Question: Below is the answer for question plz explain how to get numbers in the red box! Richard runs a small factory producing garden furniture. One
Below is the answer for question
plz explain how to get numbers in the red box!
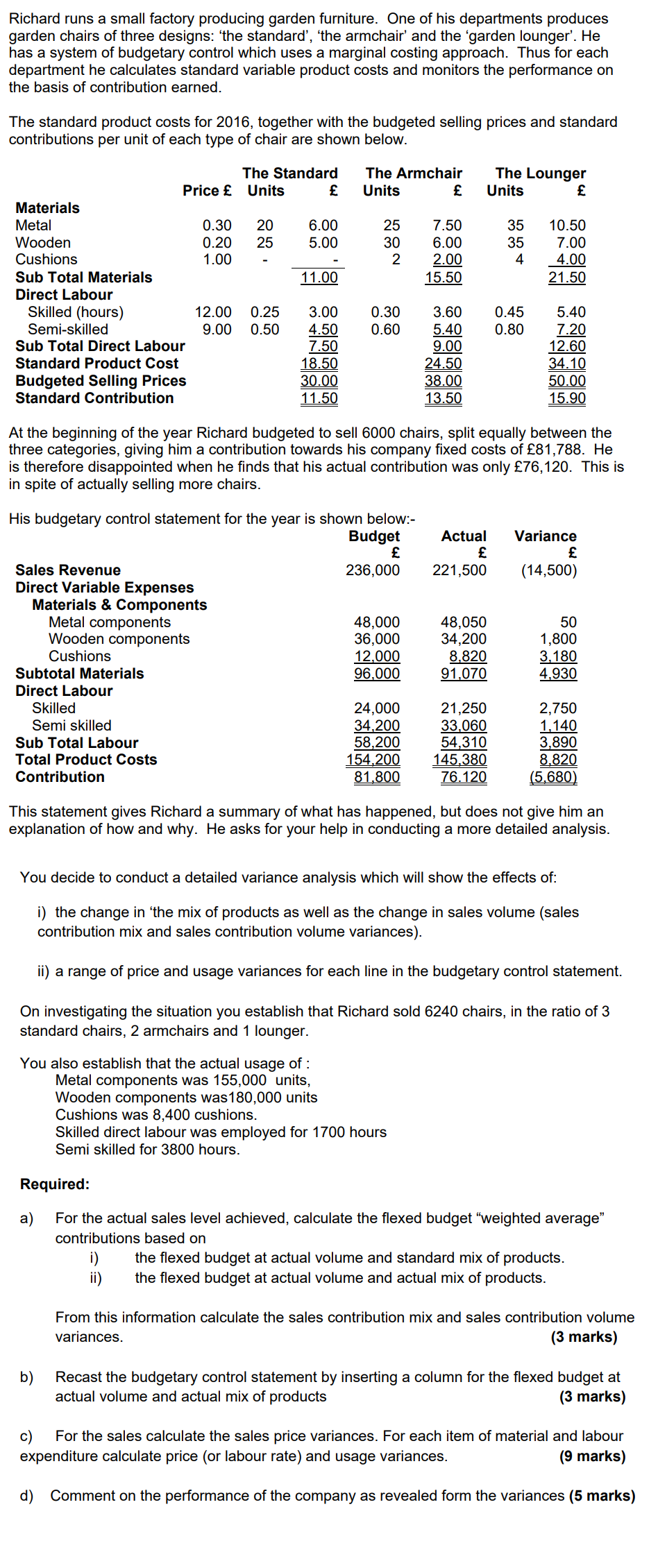
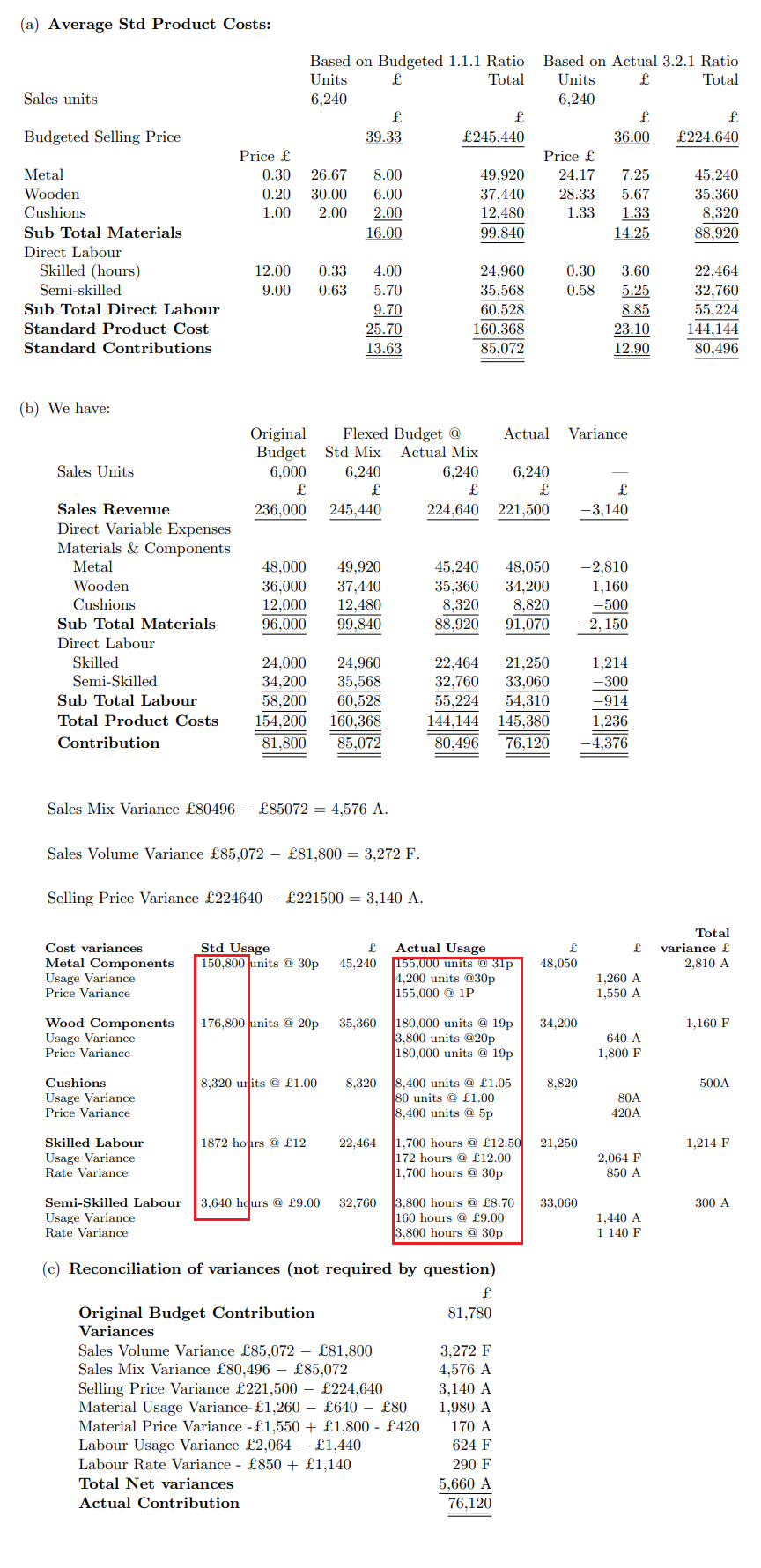
Richard runs a small factory producing garden furniture. One of his departments produces garden chairs of three designs: 'the standard', 'the armchair' and the 'garden lounger'. He has a system of budgetary control which uses a marginal costing approach. Thus for each department he calculates standard variable product costs and monitors the performance on the basis of contribution earned. The standard product costs for 2016, together with the budgeted selling prices and standard contributions per unit of each type of chair are shown below. The Standard The Armchair The Lounger Price Units Units Units Materials Metal 0.30 20 6.00 25 7.50 35 10.50 Wooden 0.20 25 5.00 30 6.00 35 Cushions 1.00 2 2.00 4 7.00 4.00 21.50 Sub Total Materials 11.00 15.50 LIW Direct Labour Skilled (hours) 12.00 0.25 3.00 0.30 3.60 0.45 5.40 Semi-skilled 9.00 0.50 4.50 0.60 5.40 0.80 7.20 Sub Total Direct Labour 7.50 9.00 12.60 Standard Product Cost 18.50 24.50 34.10 Budgeted Selling Prices 30.00 38.00 50.00 15.90 Standard Contribution 11.50 13.50 At the beginning of the year Richard budgeted to sell 6000 chairs, split equally between the three categories, giving him a contribution towards his company fixed costs of 81,788. He is therefore disappointed when he finds that his actual contribution was only 76,120. This is in spite of actually selling more chairs. His budgetary control statement for the year is shown below:- Budget Actual Variance Sales Revenue 236,000 221,500 (14,500) Direct Variable Expenses Materials & Components 48,000 48,050 50 Metal components Wooden components Cushions 36,000 34,200 1,800 12,000 8,820 3,180 Subtotal Materials 96,000 91,070 4,930 Direct Labour Skilled 24,000 21,250 2,750 Semi skilled 34,200 33,060 1,140 Sub Total Labour 58,200 54,310 3,890 Total Product Costs 154,200 145,380 8,820 Contribution 81,800 76.120 (5,680) This statement gives Richard a summary of what