Question: AVL Trees vs RB Trees In this assignment, your task is to compare the clock cycles needed to execute the insert and search operations for

 AVL Trees vs RB Trees
AVL Trees vs RB Trees
In this assignment, your task is to compare the clock cycles needed to execute the insert and search operations for AVL and Red Black (RB) trees. Insert operation for AVL and RB tree, and search operation for AVL and RB tree must be compared separately. You should follow the steps given below.
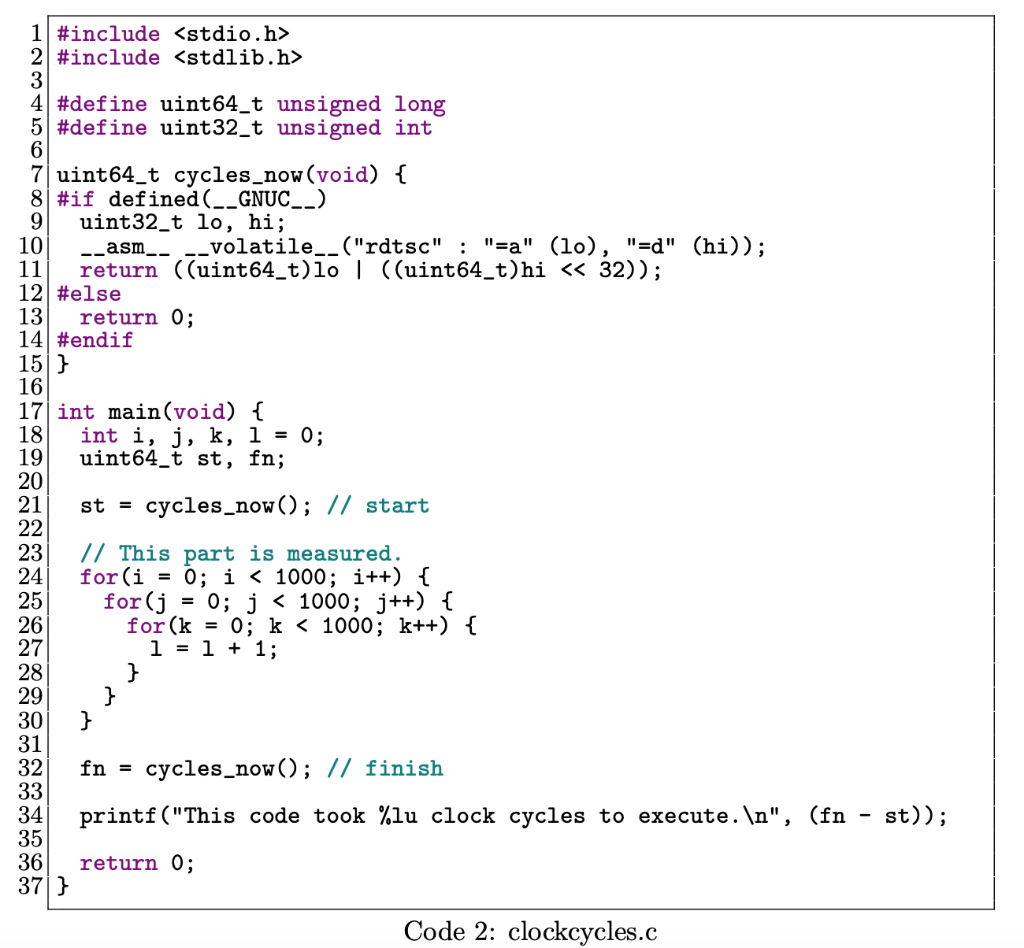
Implement an insert function for AVL trees. Implement an insert function for RB trees. Do not use parent pointer in the node structure. You should write the insert function recursively, similar to the AVL tree insert function. Insert 25, 26, 27, . . . , 225 different nodes to both trees and measure the num- ber of clock cycles after every set of insertions. To measure the clock cycles correctly, you can use the code given in 2. Note that you should insert nodes with random keys in order to get meaningful results at the end. Your keys must be defined as unsigned long. Auxiliary code for creating 64-bit random keys is given in 1. Implement a search function for binary search trees. Search 25, 26, 27, . . . , 225 different nodes in both trees and measure the number of clock cycles after every set of searches. Again, to measure the clock cycles correctly, you can use the code given in this document. Note that in every search, you should search a different node in order to get meaningful results at the end. Gather all the results of AVL and RB tree insertions and searches in a document and write a report (minimum one page) about the insertion and search comparison in AVL and RB trees. You can create a graph with the clock cycles to support your results.
1 #include
Step by Step Solution
There are 3 Steps involved in it

Get step-by-step solutions from verified subject matter experts


