Question: BASIC CALCULUS TOPIC: DISCONTINUITY SHOW THE COMPLETE SOLUTION. THE KEY ANSWER IS PROVIDED (title of the key answer in the picture is deepen), ALL YOU


BASIC CALCULUS
TOPIC: DISCONTINUITY
SHOW THE COMPLETE SOLUTION. THE KEY ANSWER IS PROVIDED (title of the key answer in the picture is "deepen"), ALL YOU NEED TO DO IS TO SHOW THE COMPLETE SOLUTION.

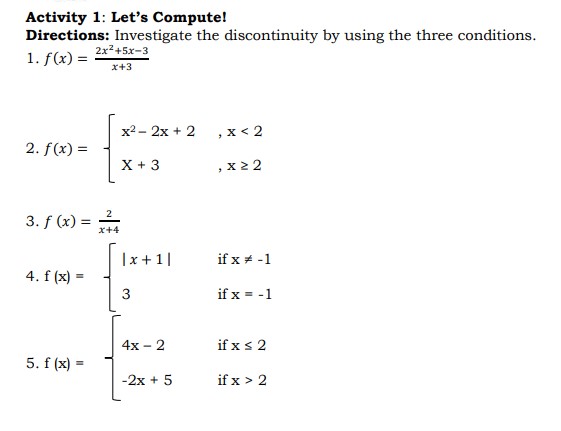


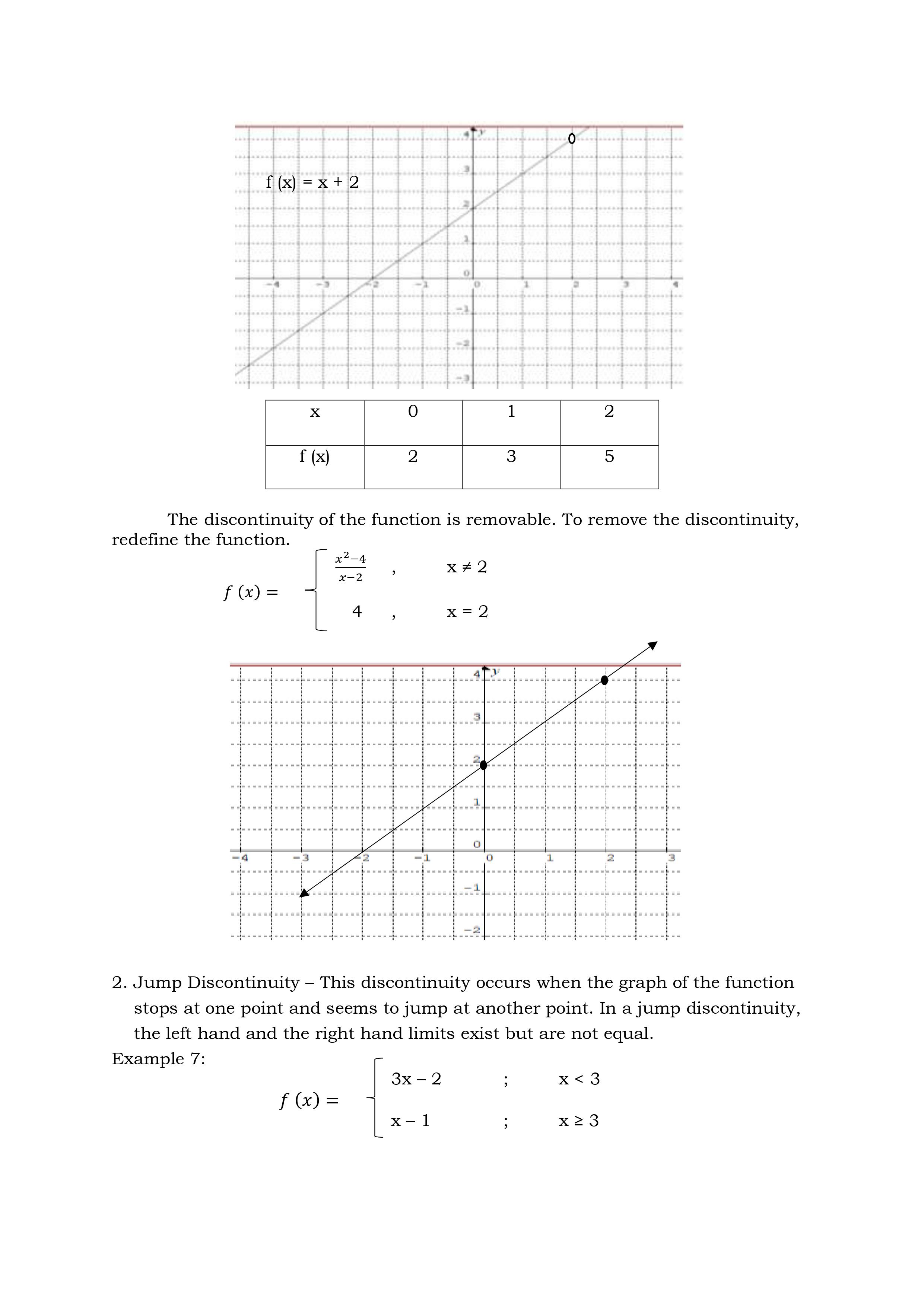
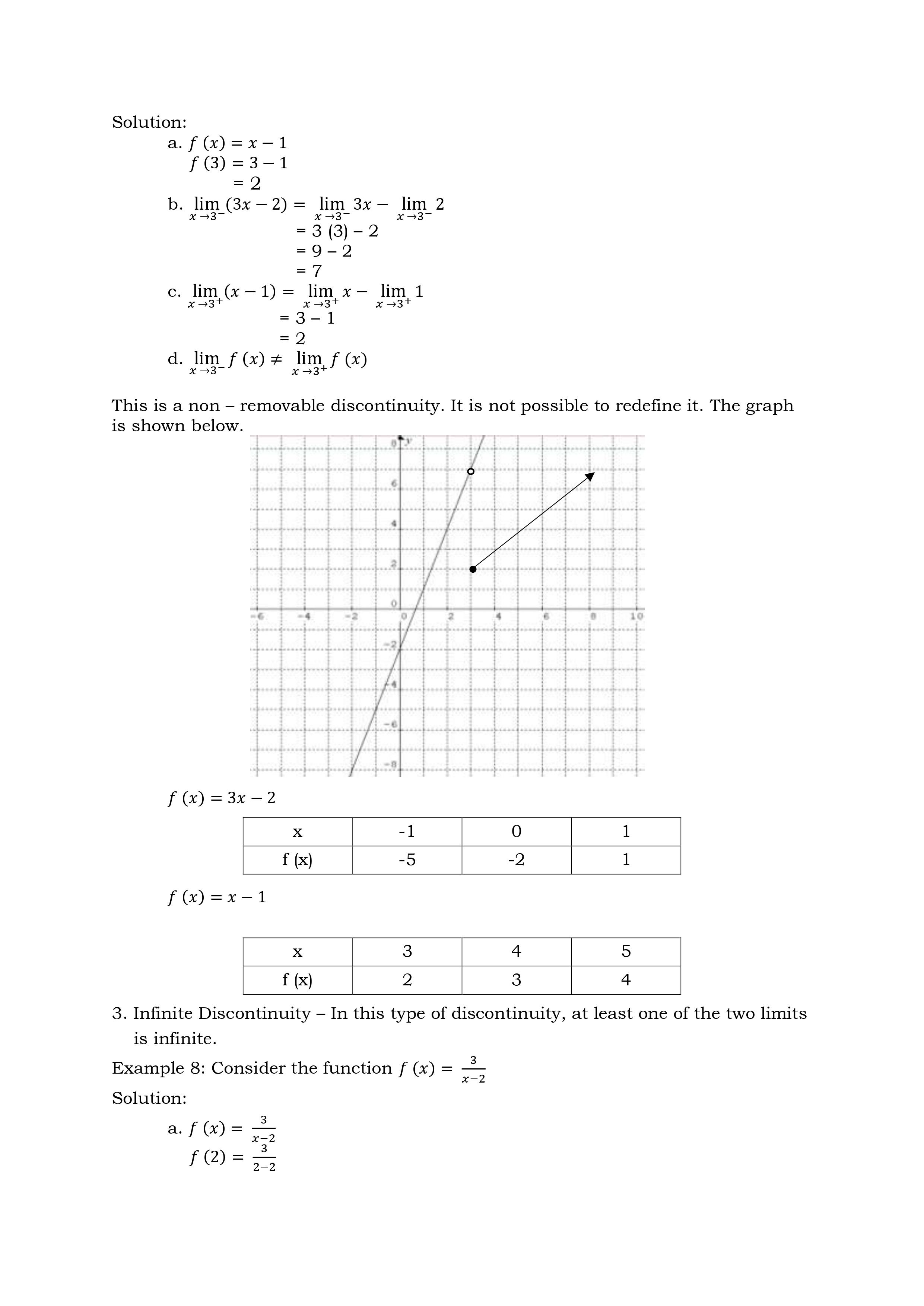