has happened, but does not give him an explanation of how and why. He asks for your help in conducting a more detailed analysis. You decide to conduct a detailed variance analysis which will show the effects of: i) the change in 'the mix of products as well as the change in sales volume (sales contribution mix and sales contribution volume variances). ii) a range of price and usage variances for each line in the budgetary control statement. On investigating the situation you establish that Richard sold 6240 chairs, in the ratio of 3 standard chairs, 2 armchairs and 1 lounger. You also establish that the actual usage of : Metal components was 155,000 units, Wooden components was 180,000 units Cushions was 8,400 cushions. Skilled direct labour was employed for 1700 hours Semi skilled for 3800 hours. Required: a) For the actual sales level achieved, calculate the flexed budget "weighted average" contributions based on i) the flexed budget at actual volume and standard mix of products. ii) the flexed budget at actual volume and actual mix of products. From this information calculate the sales contribution mix and sales contribution volume variances. (3 marks) b) Recast the budgetary control statement by inserting a column for the flexed budget at actual volume and actual mix of products (3 marks) c) For the sales calculate the sales price variances. For each item of material and labour expenditure calculate price (or labour rate) and usage variances. (9 marks) d) Comment on the performance of the company as revealed form the variances (5 marks) (a) Average Std Product Costs: Sales units Budgeted Selling Price Price Metal Wooden Cushions Sub Total Materials Direct Labour Skilled (hours) Semi-skilled Sub Total Direct Labour Standard Product Cost Standard Contributions (b) have: Based on Budgeted 1.1.1 Ratio Units Total 6,240 39.33 245,440 0.30 26.67 8.00 0.20 30.00 6.00 2.00 1.00 2.00 16.00 12.00 0.33 4.00 9.00 0.63 5.70 9.70 25.70 13.63 Flexed Budget @ Actual Original Budget Std Mix Actual Mix Sales Units 6,000 6,240 6,240 6,240 Sales Revenue 236,000 245,440 224,640 221,500 Direct Variable Expenses Materials & Components Metal 48,000 49,920 45,240 48,050 Wooden 36,000 37,440 