Question: AutoSave O OFF MAP ? C ... Force Table Equilibrium Data Sheet_Bonus Lab ~ Home Insert Draw Page Layout Formulas Data Review View Tell me
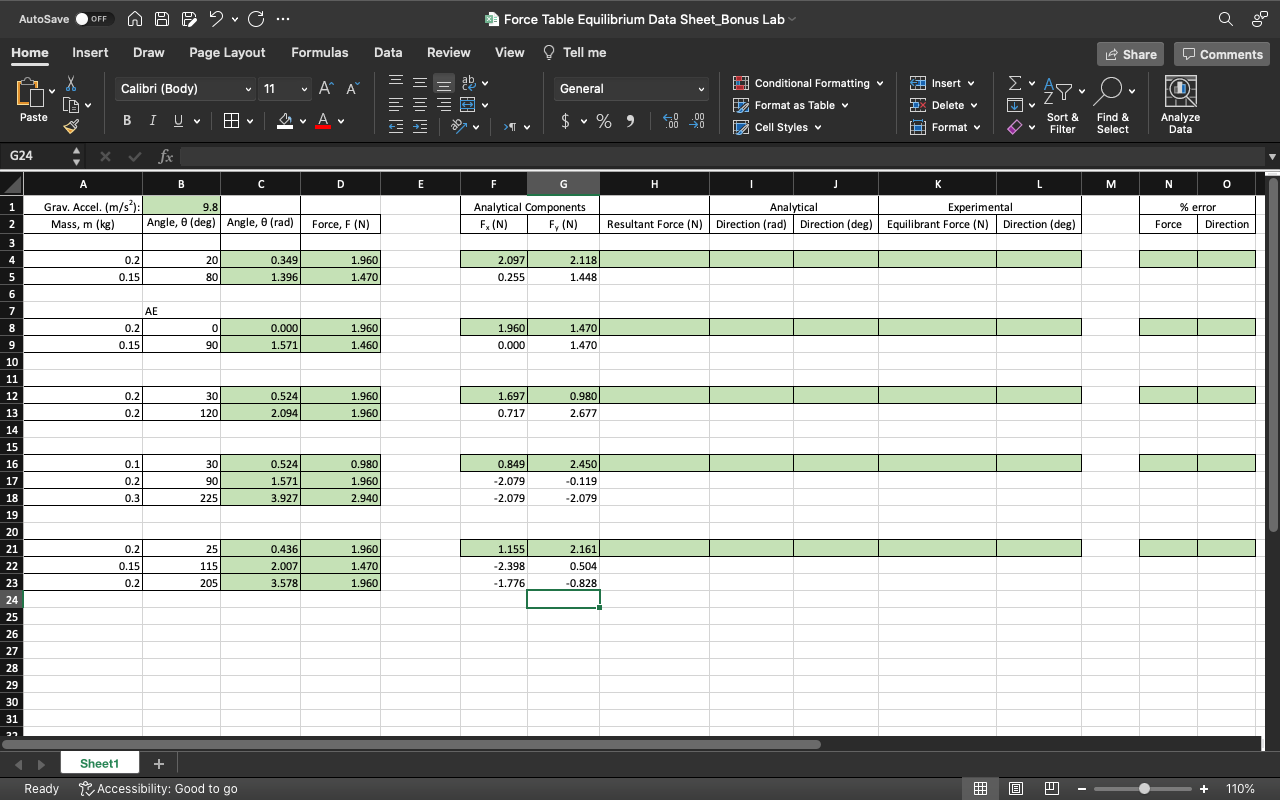
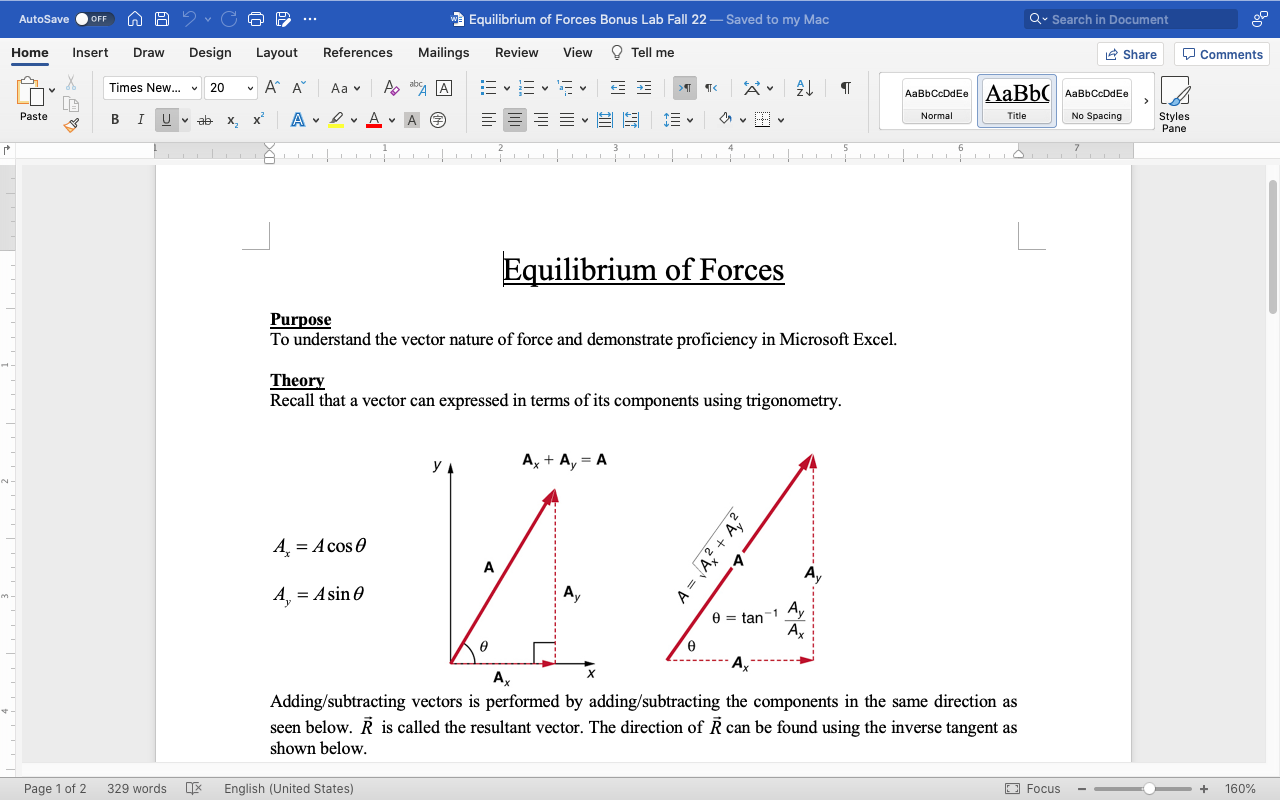
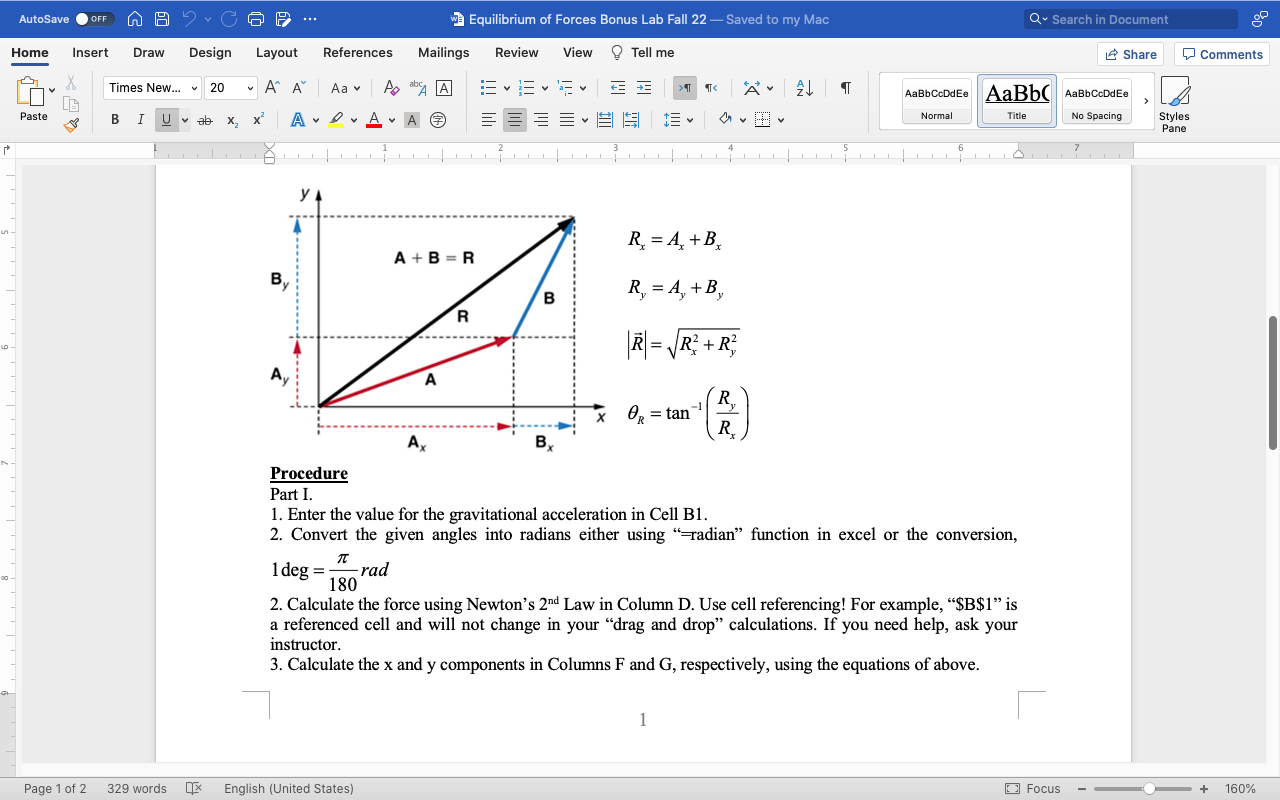
AutoSave O OFF MAP ? C ... Force Table Equilibrium Data Sheet_Bonus Lab ~ Home Insert Draw Page Layout Formulas Data Review View Tell me Share Comments Calibri (Body) 11 AA General Conditional Formatting v Insert Format as Table ax Delete v IN Paste IUV A .09 Sort & Find & Analyze Cell Styles v Format v Filter Select Data G24 X V fx B C D E F G H K M N O Grav. Accel. (m/s'): 9.8 Analytical Components Analytical Experimental error Mass, m (kg) Angle, 0 (deg) Angle, 0 (rad) Force, F (N) F, (N) F, (N) Resultant Force (N) | Direction (rad) |Direction (deg) Equilibrant Force (N) |Direction (deg) Force Direction 0.2 20 0.349 1.960 2.097 2.118 0.15 80 1.396 1.470 0.255 1.448 AE 0.21 0 0.000 1.960 1.960 1.470 0.15 90 1.571 1.460 0.000 1.470 10 11 12 0.2 30 0.524 1.960 1.697 0.980 0.2 120 2.094 1.960 0.717 2.677 0.1 30 0.524 0.980 0.849 2.450 0.2 90 1.571 1.960 2.079 0.119 0.3 225 3.927 2.940 -2.079 -2.079 0.2 25 D.436 1.960 1.155 2.161 0.15 115 2.007 1.470 2.398 0.504 205 3.578 1.960 -1.776 -0.828 Sheet1 + Ready Accessibility: Good to go + 110%AutoSave O OFF n A ? CG9 ... 