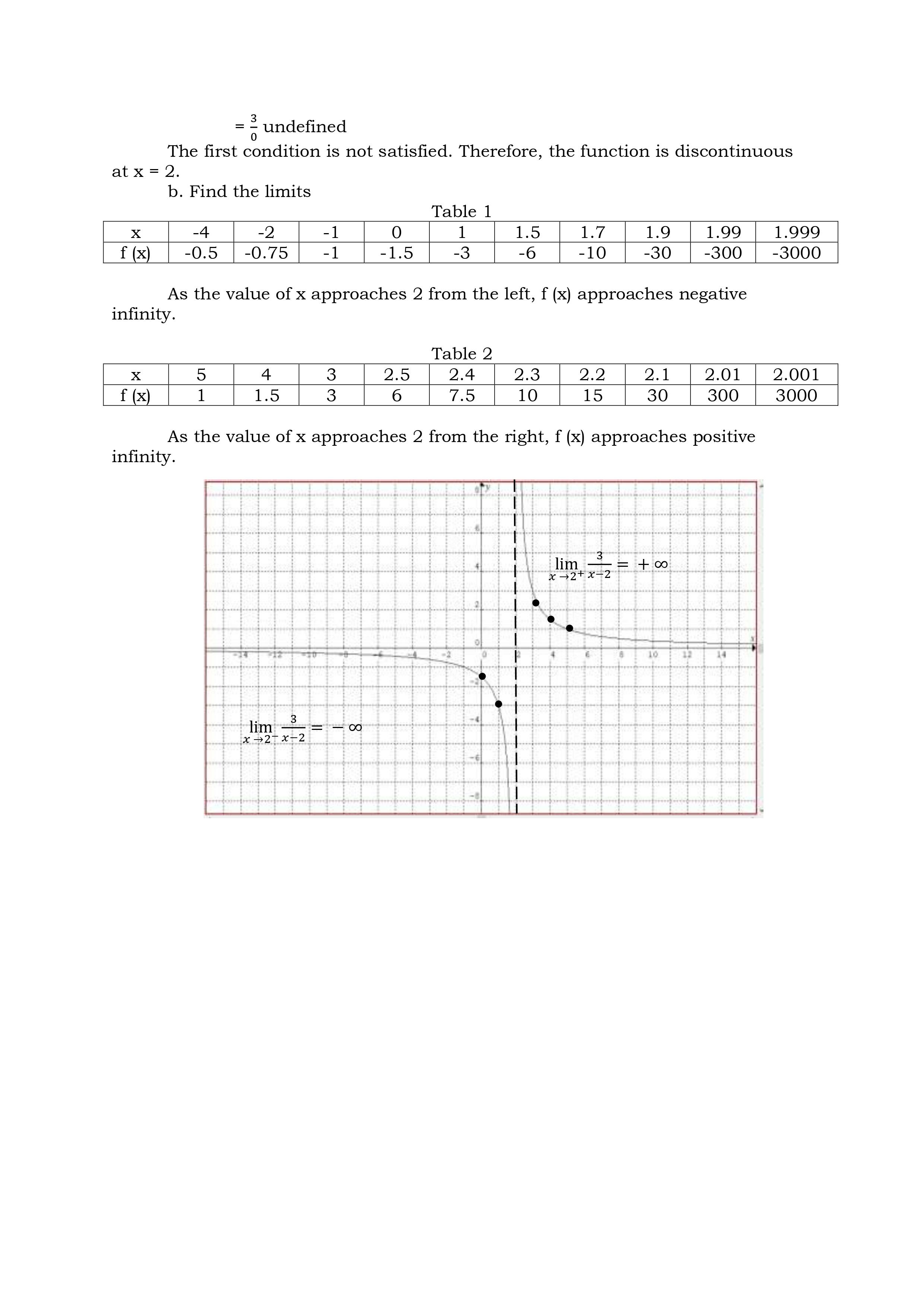
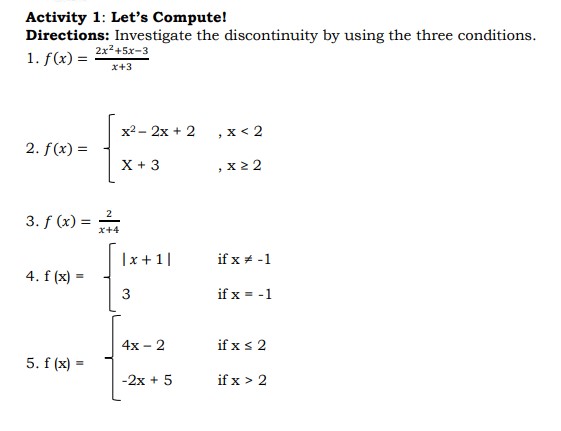
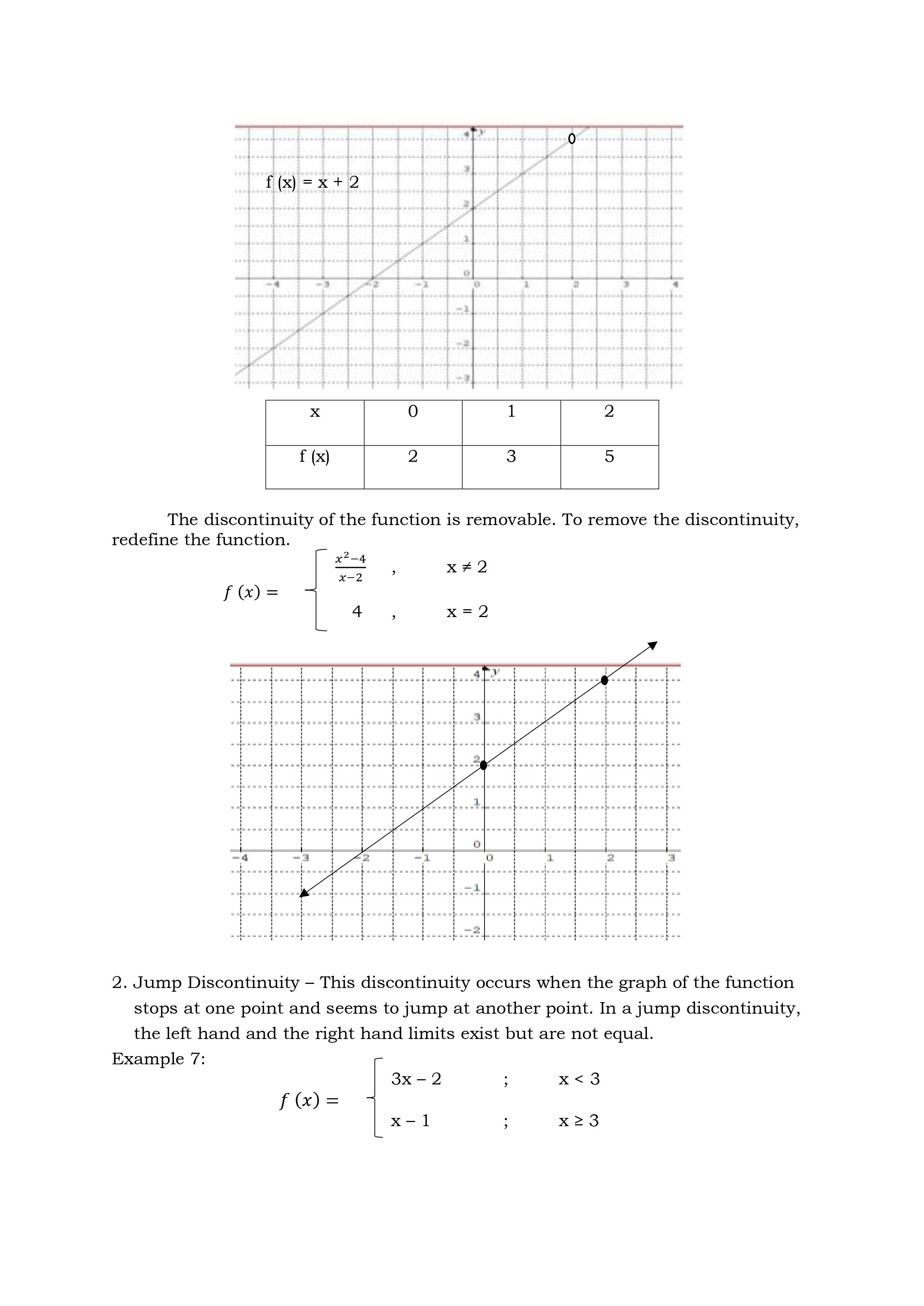
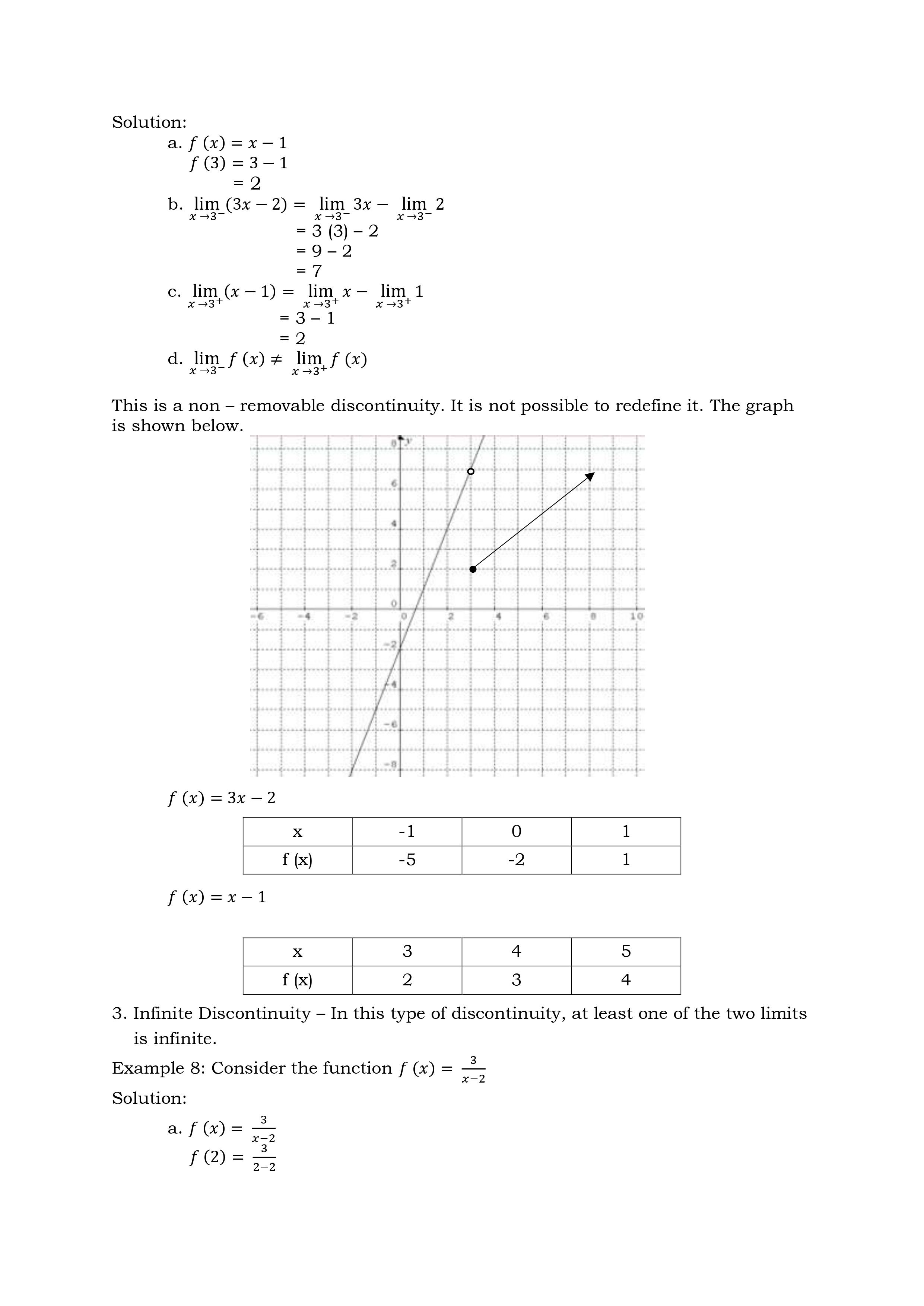
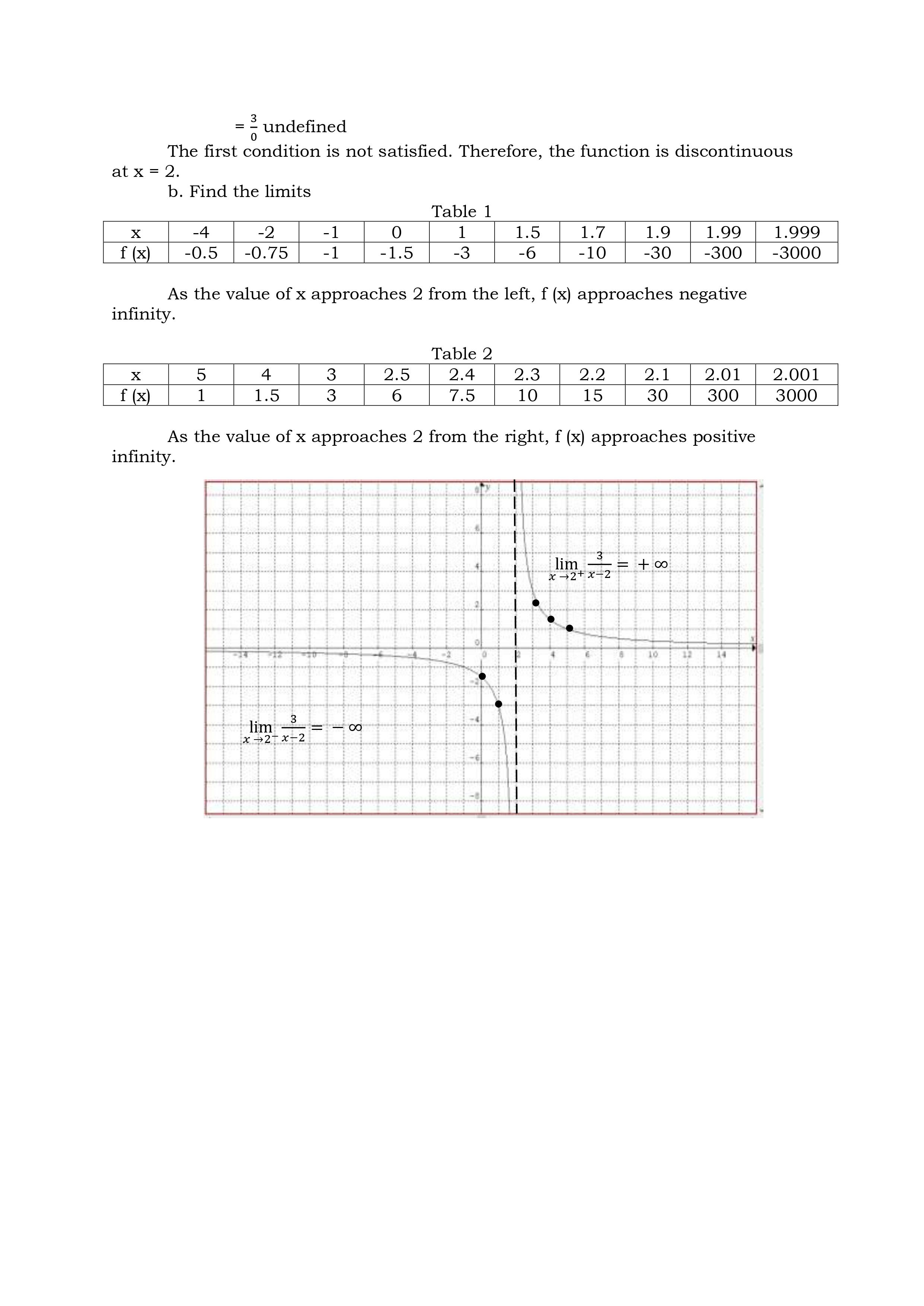
Deepen 1. a. 0/0 a. 3 b. -7 b. 0 c. discontinuous at x - -3 c. discontinuous at x - -1 2. a. 5 5. a. 6 b. 2 b. 6 c. 5 , jump discontinuity c. discontinuous at x = 2 3. a. undefined b. find the limits from left / right c. infinite discontinuityActivity 1: Let's Compute! Directions: Investigate the discontinuity by using the three conditions. 