Question: Base 8 Cipher Encryption Program Input 2 qT1oFJKx 7dMSktfP jCyc+3Em /puXUs10 eIYBGbw4 rhQ69WgZ N9A2nLvO iHzVRaD5 101 I+went+to+the+store+to+buy+12+eggs/ abcdefgh ijklmnop qrstuvwx yz012345 ABCDEFGH IJKLMNOP QRSTUVWX YZ+67/89
Base 8 Cipher Encryption Program

Input
2
qT1oFJKx 7dMSktfP jCyc+3Em /puXUs10 eIYBGbw4 rhQ69WgZ N9A2nLvO iHzVRaD5 101 I+went+to+the+store+to+buy+12+eggs/
abcdefgh ijklmnop qrstuvwx yz012345 ABCDEFGH IJKLMNOP QRSTUVWX YZ+67/89 34439 This+is+a+better+test+of+primenumber+offS+hereAreAlltheDigits/0123456789
Output
yjx1/goTOb47CA5ZdY6srXxB++7ZPpU6k79
kyB7TseIcLSY/Fq/Mh4lneIhxaN7r/sA0HhSf7+dXmb4YtJVO8R358gJm0zCbhQImO7hHK8+
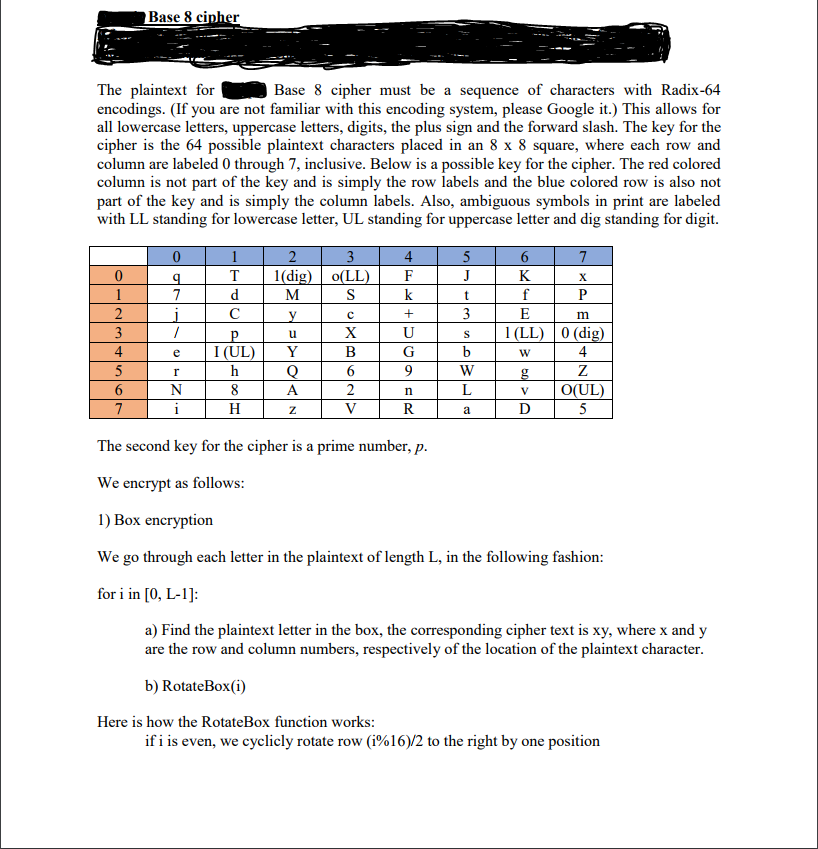
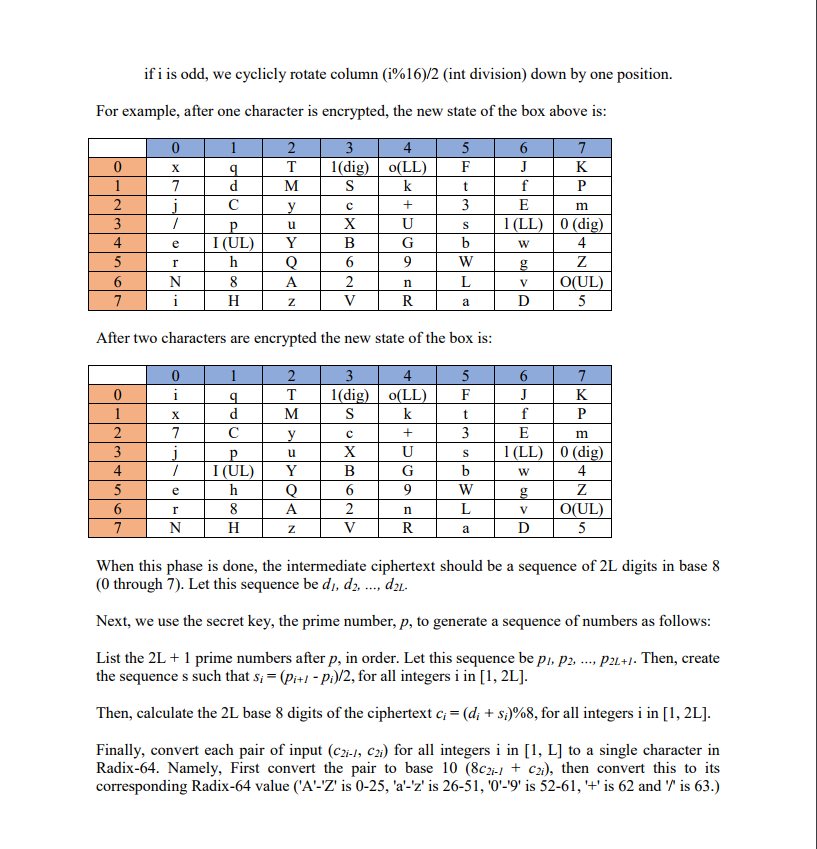
Base 8 cipher The plaintext for encodings. (If you are not familiar with this encoding system, please Google it.) This allows for all lowercase letters, uppercase letters, digits, the plus sign and the forward slash. The key for the cipher is the 64 possible plaintext characters placed in an 8 x 8 square, where each row and column are labeled 0 through 7, inclusive. Below is a possible key for the cipher. The red colored column is not part of the key and is simply the row labels and the blue colored row is also not part of the key and is simply the column labels. Also, ambiguous symbols in print are labeled with LL standing for lowercase letter, UL standing for uppercase letter and dig standing for digit. Base 8 cipher must be a sequence of characters with Radix-64 sl (LL) 0 (dig) e IUL UL The second key for the cipher is a prime number We encrypt as follows: 1) Box encryption We go through each letter in the plaintext of length L, in the following fashion: for i in [0, L-1]: a) Find