Question: As a small business, NGS has made changes in their Accounts Receivable Policy in the past year. But Nicole is unsure whether the changes have
As a small business, NGS has made changes in their Accounts Receivable Policy in the past year. But Nicole is unsure whether the changes have made a difference.
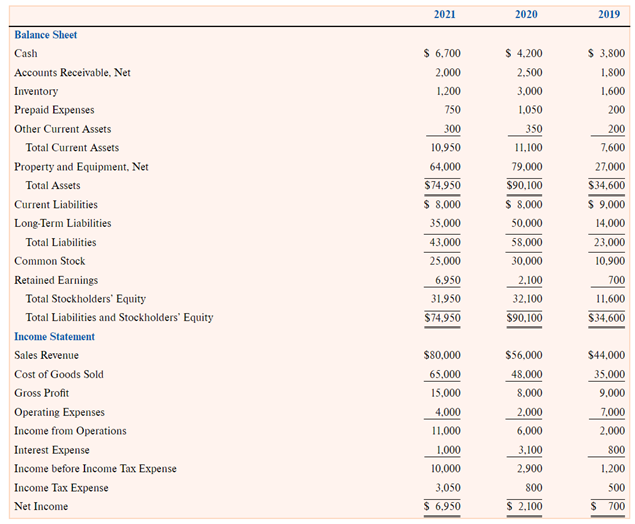
Calculate ?and ?Days to Collect Receivable and Receivables Turnover. Evaluate the shortterm solvency for NGS based on the yearoveryear change.
Provide recommendations for Accounts Receivable policies that could reduce the days to collect.
CLO : NGS is considering purchasing a tanning bed for $ ?to add a new service to her business. Nicole was not aware that there were different methods for calculating amortization. Nicole would like to understand the difference between each method, and which method is suitable for her business.
Calculate amortization and record the journal entry for Year ?using the following methods:
Straight line methodology assuming a useful life of ?years.
Double declining methodology assuming a rate of
Units of production methodology, where a total of ?uses. Nicole forecasts that the tanning bed will be used ?times in Year ?
What is the difference between the three methods? Advise NGS which amortization methodology is suitable for her business and why.
CLO : NGS is owned by Nicole, who is a sole proprietor.
NGS has recently heard about incorporation. Advise NGS as what are the advantages for having a corporation.
Calculate NGSs return on assets and return on equity for ?and ?Explain what the change in each ratio means.
CLO : NGS has been growing in revenue over the past three years. NGS would like to expand to a new location, but NGS does not have enough funding for expansion. NGS would like to explore options to raise funds through incurring debt.
Explain the three options of raising financing available to NGS:
Bank Loan
Corporate Bond
Private Capital
A bank loan focuses on two ratios: DebttoAssets Ratio and Times Interest Earned Ratio. Calculate these two ratios for ?and ?Explain to NGS as to what these two ratios represent.
The bank requires a DebttoAsset ratio of less than one. Explain the DebttoAsset ratio for NGS ?and whether NGS will meet the bank criteria or not.
CLO : NGS wants a financial analysis of its performance for ?and ?Note: express analysis as percentage.
Calculate the horizonal analysis for the balance sheet and income statement. Discuss the results of the horizontal analysis.
Calculate the vertical analysis for the balance sheet and income statement. Discuss the results of the vertical analysis.
This Case Study is worth ?of your overall grade. It will allow you to demonstrate your understanding of the following concepts covered during Days ?and :
CLO : Demonstrate an understanding of temporary investments, accounts receivable, and bad debts.
CLO : Analyze the effects of various factors on financial statements.
CLO : Demonstrate and apply an understanding of shareholder's equity section of the balance sheet including capital contributions and dividends.
CLO : Analyze corporate debt transactions and explain its impact on financial statements.
Analyze financial statement information using ratios and other techniques.
2021 2020 2019 Balance Sheet Cash Accounts Receivable, Net Inventory Prepaid Expenses Other Current Assets Total Current Assets Property and Equipment, Net Total Assets Current Liabilities Long-Term Liabilities Total Liabilities $ 6,700 $ 4,200 $ 3,800 2,000 2,500 1,800 1,200 3,000 1,600 750 1,050 200 300 350 200 10,950 11,100 7,600 64,000 79,000 27,000 $74,950 $90,100 $34,600 $ 8,000 $ 8,000 $ 9,000 35,000 50,000 14,000 43,000 58,000 23,000 Common Stock 25,000 30,000 10,900 Retained Earnings 6,950 2,100 700 Total Stockholders' Equity 31,950 32,100 11,600 Total Liabilities and Stockholders' Equity $74,950 $90,100 $34,600 Income Statement Sales Revenue Cost of Goods Sold Gross Profit Operating Expenses Income from Operations Interest Expense Income before Income Tax Expense Income Tax Expense Net Income $80,000 $56,000 $44,000 65,000 48,000 35,000 15,000 8,000 9.000 4,000 2,000 7,000 11,000 6,000 2,000 1,000 3,100 800 10,000 2,900 1,200 3,050 800 500 $ 6,950 $ 2,100 $ 700
Step by Step Solution
There are 3 Steps involved in it

Get step-by-step solutions from verified subject matter experts


