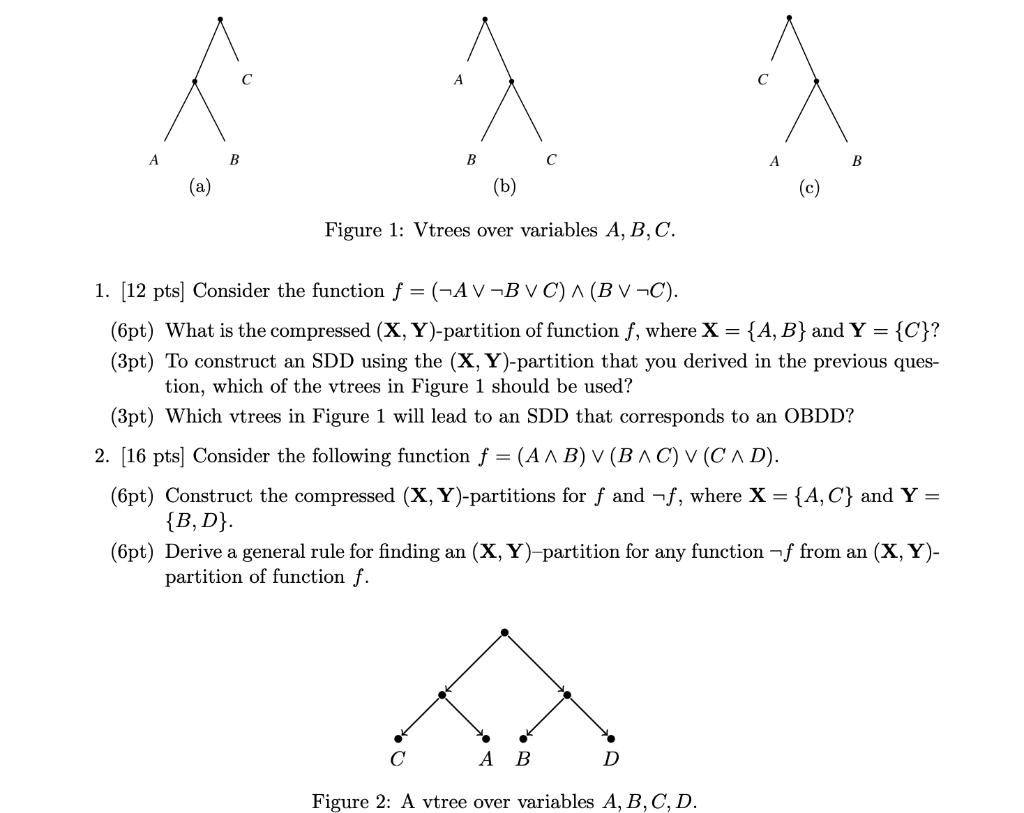
Question: B B A B (a) (b) Figure 1: Vtrees over variables A, B, C. 1. [12 pts] Consider the function f = (-AV-B VC) ^
![A, B, C. 1. [12 pts] Consider the function f = (-AV-B](https://dsd5zvtm8ll6.cloudfront.net/si.experts.images/questions/2024/10/66fbb25ea25f1_23066fbb25e23c4c.jpg)

B B A B (a) (b) Figure 1: Vtrees over variables A, B, C. 1. [12 pts] Consider the function f = (-AV-B VC) ^ (BV-C). (opt) What is the compressed (X, Y)-partition of function f, where X = {A, B} and Y = {C}? (3pt) To construct an SDD using the (X, Y)-partition that you derived in the previous ques- tion, which of the vtrees in Figure 1 should be used? (3pt) Which vtrees in Figure 1 will lead to an SDD that corresponds to an OBDD? 2. [16 pts] Consider the following function f = (AAB) V(BAC) V(CAD). (6pt) Construct the compressed (X, Y)-partitions for f and -f, where X = {A,C} and Y = {B, D}. (6pt) Derive a general rule for finding an (X, Y)-partition for any function -f from an (X, Y)- partition of function f. A B D Figure 2: A vtree over variables A, B, C, D. 3. (14 pts) Construct an SDD for the function f = (AA-B) V(BAC) V(CAD) based on the vtree in Figure 2. 4. (12 pts] Consider a structured space which corresponds to selecting k or more items from a set of n items, where n > 1 and 0
Step by Step Solution
There are 3 Steps involved in it

Get step-by-step solutions from verified subject matter experts


