Question: Bayesian Inference on Imperfect Information We have a Bayesian agent running on a computer, trying to learn information about what the pa rameter 9 could

Bayesian Inference on Imperfect Information

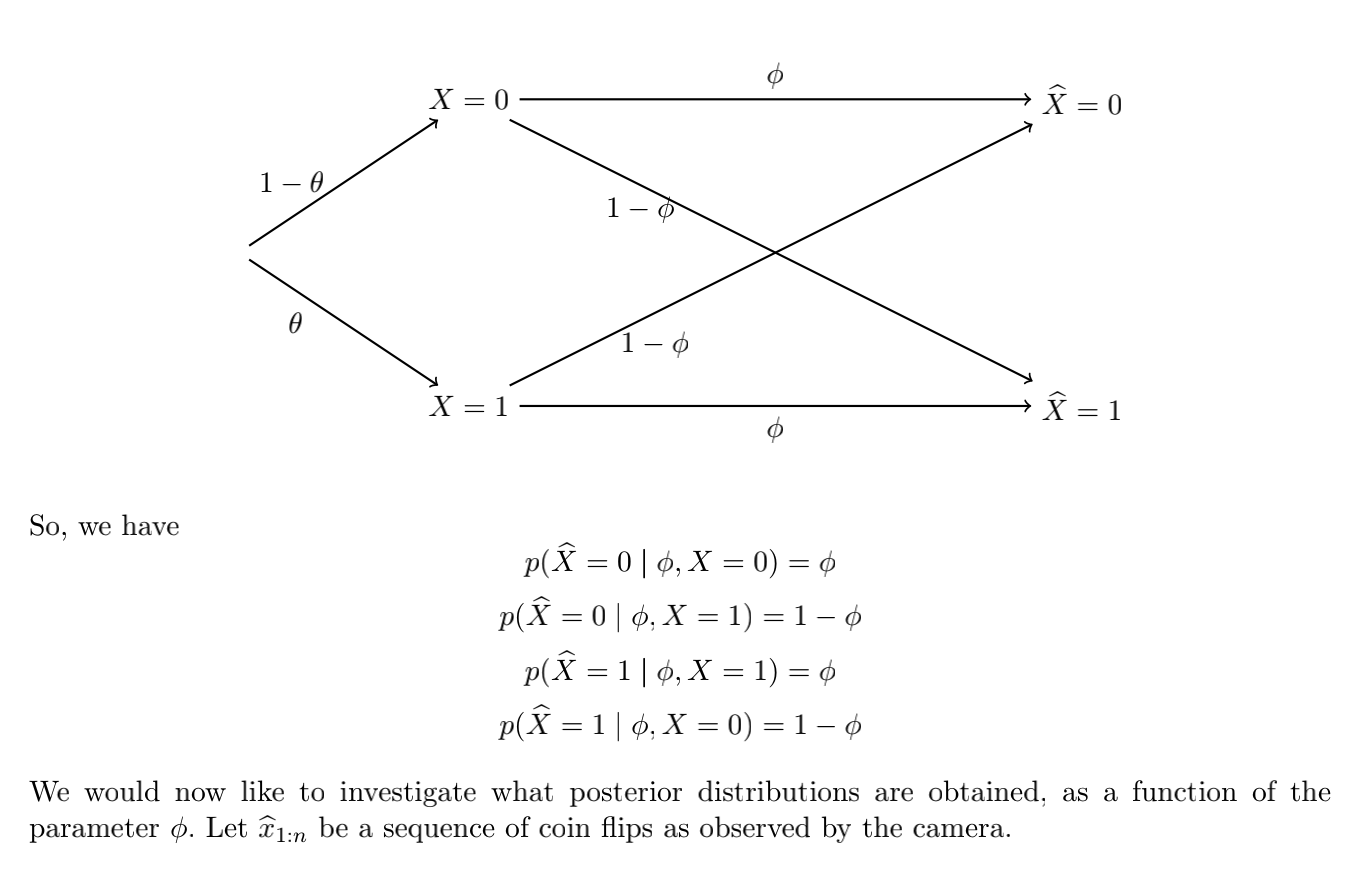

We have a Bayesian agent running on a computer, trying to learn information about what the pa rameter 9 could be in the coin ip problem, based on observations through a noisy camera. The noisy camera takes a photo of each coin ip and reports back if the result was a 0 or a 1. Unfortunately, the side of the coin with a \"1\" on it is very shiny, and the reected light causes the camera to sometimes report back the wrong resultEl The probability that the camera returns a correct answer is parame terised by q E [0, 1]. Letting X denote the true outcome of the coin, and I? denoting what the camera reported back7 we can draw the relationship between X and X: as shown. So, we have p(2'5:0I,X:0): p(2'5:0|gx:1):1 mi:max:n: p()'?:ll,X:0):1 We would now like to investigate what posterior distributions are obtained: as a function of the parameter :5. Let 331:\" be a sequence of coin ips as observed by the camera. a) (5 credits) Briey comment about how the camera behaves for ct = 1, ct = 0.5. ct = 0. How you expect this would change how the agent updates it's prior to a posterior on 6. given an observation of X. (No equations required.) A b) (10 credits) Compute p(X = Ill?) for all a: E {0,1}. c) (15 credits) The coin is ipped, and the camera reports seeing a zero. (ie. that 55A: 0.) Given an arbitrary prior p09), compute the posterior 19le = 0). What does p(t9|X = 0) simplify to when gt = 1? When gt = 1/2? When gt 2 0? Explain your observations. (1) (10 credits) Compute 30(6) | 55 = U) for the same choice of prior p09) = 3062(1 (9)2 as before. Simplify your expression. e) [10 credits) Plot p(6 | J? = 0) as a function of (9, for all (t E {0,025,015, 0.75.1} on the same graph to compare them. Comment on how the shape of the distribution changes with gt. Explain your observations
Step by Step Solution
There are 3 Steps involved in it

Get step-by-step solutions from verified subject matter experts