35,360 34,200 Cushions 12,000 12,480 8,320 8,820 96.000 99,840 88,920 91,070 Sub Total Materials Direct Labour Skilled 22,464 21,250 Semi-Skilled 24,000 24,960 34,200 35,568 58.200 60,528 32,760 33,060 55,224 54,310 Sub Total Labour Total Product Costs Contribution 144,144 145,380 154,200 160,368 81,800 85,072 80,496 76,120 Sales Mix Variance 80496 85072 = 4,576 A. Sales Volume Variance 85,072 - 81,800 = 3,272 F. Selling Price Variance 224640 - 221500 = 3,140 A. Cost variances Std Usage 150,800 units @ 30p 45,240 Metal Components Usage Variance Price Variance Wood Components 176,800 units @ 20p 35,360 Usage Variance Price Variance 8,320 units @ 1.00 8.320 Cushions Usage Variance Price Variance 1872 hours @ 12 22,464 Skilled Labour Usage Variance Rate Variance Semi-Skilled Labour 3,640 hours @ 9.00 32,760 Usage Variance Rate Variance (c) Reconciliation of variances (not required Original Budget Contribution Variances Sales Volume Variance 85,072 81,800 Sales Mix Variance 80,496 - 85,072 Selling Price Variance 221,500 - 224,640 Material Usage Variance-1,260 - 640 - 80 Material Price Variance -1,550 + 1,800 - 420 Labour Usage Variance 2,064 - 1,440 Labour Rate Variance - 850 + 1,140 Total Net variances Actual Contribution Based on Actual 3.2.1 Ratio Units Total 6,240 36.00 224,640 Price 49,920 24.17 7.25 45,240 37,440 28.33 5.67 35,360 12,480 1.33 1.33 8,320 99,840 14.25 88,920 24,960 0.30 3.60 22,464 35,568 0.58 5.25 32,760 60,528 8.85 55,224 160,368 23.10 144,144 85,072 12.90 80,496 Actual Usage 155,000 units @31p 4,200 units @30p 155,000 @ 1P 180,000 units @ 19p 3,800 units @20p 180,000 units @ 19p 8,400 units @ 1.05 80 units @ 1.00 8,400 units @ 5p 1,700 hours @12.50 172 hours @ 12.00 1,700 hours @ 30p 3,800 hours @ 8.70 160 hours @ 9.00 3,800 hours @ 30p question) 81.780 3,272 F 4,576 A 3,140 A 1,980 A 170 A 624 F 290 F 5,660 A 76,120 Variance -3,140 -2,810 1,160 -500 -2, 150 1,214 -300 -914 1,236 -4,376 48,050 34,200 8,820 21,250 33,060 1,260 A 1,550 A 640 A 1,800 F 80A 420A 2,064 F 850 A 1,440 A 1 140 F Total variance 2,810 A 1,160 F 500A 1,214 F 300 A
Step by Step Solution
There are 3 Steps involved in it

Get step-by-step solutions from verified subject matter experts


