Question: A cyclist must cycle, with a constant speed v = 10 m/s relative to the ground, from A to B and back again. A
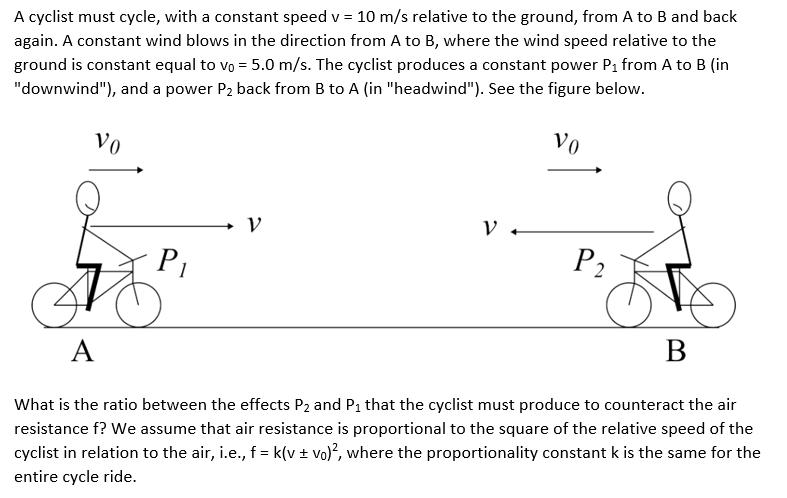
A cyclist must cycle, with a constant speed v = 10 m/s relative to the ground, from A to B and back again. A constant wind blows in the direction from A to B, where the wind speed relative to the ground is constant equal to vo = 5.0 m/s. The cyclist produces a constant power P from A to B (in "downwind"), and a power P back from B to A (in "headwind"). See the figure below. Vo Vo P V V P A B What is the ratio between the effects P and P that the cyclist must produce to counteract the air resistance f? We assume that air resistance is proportional to the square of the relative speed of the cyclist in relation to the air, i.e., f = k(v + vo), where the proportionality constant k is the same for the entire cycle ride.
Step by Step Solution
3.42 Rating (165 Votes )
There are 3 Steps involved in it
While Moving Point A to Point Be its Relative Speed V1VV0 10515... View full answer

Get step-by-step solutions from verified subject matter experts


