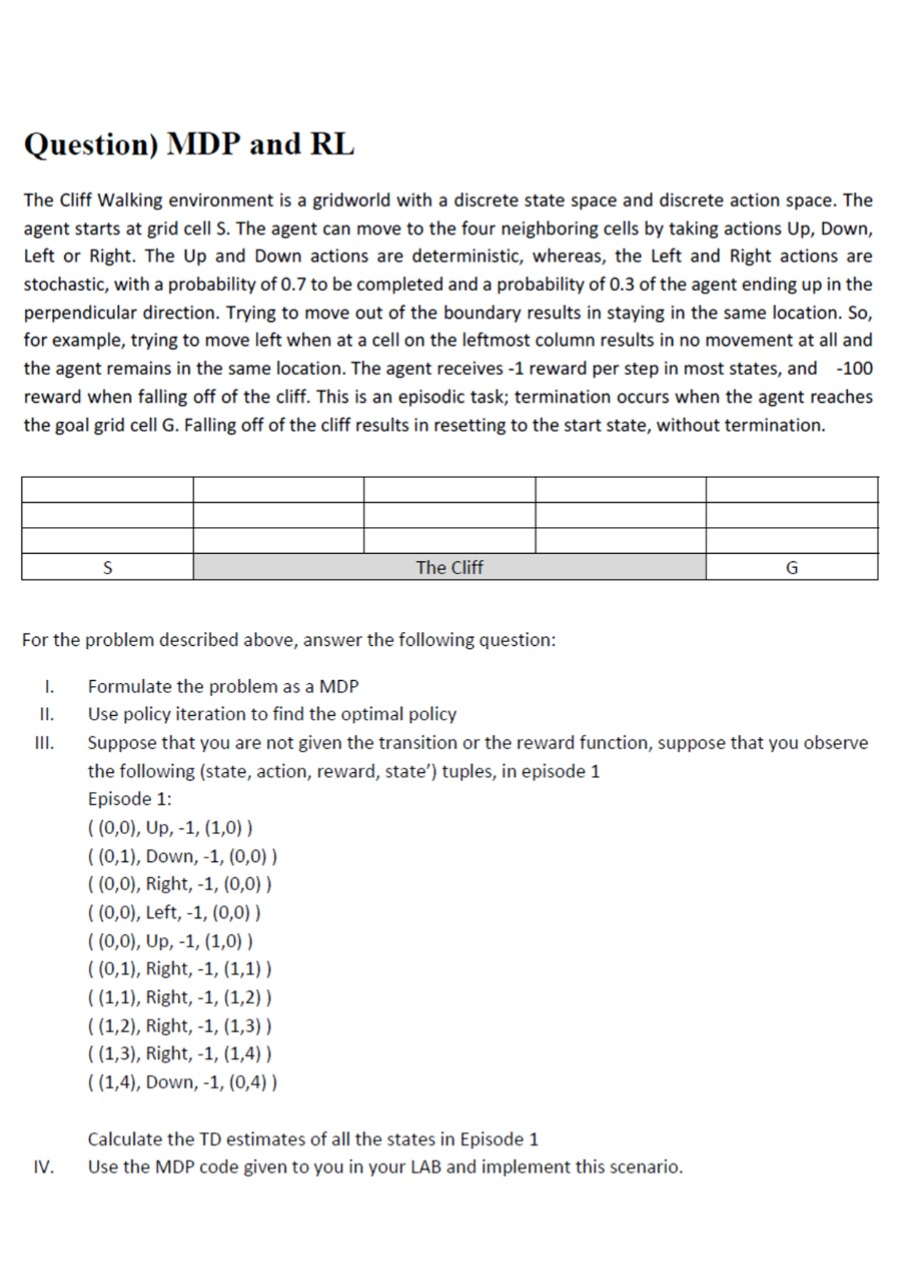
Question) MDP and RL The Cliff Walking environment is a gridworld with a discrete state space and discrete action space. The agent starts at grid cell S. The agent can move to the four neighboring cells by taking actions Up, Down, Left or Right. The Up and Down actions are deterministic, whereas, the Left and right actions are stochastic, with a probability of 0.7 to be completed and a probability of 0.3 of the agent ending up in the perpendicular direction. Trying to move out of the boundary results in staying in the same location. So, for example, trying to move left when at a cell on the leftmost column results in no movement at all and the agent remains in the same location. The agent receives -1 reward per step in most states, and -100 reward when falling off of the cliff. This is an episodic task; termination occurs when the agent reaches the goal grid cell G. Falling off of the cliff results in resetting to the start state, without termination. S The Cliff G For the problem described above, answer the following question: 1. II. III. Formulate the problem as a MDP Use policy iteration to find the optimal policy Suppose that you are not given the transition or the reward function, suppose that you observe the following (state, action, reward, state') tuples, in episode 1 Episode 1: (10,0), Up,-1, (1,0)) ((0,1), Down,-1, (0,0)) ((0,0), Right,-1, (0,0)) ((0,0), Left, -1, (0,0)) ((0,0), Up, -1, (1,0)) ((0,1), Right, -1, (1,1)) ((1,1), Right, -1, (1,2)) ((1,2), Right, -1, (1,3)) ((1,3), Right, -1, (1,4)) ((1,4), Down, -1, (0,4)) Calculate the TD estimates of all the states in Episode 1 Use the MDP code given to you in your LAB and implement this scenario. IV. Question) MDP and RL The Cliff Walking environment is a gridworld with a discrete state space and discrete action space. The agent starts at grid cell S. The agent can move to the four neighboring cells by taking actions Up, Down, Left or Right. The Up and Down actions are deterministic, whereas, the Left and right actions are stochastic, with a probability of 0.7 to be completed and a probability of 0.3 of the agent ending up in the perpendicular direction. Trying to move out of the boundary results in staying in the same location. So, for example, trying to move left when at a cell on the leftmost column results in no movement at all and the agent remains in the same location. The agent receives -1 reward per step in most states, and -100 reward when falling off of the cliff. This is an episodic task; termination occurs when the agent reaches the goal grid cell G. Falling off of the cliff results in resetting to the start state, without termination. S The Cliff G For the problem described above, answer the following question: 1. II. III. Formulate the problem as a MDP Use policy iteration to find the optimal policy Suppose that you are not given the transition or the reward function, suppose that you observe the following (state, action, reward, state') tuples, in episode 1 Episode 1: (10,0), Up,-1, (1,0)) ((0,1), Down,-1, (0,0)) ((0,0), Right,-1, (0,0)) ((0,0), Left, -1, (0,0)) ((0,0), Up, -1, (1,0)) ((0,1), Right, -1, (1,1)) ((1,1), Right, -1, (1,2)) ((1,2), Right, -1, (1,3)) ((1,3), Right, -1, (1,4)) ((1,4), Down, -1, (0,4)) Calculate the TD estimates of all the states in Episode 1 Use the MDP code given to you in your LAB and implement this scenario. IV
Step by Step Solution
There are 3 Steps involved in it

Get step-by-step solutions from verified subject matter experts


