Question: Bellman Ford distance vector algorithm: Consider the scenario shown below, where at t=1, node e receives distance vectors from neighboring nodes d, b, h and
Bellman Ford distance vector algorithm: Consider the scenario shown below, where at t=1, node e receives distance vectors from neighboring nodes d, b, h and f. The (old) distance vector at e (the node at the center of the network) is also shown, before receiving the new distance vector from its neighbors.
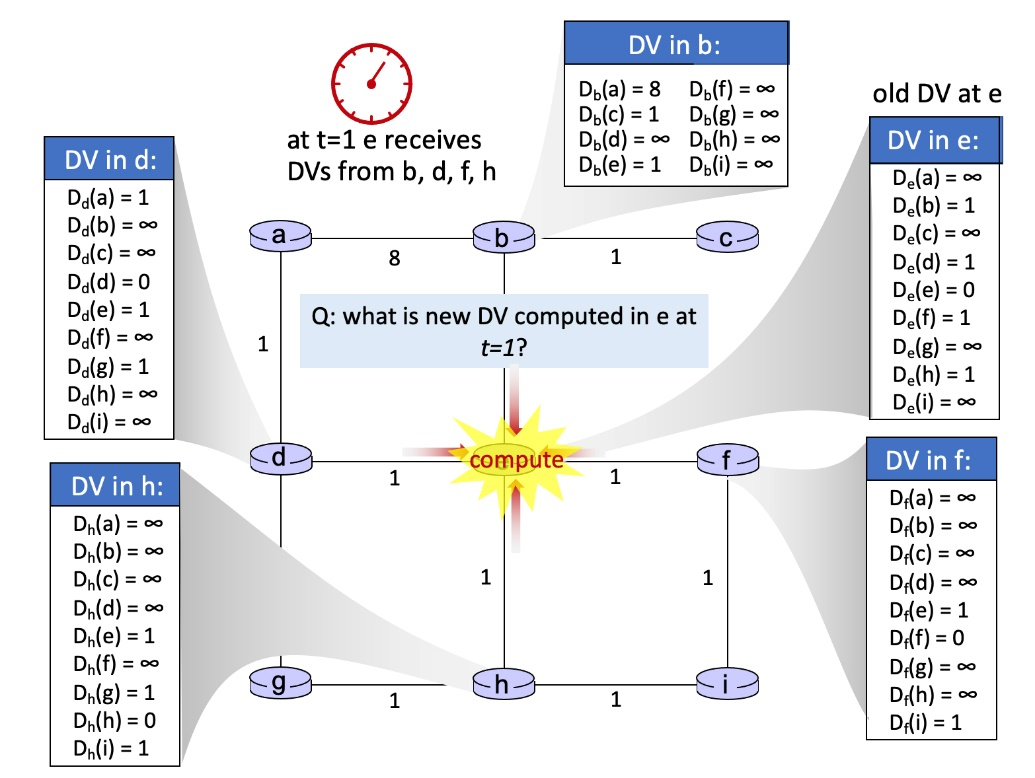
- Indicate which of the components of new distance vector at e have a value of 1 after e has received the distance vectors from its neighbors and updated its own distance vector.
- Indicate which of the components of new distance vector at e have a value of 2 after e has received the distance vectors from its neighbors and updated its own distance vector.
DV in b: old DV at e = OO Db(a) = 8 Db(f) = 0 Db(c) = 1 Dolg) Db(d) = 0 Doch) Dble) = 1 Db(i) = at t=1 e receives DVs from b, d, f, h = oo 0 = OO Oo a 8 1 DV in d: Dd(a) = 1 Dalb) = Dd(c) = 0 Dd(d) = 0 Dd(e) = 1 Dalf) Dog) = 1 Dah) Dali) DV in e: De(a) De(b) = 1 Dec) = 0 De(d) = 1 Dele) = 0 De(f) = 1 De(g) = 0 De(h) = 1 Deli) = 0 = OO Q: what is new DV computed in e at t=1? 1 = OO = OO compute 1 1 OO 1 1 = oo DV in h: Dh(a) = 0 Dh(b) = 0 Dh(c) = Dh(d) = 0 Dh(e) = 1 Dh(f) = 0 Dh(g) = 1 Dh(h) = 0 Dh(i) = 1 DV in f: Dr(a) = 0 Di(b) DH(C) = 0 Di(d) Dr(e) = 1 D:(f) = 0 Di(g) Di(h) Dr(i) = 1 = OO 1 1 =oO
Step by Step Solution
There are 3 Steps involved in it

Get step-by-step solutions from verified subject matter experts


