Question: Based on the graph and matlab code, can you explain these questions. We know the error has the form O (1/Np ); what is p
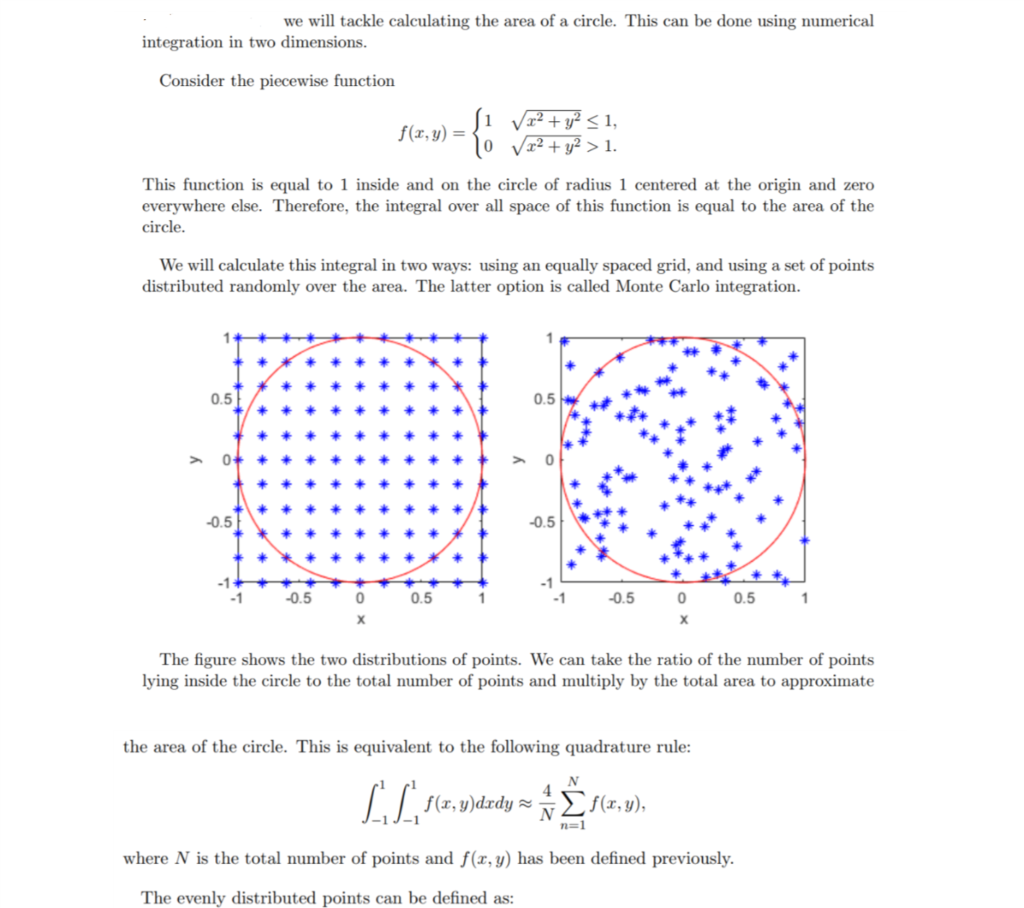

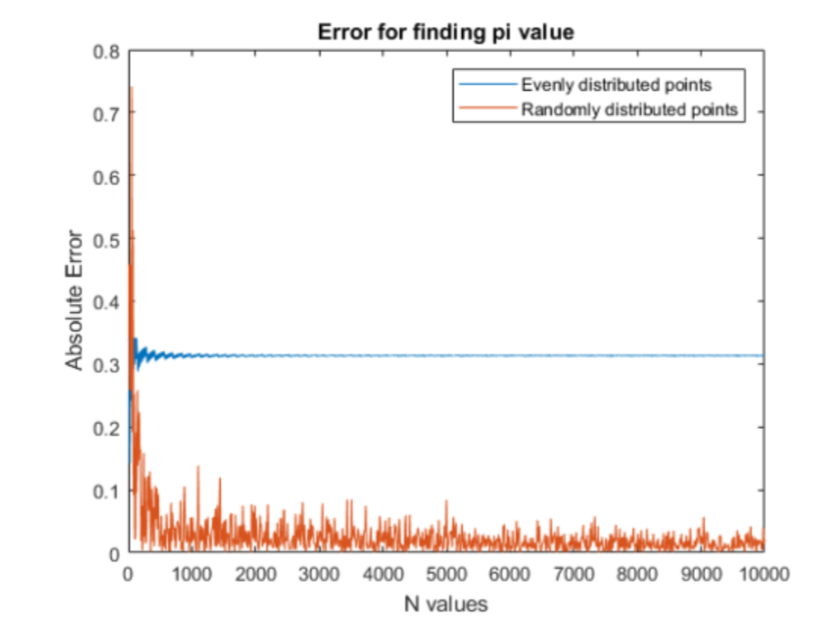 Based on the graph and matlab code, can you explain these questions. We know the error has the form O (1/Np ); what is p for evenly distributed points? What restrictions are there on the number N for this distribution of points? What is p for Monte Carlo integration? Why might Monte Carlo integration fail? And can you explain why for each. Here is the matlab code I used :
Based on the graph and matlab code, can you explain these questions. We know the error has the form O (1/Np ); what is p for evenly distributed points? What restrictions are there on the number N for this distribution of points? What is p for Monte Carlo integration? Why might Monte Carlo integration fail? And can you explain why for each. Here is the matlab code I used :
clc; clear all; close all; m1 = linspace (10, 10000, 1000); count = 0; for j=1:length(m1) m = m1(j); s = 0; for i = 1:m+1 xx = -1+(2*(i-1))/m; yy = -1+(2*(i-1))/m; f=sqrt(xx.^2+yy.^2); if f we will tackle calculating the area of a circle. This can be done using numerical integration in two dimensions. Consider the piecewise function f(x, g)- This function is equal to inside and on the circle of radius 1 centered at the origin and zero everywhere else. Therefore, the integral over all space of this function is equal to the area of the circle We will calculate this integral in two ways: using an equally spaced grid, and using a set of points distributed randomly over the area. The latter option is called Monte Carlo integration 0.5 0.5 0.5 -1 0.5 0 0.5 0.5 0.5 The figure shows the two distributions of points. We can take the ratio of the number of points lying inside the circle to the total number of points and multiply by the total area to approximate the area of the circle. This is equivalent to the following quadrature rule: -i J-1 f(z.yjdzdy ~ N ? f(z.y). where N is the total number of points and f(x, y) has been defined previously. The evenly distributed points can be defined as: we will tackle calculating the area of a circle. This can be done using numerical integration in two dimensions. Consider the piecewise function f(x, g)- This function is equal to inside and on the circle of radius 1 centered at the origin and zero everywhere else. Therefore, the integral over all space of this function is equal to the area of the circle We will calculate this integral in two ways: using an equally spaced grid, and using a set of points distributed randomly over the area. The latter option is called Monte Carlo integration 0.5 0.5 0.5 -1 0.5 0 0.5 0.5 0.5 The figure shows the two distributions of points. We can take the ratio of the number of points lying inside the circle to the total number of points and multiply by the total area to approximate the area of the circle. This is equivalent to the following quadrature rule: -i J-1 f(z.yjdzdy ~ N ? f(z.y). where N is the total number of points and f(x, y) has been defined previously. The evenly distributed points can be defined as
Step by Step Solution
There are 3 Steps involved in it

Get step-by-step solutions from verified subject matter experts


