Question: Assume that the following classes have been defined: public class A extends B { public void method2() { System.out.print(a 2 ); method1(); public class C
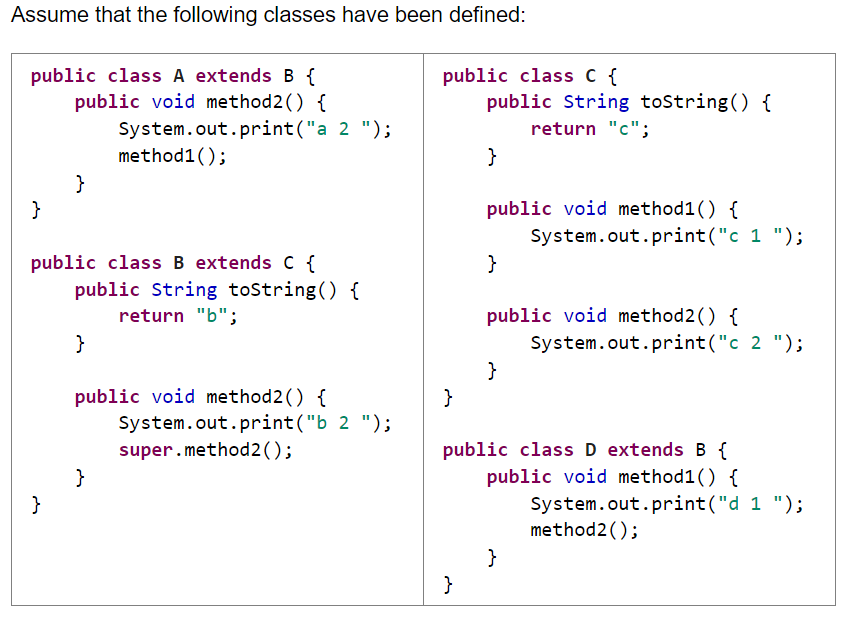
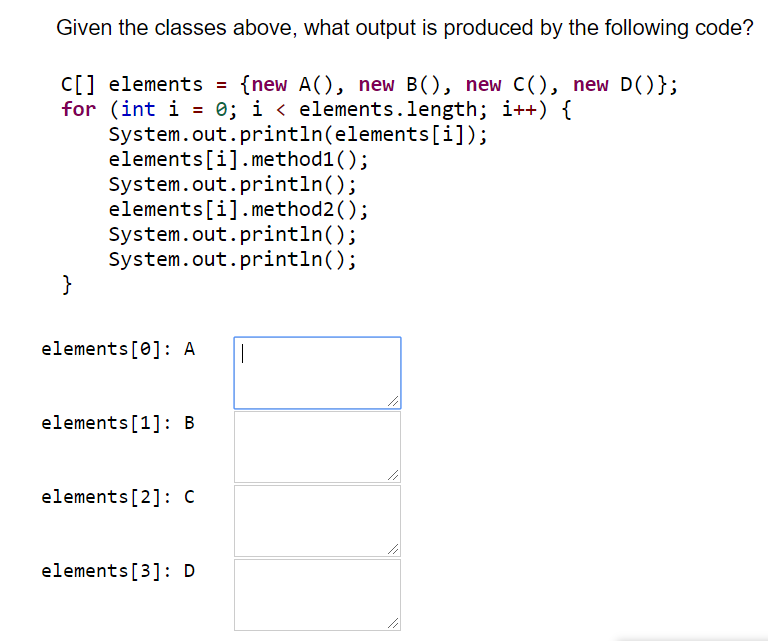
Assume that the following classes have been defined: public class A extends B { public void method2() { System.out.print("a 2 "); method1(); public class C { public String tostring() { return "c"; public void method1() { System.out.print("c 1 "); public class B extends C { public String tostring() { public void method2() { System.out.print("c 2 "); return "b"; public void method2() { System.out.print("b 2 "); public class D extends B { public void method1() { System.out.print("d 1 "); method2(); super.method2(); Given the classes above, what output is produced by the following code? C[] elements = {new A(), new B(), new C(), new D()}; for (int i = 0; i
Step by Step Solution
There are 3 Steps involved in it

Get step-by-step solutions from verified subject matter experts


