Question: b. This problems uses a matrix inner product and norm (the inner product simplifies when A is symmetric) (A,B) := Tr(AB), || A|| = V
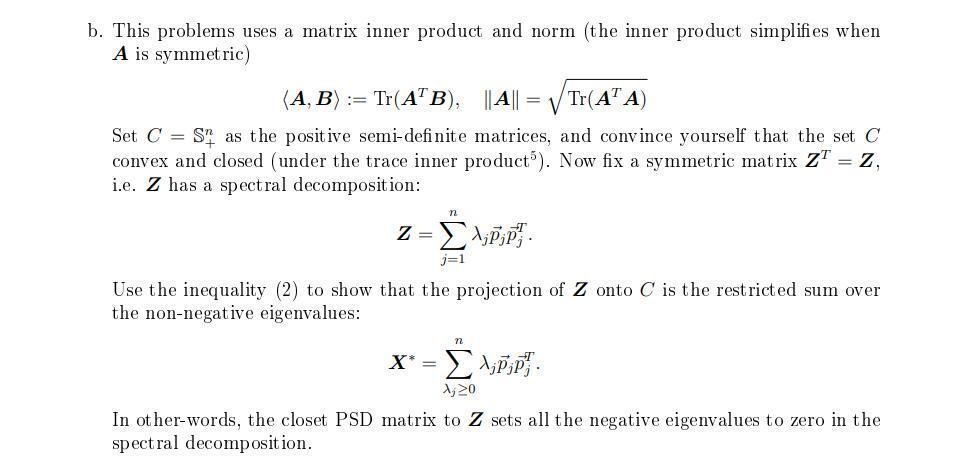
b. This problems uses a matrix inner product and norm (the inner product simplifies when A is symmetric) (A,B) := Tr(A"B), || A|| = V Tr(A' A) Set C = S as the positive semi-definite matrices, and convince yourself that the set C convex and closed (under the trace inner product"). Now fix a symmetric matrix ZT = Z, i.e. Z has a spectral decomposition: n 2= 1;DP). j=1 Use the inequality (2) to show that the projection of Z onto C is the restricted sum over the non-negative eigenvalues: n X* = 1;P;P 1,20 In other-words, the closet PSD matrix to Z sets all the negative eigenvalues to zero in the spectral decomposition. b. This problems uses a matrix inner product and norm (the inner product simplifies when A is symmetric) (A,B) := Tr(A"B), || A|| = V Tr(A' A) Set C = S as the positive semi-definite matrices, and convince yourself that the set C convex and closed (under the trace inner product"). Now fix a symmetric matrix ZT = Z, i.e. Z has a spectral decomposition: n 2= 1;DP). j=1 Use the inequality (2) to show that the projection of Z onto C is the restricted sum over the non-negative eigenvalues: n X* = 1;P;P 1,20 In other-words, the closet PSD matrix to Z sets all the negative eigenvalues to zero in the spectral decomposition
Step by Step Solution
There are 3 Steps involved in it

Get step-by-step solutions from verified subject matter experts