the plaintext letter in the box, the corresponding cipher text is xy, where x and y are the row and column numbers, respectively of the location of the plaintext character b) RotateBox(i) Here is how the RotateBox function works: ifi is even, we cyclicly rotate row (i% 16)/2 to the right by one position Base 8 cipher The plaintext for encodings. (If you are not familiar with this encoding system, please Google it.) This allows for all lowercase letters, uppercase letters, digits, the plus sign and the forward slash. The key for the cipher is the 64 possible plaintext characters placed in an 8 x 8 square, where each row and column are labeled 0 through 7, inclusive. Below is a possible key for the cipher. The red colored column is not part of the key and is simply the row labels and the blue colored row is also not part of the key and is simply the column labels. Also, ambiguous symbols in print are labeled with LL standing for lowercase letter, UL standing for uppercase letter and dig standing for digit. Base 8 cipher must be a sequence of characters with Radix-64 sl (LL) 0 (dig) e IUL UL The second key for the cipher is a prime number We encrypt as follows: 1) Box encryption We go through each letter in the plaintext of length L, in the following fashion: for i in [0, L-1]: a) Find the plaintext letter in the box, the corresponding cipher text is xy, where x and y are the row and column numbers, respectively of the location of the plaintext character b) RotateBox(i) Here is how the RotateBox function works: ifi is even, we cyclicly rotate row (i% 16)/2 to the right by one position
Step by Step Solution
There are 3 Steps involved in it

Get step-by-step solutions from verified subject matter experts