1. f (x) = = 2x-+5x-3 x+3 x2- 2x + 2 , x 2Discover Continuity at a Number A function f (x) is said to be continuous at the number if all the following three conditions are satisfied. a. f (a) exists b. lim f (x) exists x - a c. lim f(x) = f(a) x -a' Note: If any one or more of the above three conditions fail, the function f(x) is said to be continuous at a number a. Example 1: Determine whether f(x) = 4x2 + x - 2 is continuous at x = 1 Solution: a. f (x) = 4x2 +x-2 = 4 (1)2 + 1 - 2 = 3 b. lim f (x) = 4x2 + x -2 x -1 = 4 (1)2 + 1 -2 = 3 c. lim f (x) = f (1) x -1 The three conditions are satisfied. The function is continuous at x = 1. Example 2: Determine whether the function f (x) = _ _ is continuous at: 1. x = 0 2. X = 2 3. x = 3 Solution: 1. At x = 0 a. f ( x ) = *-9 f(0) = 02-9 0 - 3 = 3 b. lim *2-9 lim x2-9 - = x -0x-3 lim x-3 lim x2 - lim 9 =X-0 X 20 lim x- lim 3 = 3 c. lim f (x) = f(0) The three conditions are satisfied. Hence, f(x) is continuous at x = 0d. f(3) = V9x2 = 9 (3)2 e. xLim3+f (x) = #9 (x)2 = m =0 x9g+fo)=f(o It is continuous from the right of X = 3. Hence, the function is continuous on the interval [ 3, 3 ]. Types of Discontinuity 1. Removable Discontinuity This discontinuity occurs when there is a hole in the graph of the function. Example 6: Consider the following function. x274 Ho=k2 The denominator of this rational function should not be equal to zero, that is, X 2 0. If X 2 = 0, then X = 2. Substituting 2 in place of X will make the rational fraction equal to g which is undened. This means that the function is discontinuous at X = 2. This can be veried by using the denition of continuity. arm: x24 x2 224 22 f(2)= _0 indeterminate In the language of Calculus, % is indeterminate 2_ _ b. limx 4 = lim (x+2)(x 2) x >2 3672 x >2 (x72) = lim x + 2 x42 =1imx+ lim2 x62 x62 =2+2 =4 c.QlCi_rgf(x)f(2) Hence, the function is discontinuous at X = 2. The graph is shown below, there is a hole in the graph. f ( x) = x +2 X O 1 2 f (x) 2 3 5 The discontinuity of the function is removable. To remove the discontinuity, redefine the function. x2 - X - 2 x + 2 f ( x ) = 4 X = 2 2. Jump Discontinuity - This discontinuity occurs when the graph of the function stops at one point and seems to jump at another point. In a jump discontinuity, the left hand and the right hand limits exist but are not equal. Example 7: 3x - 2 X
Step by Step Solution
There are 3 Steps involved in it

Get step-by-step solutions from verified subject matter experts


