Question: Attempts 2 2 Keep the Highest 2/3 1. Net present value (NPV) Evaluating cash flows with the NPV method The net present value (NPV) rule
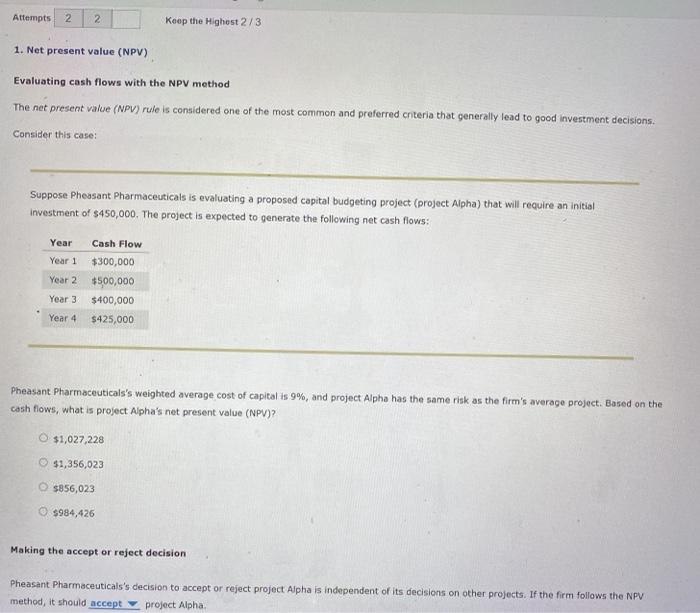
Attempts 2 2 Keep the Highest 2/3 1. Net present value (NPV) Evaluating cash flows with the NPV method The net present value (NPV) rule is considered one of the most common and preferred criteria that generally lead to good investment decisions. Consider this case: Suppose Pheasant Pharmaceuticals is evaluating a proposed capital budgeting project (project Alpha) that will require an initial Investment of $450,000. The project is expected to generate the following net cash flows: Year Year 1 Cash Flow $300,000 $500,000 Year 2 Year 3 $400,000 Year 4 $425,000 Pheasant Pharmaceuticals's weighted average cost of capital is 9%, and project Alpha has the same risk as the firm's average project. Based on the cash flows, what is project Alpha's net present value (NPV)? $1,027,228 $1,356,023 $856,023 $984,426 Making the accept or reject decision Pheasant Pharmaceuticals's decision to accept or reject project Alpha is independent of its decisions on other projects. If the firm follows the NPV method, it should accept project Alpha
Step by Step Solution
There are 3 Steps involved in it

Get step-by-step solutions from verified subject matter experts


