Question: b. Determine the critical value(s) for the hypothesis test. Round to two decimal places if necessary Enter 0 if normal approximation to the binomial

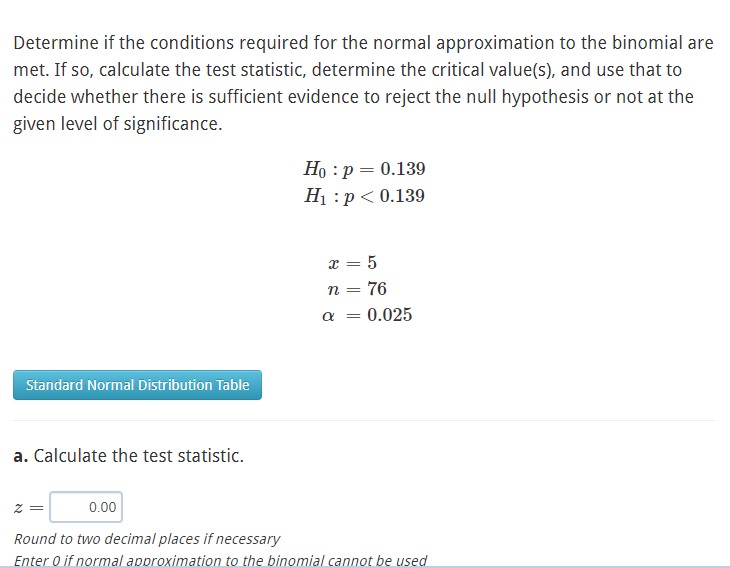
b. Determine the critical value(s) for the hypothesis test. Round to two decimal places if necessary Enter 0 if normal approximation to the binomial cannot be used c. Conclude whether to reject the null hypothesis or not based on the test statistic. Reject Fail to Reject O Cannot Use Normal Approximation to Binomial Determine if the conditions required for the normal approximation to the binomial are met. If so, calculate the test statistic, determine the critical value(s), and use that to decide whether there is sufficient evidence to reject the null hypothesis or not at the given level of significance. Ho p = 0.139 H: p < 0.139 Standard Normal Distribution Table a. Calculate the test statistic. x = 5 n = = 76 0.025 z = 0.00 Round to two decimal places if necessary Enter 0 if normal approximation to the binomial cannot be used
Step by Step Solution
There are 3 Steps involved in it

Get step-by-step solutions from verified subject matter experts


