Question: Background In thermodynamics, we are often interested in knowing how much space a fluid take up , which we specify using the fluid's volume. The
Background
In thermodynamics, we are often interested in knowing how much space a fluid take up which we specify using the fluid's volume. The fluid volume is useful, but it turns out that a more useful thermodynamic property is the volume perunitmass, or the specific volume
Note that the specific volume is just the inverse of the morefamiliar density. The specific volume of singlephase fluids eg steam is just something you can look up in a table. The specific volume of a liquidvapor mixture, however, depends on the fractionsof liquid and vapor in the mixture. The mass fraction of vapor to total fluid is called the quality
of the fluid. The quality of a liquidvapor mixture can range from for a pure liquid to for a pure vapor Using the quality, we can calculate the average specific volume of a socalled saturated liquidvapor mixtureas
where and are the specific volumes of the liquid and vapor parts of the mixture, respectively. The second equals sign introduces the common shorthand
The specific volumes of the vapor and liquid parts of the mixture depend on the mixture's temperature and pressure and the type of fluid. Here, you will only account for the differences in fluid.
Your Task
Write a function called SpecificVolumethat calculates the specific volume of a liquidvapor mixture given its quality and the type of fluid water or Ra
Your function will take a single input and return a single output.
The input will be a m x vector where the first column represents the quality of a saturated mixture and the second column represents the substance either for water or for Ra
The output will be a m x column vector of the calculated specific volumes. Each row of your output should correspond to the same row of the input.
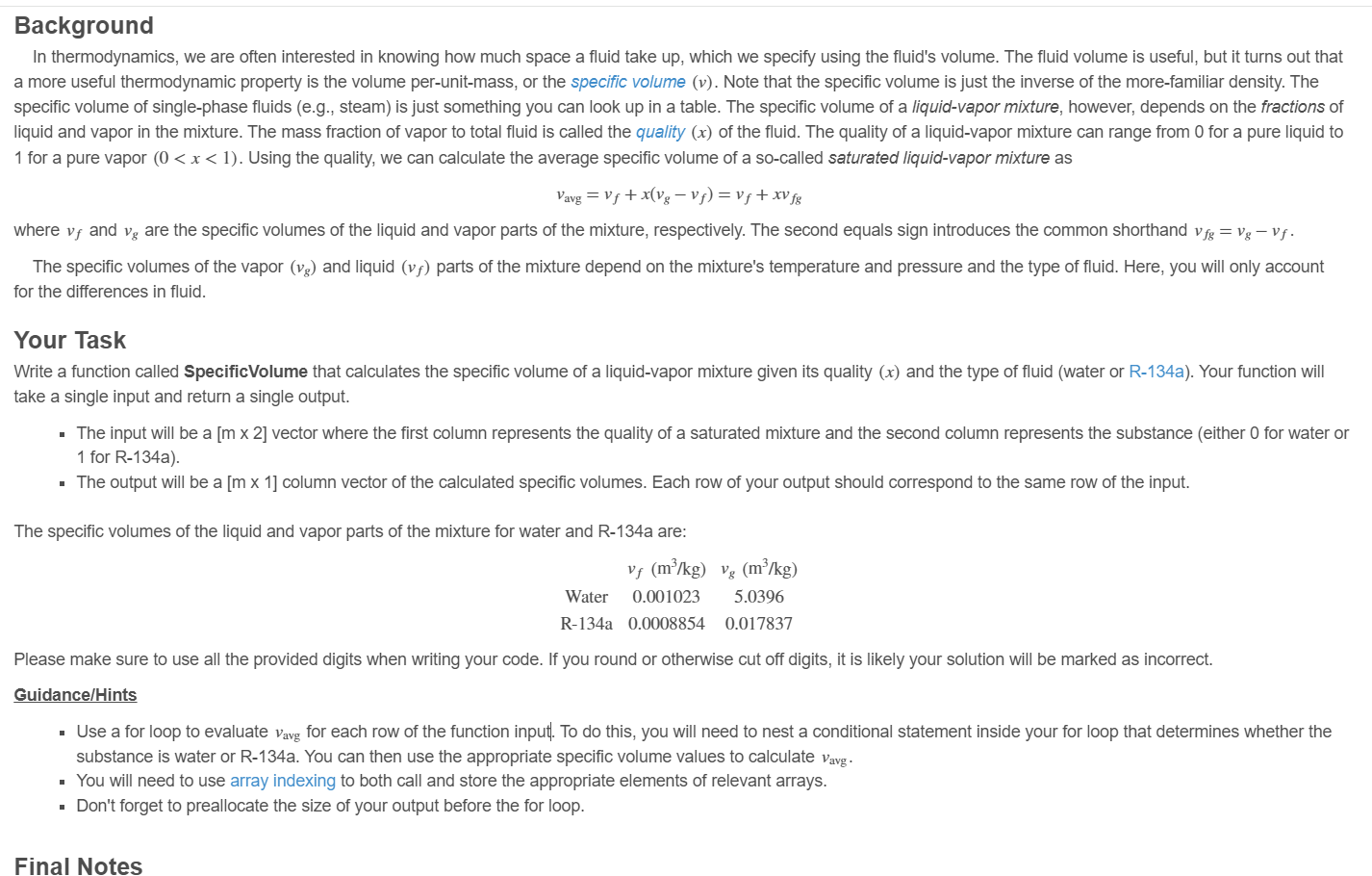
The specific volumes of the liquid and vapor parts of the mixture for water and Ra are:
Please make sure to use all the provided digits when writing your code. If you round or otherwise cut off digits, it is likely your solution will be marked as incorrect.
GuidanceHints
Use a for loop to evaluate for each row of the function input. To do this, you will need to nest a conditional statement inside your for loop that determines whether the substance is water or Ra You can then use the appropriate specific volume values to calculate
You will need to use array indexing
to both call and store the appropriate elements of relevant arrays.
Don't forget to preallocate the size of your output before the for loop.
Final Notes
I know that not all of you have taken thermodynamics. Please note, however, that this is fundamentally just a math problem and you do not need any knoweldge of thermodynamics to complete it Thermodynamics is simply an interestinguseful lens through which to view this math problem, given that most of you are mechanical and aerospace engineers and you will study thermodynamics in appreciable depth during the next couple of years. Background
In thermodynamics, we are often interested in knowing how much space a fluid take up which we specify using the fluid's volume. The fluid volume is useful, but it turns out that a more useful thermodynamic property is the volume perunitmass, or the specific volume v Note that the specific volume is just the inverse of the morefamiliar density. The specific volume of singlephase fluids eg steam is just something you can look up in a table. The specific volume of a liquidvapor mixture, however, depends on the fractions of liquid and vapor in the mixture. The mass fraction of vapor to total fluid is called the quality x of the fluid. The quality of a liquidvapor mixture can range from for a pure liquid to for a pure vapor
Step by Step Solution
There are 3 Steps involved in it
1 Expert Approved Answer
Step: 1 Unlock


Question Has Been Solved by an Expert!
Get step-by-step solutions from verified subject matter experts
Step: 2 Unlock
Step: 3 Unlock