3 Equilibrium of Forces Bonus Lab Fall 22 - Saved to my Mac Q . Search in Document Home Insert Draw Design Layout References Mailings Review View Tell me Share Comments Times New... 20 " A A Aav A bA A AaBbCcDdEe AaBb( AaBbCcDdEe Paste BI Uva X2 x Av DAVAO Normal Title No Spacing Styles Pane Equilibrium of Forces Purpose To understand the vector nature of force and demonstrate proficiency in Microsoft Excel. Theory Recall that a vector can expressed in terms of its components using trigonometry. YA A + Ay = A A = Acos 0 A = A2 + A2 A Av A = Asin 0 Av 0 = tan-1 Ay Ax Ax Adding/subtracting vectors is performed by adding/subtracting the components in the same direction as seen below. R is called the resultant vector. The direction of R can be found using the inverse tangent as shown below. Page 1 of 2 329 words * English (United States) Focus + 160%AutoSave O OFF WA ? CG9 ... 3 Equilibrium of Forces Bonus Lab Fall 22 - Saved to my Mac Q . Search in Document Home Insert Draw Design Layout References Mailings Review View Tell me Share Comments Times New... 20 " A A Aav A bA A AaBbCcDdEe AaBb( AaBbCcDdEe Paste B I Uvb X2 x Normal Title No Spacing Styles Pane yl R. = A+B. A + B = R B B R, = A, +B, R R = R2 + R3 A A x OR = tan -1 Ry Ax Bx Procedure Part I. 1. Enter the value for the gravitational acceleration in Cell B1. 2. Convert the given angles into radians either using " radian" function in excel or the conversion, 1 deg = -rad 180 2. Calculate the force using Newton's 2nd Law in Column D. Use cell referencing! For example, "$B$1" is a referenced cell and will not change in your "drag and drop" calculations. If you need help, ask your instructor. 3. Calculate the x and y components in Columns F and G, respectively, using the equations of above. Page 1 of 2: 329 words x English (United States) Focus - + 160%AutoSave O OFF n A ? CG9 ... 