Assume the five-year lease in which ELC entered requires the same lease payments as the preceding operating
Question:
Assume the five-year lease in which ELC entered requires the same lease payments as the preceding operating lease. That is, Estée Lauder agrees to pay $150,000 in year 1, $155,000 in year 2, $159,000 in year 3, $163,000 in year 4, $167,000 in year 5. Payments will be made at the end of each year. And the discount rate is still 0.7 percent. ELC amortizes the ROU asset on a straight-line basis over the lease term.
At the commencement of the finance lease, the capitalized ROU asset and lease liability are still $777,000, the same value we calculated in the operating lease case, because the present value of future lease payments is unchanged.
In the following section, you’ll need to build journal entries for the next five years. To get you started, the journal entries for years 1 and 2 have been completed. Please take a close look at how transactions are recorded and apply the same process to transactions in the remaining years.
At the end of year 1:
- Record straight-line amortization expense ($777/5 = $155.4) and adjust the ROU asset accordingly
- Record interest expense ($777 × 0.7% = $5.4) and reduction in principal ($150 – $777 × 0.7% = $144.6) for lease liability
(in thousands of dollars)
| DATE | ACCOUNTS | DEBIT | CREDIT |
|---|---|---|---|
| 12/31/21 | Amortization Expense | $155.4 | |
| ROU Asset | $155.4 | ||
| 12/31/21 | Interest Expense | $5.4 | |
| Finance Lease Liability | $144.6 | ||
| Cash | $150.0 |
At the end of year 2:
- Record straight-line amortization expense ($777/5 = $155.4) and adjust the ROU asset accordingly
- Record interest expense (($777 − $144.6) × 0.7% = $4.4) and reduction in principal ($155 − ($777 − $144.6) × 0.7% = $150.6) for lease liability
(in thousands of dolllars)
| DATE | ACCOUNTS | DEBIT | CREDIT |
|---|---|---|---|
| 12/31/22 | Amortization Expense | $155.4 | |
| ROU Asset | $155.4 | ||
| 12/31/22 | Interest Expense | $4.4 | |
| Finance Lease Liability | $150.6 | ||
| Cash | $155.0 |
Please fill in ROU Asset, Lease Liability, Amortization Expense, and Interest Expense based on preceding journal entries. Assuming there is no tax and gross profit at a constant $650,000/year.
HINT: Take a close look at the embedded Year 1 formulas. Try to answer with spreadsheet formulas to avoid rounding errors.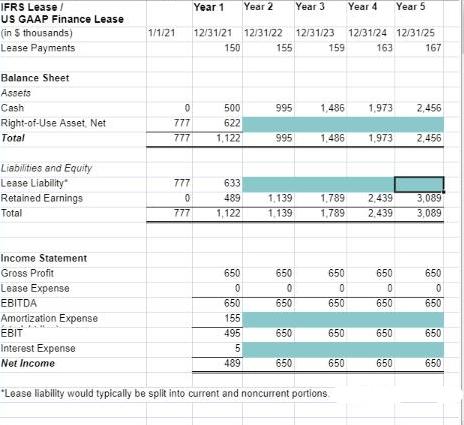

Financial Reporting Financial Statement Analysis and Valuation
ISBN: 978-0324302950
6th edition
Authors: Clyde P. Stickney




