Question: B 3 . In a space mission, a single stage rocket containing a space shuttle is launched into space from Earth's surface. During the launch,
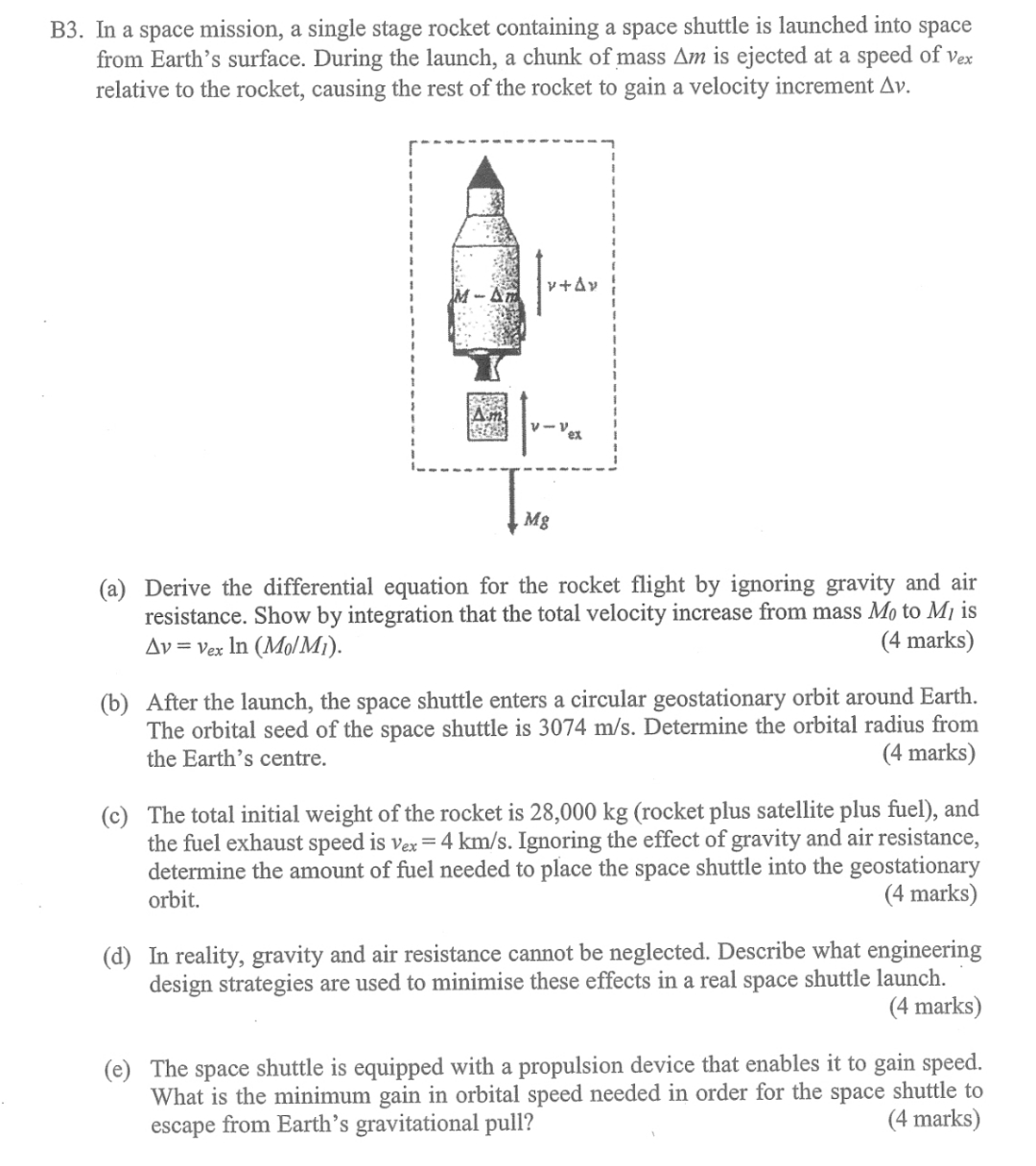
B In a space mission, a single stage rocket containing a space shuttle is launched into space from Earth's surface. During the launch, a chunk of mass is ejected at a speed of relative to the rocket, causing the rest of the rocket to gain a velocity increment
a Derive the differential equation for the rocket flight by ignoring gravity and air resistance. Show by integration that the total velocity increase from mass to is
marks
b After the launch, the space shuttle enters a circular geostationary orbit around Earth. The orbital seed of the space shuttle is Determine the orbital radius from the Earth's centre.
marks
c The total initial weight of the rocket is rocket plus satellite plus fuel and the fuel exhaust speed is Ignoring the effect of gravity and air resistance, determine the amount of fuel needed to place the space shuttle into the geostationary orbit.
marks
d In reality, gravity and air resistance cannot be neglected. Describe what engineering design strategies are used to minimise these effects in a real space shuttle launch.
marks
e The space shuttle is equipped with a propulsion device that enables it to gain speed. What is the minimum gain in orbital speed needed in order for the space shuttle to escape from Earth's gravitational pull?
marks
Step by Step Solution
There are 3 Steps involved in it
1 Expert Approved Answer
Step: 1 Unlock


Question Has Been Solved by an Expert!
Get step-by-step solutions from verified subject matter experts
Step: 2 Unlock
Step: 3 Unlock