3 Equilibrium of Forces Bonus Lab Fall 22 - Saved to my Mac Q . Search in Document Home Insert Draw Design Layout References Mailings Review View Tell me Share Comments Times New... 20 " A A Aa A bA A AaBbCcDdEe AaBb( AaBbCcDdEe Paste B I Uva XZ X Normal Title No Spacing Styles Pane 4. Calculate the magnitude of the resultant force in Column H using the equations above. 5. Calculate the angle of the resultant vector in Column I (it will automatically be in radians) then convert it to degrees using "=degrees" in Column J. To compute the inverse tangent in excel, use the function, "-atan". Part II. 1. Set up the Force Table according to each configuration in the excel data sheet. The first trial has 2 masses, my = 0.2 kg at 01 = 20 and my = 0.15 kg at 0 = 80. Using the information, you gathered in Part I, find the equilibrant vector. The equilibrant vector is in the opposite direction of the resultant vector. On the force table, this is achieved by adding 180 to the resultant vector direction. 2. Record the equilibrant vector and the angle in Columns K and L, respectively. 3. Calculate the percent error between the resultant and equilibrant and the directions in Columns N and O, respectively. 4. Repeat for the additional masses and angles as listed in the excel sheet. Page 2 of 2 3 329 words x English (United States) Focus - + 160%
Step by Step Solution
There are 3 Steps involved in it

Get step-by-step solutions from verified subject matter experts


