Question: b. Create a new section of your code titled Part 2. Copy the code provided in Exercise 3 to perform back substition on the

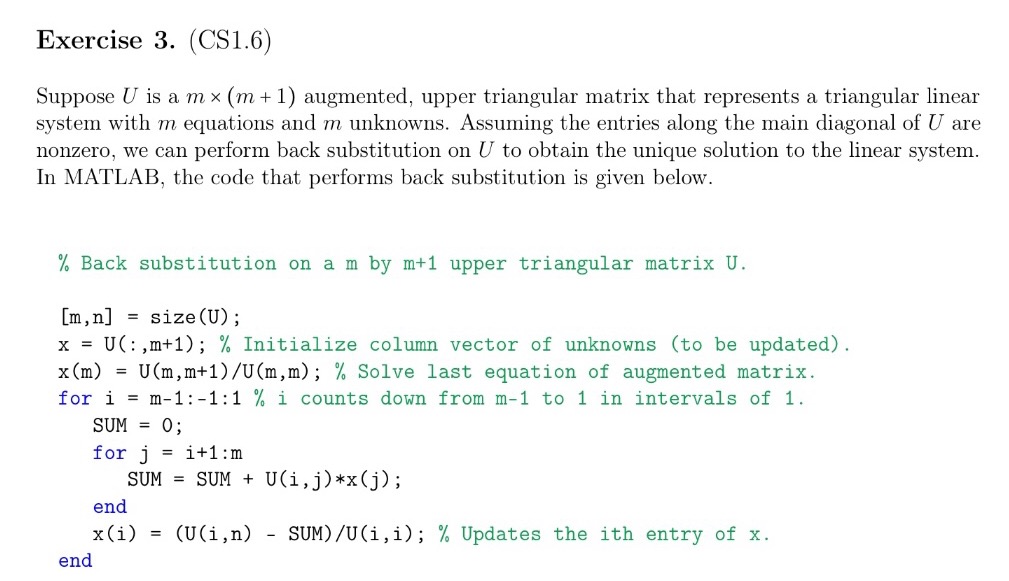

b. Create a new section of your code titled "Part 2." Copy the code provided in Exercise 3 to perform back substition on the upper triangular augmented matrix obtained from Part 1. Display the resulting solution vector to the Command Window. Use format long to show all significant digits of this matrix. Exercise 3. (CS1.6) Suppose U is a mx (m + 1) augmented, upper triangular matrix that represents a triangular linear system with m equations and m unknowns. Assuming the entries along the main diagonal of U are nonzero, we can perform back substitution on U to obtain the unique solution to the linear system. In MATLAB, the code that performs back substitution is given below. % Back substitution on a m by m+1 upper triangular matrix U. [m, n] = size (U); x = U(:,m+1); % Initialize column vector of unknowns (to be updated). x (m) = U(m, m+1)/U(m, m); % Solve last equation of augmented matrix. for im-1:-1:1 % i counts down from m-1 to 1 in intervals of 1. SUM = 0; for = i +1:m SUM SUM + U(i, j)*x(j); end x(i) = (U(i,n) SUM) /U(i, i); % Updates the ith entry of x. end Multi-Step Problem Note: This problem will involve programming. Please attach your code and its output to the end of your homework assignment. Suppose we have a linear system with m equations and m unknowns. Let A be the mxm co- efficient matrix associated with this system, and b be the mx 1 column vector of knowns. The following MATLAB code performs regular Gaussian elimination on this system, when possible. M = [A, b]; [m, n] = size (M); for j = 1:m if M(j, j)==0 error('System cannot be solved by regular Gaussian elimination. '); end for i j+1:m = 1_ij M(i, j:n) end end M(i, j)/M(j, j); = M(i, j:n)-1_ij*M(j, j:n); To test out this algorithm, let's consider the following linear system: -2 1 0 0 1 1 0 U2 2 1 0 -2 1 30-40 63 0 1 -2 1 0 U5 -2 1 0 0 0 1 -2 For those familiar with numerical methods for ordinary differential equations, the system above is a finite-difference discretization of the boundary value problem Ju" = x |u(0) = u(1) = 0 5 0 < x < 1 with five equally spaced interior nodes. Remark: the coefficient matrix above is called a tridiagonal matrix because all of its nonzero entries are concentrated along the three main diagonals of the matrix. a. Create a new script in MATLAB called hw2_msp.m. In your new script, create a section ti- tled "Part 1." In this section, copy the provided code to perform regular Gaussian elimination on the augmented matrix that represents the linear system above. In your code, display the resulting upper triangular augmented matrix to the Command Window. Use format long to show all significant digits of this matrix.
Step by Step Solution
There are 3 Steps involved in it

Get step-by-step solutions from verified subject matter experts


