Question: Based on this C code, could you implement read _ record, sift _ up , sift _ down, heap _ insert and heap _ remove
Based on this C code, could you implement readrecord, siftup siftdown, heapinsert and heapremove in asembly code for Windows. Ive done heapswap and heapcount alreadyincluded in images Basically commenting out the definition in C code, leaving the prototype, and then implementing it in Assembly.
C:
void heapswapint i int j
RECORD temp heapi;
heapi heapj;
heapj temp;
Assembly:
text
globl heapswap
heapswap:
# Load the address of heap array into rax
leaq heapriprax # rax address of heap
# Load heapiusing rcx as i into r
movq rax, rcxr # r heapi
# Load heapjusing rdx as j into r
movq rax, rdxr # r heapj
# Swap heapi and heapj
movq rrax, rcx # heapi heapj
movq rrax, rdx # heapj heapi
ret
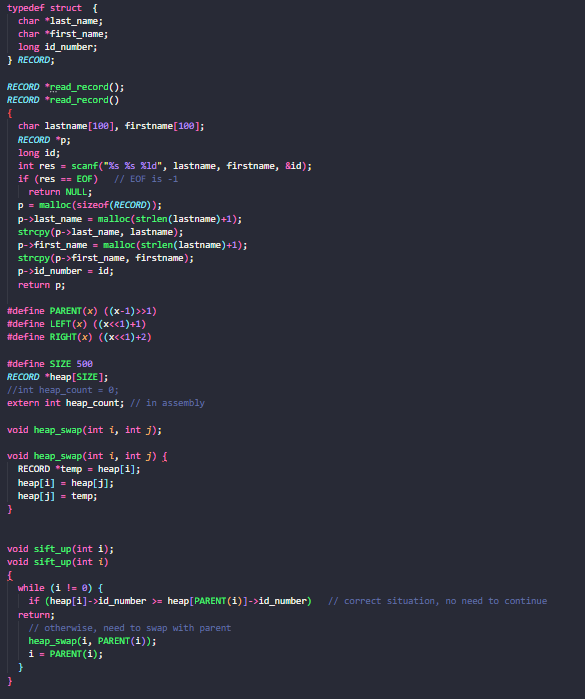
typedef struct
char lastname;
char firstname;
long idnumber;
RECORD;
RECORD readrecord;
RECORD readrecord
char lastname firstname;
RECORD p;
long id;
int res scanfs s ld lastname, firstname, id;
if res EOF EOF is
return NLLL;
p mallocsizeofRECORD;
plastname mallocstrlenlastname;
strcpyplastname, lastname;
pfirstname mallocstrlenlastname;
strcpypfirstname, firstname;
pidnumber id;
return p;
##define PARENTxx
##define LEFTxx
##define RIGHTxx
##define SIZE
RECORD heapSIZE;
int heapcount ;
extern int heapcount; in assembly
void heapswapint i int j;
void heapswapint i int j
RECORD temp heapi;
heapi heapj;
heapj temp;
void siftupint i;
void siftupint i
while i
if heapiidnumber heapPARENTiidnumber correct situation, no need to continue
return;
otherwise, need to swap with parent
heapswapi PARENTi;
i PARENTi;
void siftdown;
void siftdomn
int i ;
int lastparent PARENTheapcount ;
int minchild;
while i lastparent
if RIGHTi heapcount
heapLEFTiidnumber heapRIGHTiidnumber
minchild LEFTi;
else
minchild RIGHTi;
if heapiidnumber heapminchildidnumber
heapswapi minchild;
i minchild;
else done sifting down
return;
void heapinsertRECORD p;
void heapinsertRECORD p
if heapcount SIZE
printfError: Heap is full
;
exit;
heapheapcount p;
siftupheapcount;
heapcount;
RECORD heapremove;
RECORD heapremove
if heapcount
printfError: Heap is empty
;
exit;
RECORD result heap;
heapcount;
heap heapheapcount;
siftdown;
return result;
text
globl heapswap
globl heapinsert
globl readrecord
heapswap:
Load the address of heap array into rax
leaq heapriprax # rax address of heap
Load heapiusing rcx as i into r
movq rax, rcxr # r heapi
Load heapjusing rdx as j into r
movq rax, rdxr # r heapj
Swap heapi and heapj
movq rrax, rcx # heapi heapj
movq rrax, rdx # heapj heapi
ret
text
globl heapswap
globl heapinsert
globl readrecord
heapswap:
Load the address of heap array into rax
leaq heapriprax # Xrax address of heap
Load heapiusing rcx as i into r
movq rax, rcxr # r heapi
Load heapjusing rdx as j into r
movq rax, rdxr # r heapj
Swap heapi and heapj
movq rrax, rcx # heapi heapj
movq rrax, rdx # heapj heapi
ret
data
globl heapcount
heapcount:
long # Initialize heapcount to
Step by Step Solution
There are 3 Steps involved in it
1 Expert Approved Answer
Step: 1 Unlock


Question Has Been Solved by an Expert!
Get step-by-step solutions from verified subject matter experts
Step: 2 Unlock
Step: 3 Unlock


