Question: attached is the MS and Intel example Q5. Firm ABC has a bond with face value of $25,000,000 and ABC pays it's bondholders a fixed




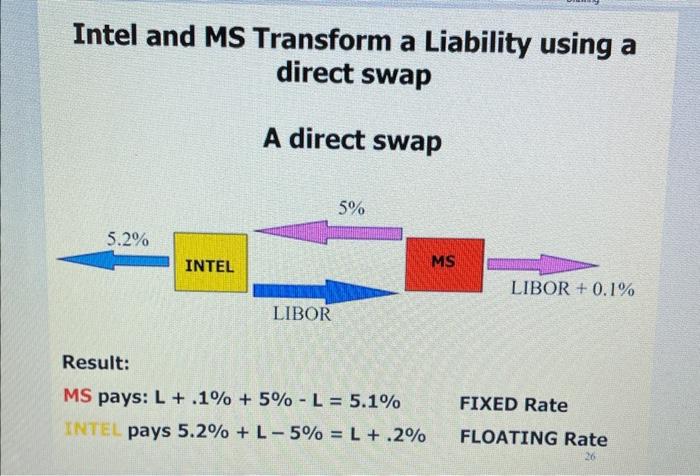
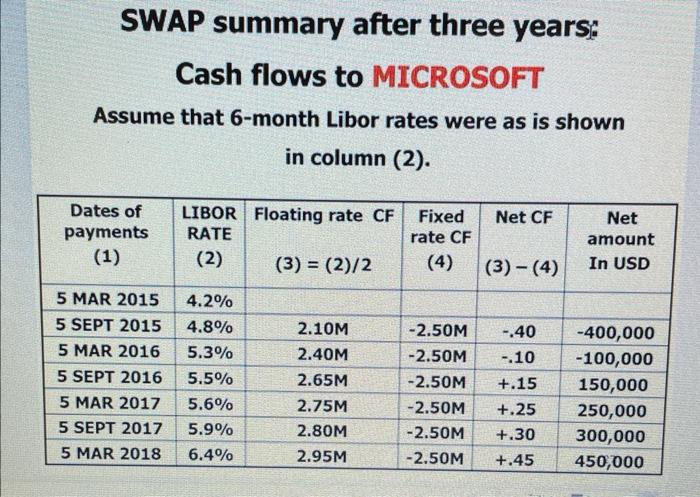
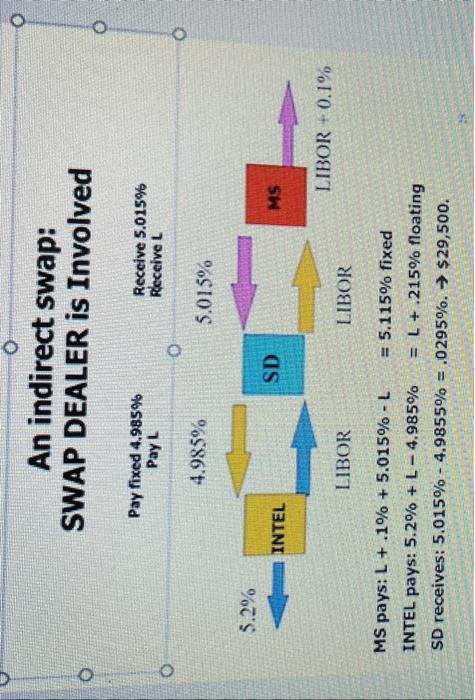
Q5. Firm ABC has a bond with face value of $25,000,000 and ABC pays it's bondholders a fixed annual rate of 7%. Firm XY pay it's bondholders a floating rate of IIBOR + . 2% on a bond of $25,000,000. Both firms wish to change the nature of their payment so, they enter into the following direct swap for the next 5 years: on specific dates, ABC will pay XY/IIBOR - . 1%, while XY/ will pay ABC6.8%. Use the example of INIEL and MS from CH. 7 to describe a chart of the above swap based on $25,000,000 notional amount and annual payments for the next 5 years. Another Example of a "Plain Vanilla" Interest Rate Swap An SWAP between: MICROSOFT and Each firm wish to change the nature of the cash flows associated with their debts. Some time ago Intel issued a fixed 5.2% rate, $100,000,000 FV bond. Also, several years back, Microsoft (MS) issued a floating LIBOR +10 bps rate $100,000,000 FC bond. There are 3 years to the maturity remaining for these bonds. Intel wishes to pay a floating rate. MS wishes to pay a fixed rate. They enter a swap to achieve these goals. The principal amount USD100.000.000. The cash flows are. Semiannual Tenor. 3 years A direct swap Intel 4monthLIBOR5%FixedRateMS Intel and MS Transform a Liability using a direct swap A direct swap Result: MS pays: L+.1%+5%L=5.1% FIXED Rate pays 5.2%+L5%=L+.2% FLOATING Rate SWAP summary after three years: Cash flows to MICROSOFT Assume that 6-month Libor rates were as is shown in column (2). INTEL pays: 5.2%+L4.985%=L+.215% floating SD receives: 5.015%4.9855%=.0295%.$29,500 Q5. Firm ABC has a bond with face value of $25,000,000 and ABC pays it's bondholders a fixed annual rate of 7%. Firm XY pay it's bondholders a floating rate of IIBOR + . 2% on a bond of $25,000,000. Both firms wish to change the nature of their payment so, they enter into the following direct swap for the next 5 years: on specific dates, ABC will pay XY/IIBOR - . 1%, while XY/ will pay ABC6.8%. Use the example of INIEL and MS from CH. 7 to describe a chart of the above swap based on $25,000,000 notional amount and annual payments for the next 5 years. Another Example of a "Plain Vanilla" Interest Rate Swap An SWAP between: MICROSOFT and Each firm wish to change the nature of the cash flows associated with their debts. Some time ago Intel issued a fixed 5.2% rate, $100,000,000 FV bond. Also, several years back, Microsoft (MS) issued a floating LIBOR +10 bps rate $100,000,000 FC bond. There are 3 years to the maturity remaining for these bonds. Intel wishes to pay a floating rate. MS wishes to pay a fixed rate. They enter a swap to achieve these goals. The principal amount USD100.000.000. The cash flows are. Semiannual Tenor. 3 years A direct swap Intel 4monthLIBOR5%FixedRateMS Intel and MS Transform a Liability using a direct swap A direct swap Result: MS pays: L+.1%+5%L=5.1% FIXED Rate pays 5.2%+L5%=L+.2% FLOATING Rate SWAP summary after three years: Cash flows to MICROSOFT Assume that 6-month Libor rates were as is shown in column (2). INTEL pays: 5.2%+L4.985%=L+.215% floating SD receives: 5.015%4.9855%=.0295%.$29,500
Step by Step Solution
There are 3 Steps involved in it

Get step-by-step solutions from verified subject matter experts


