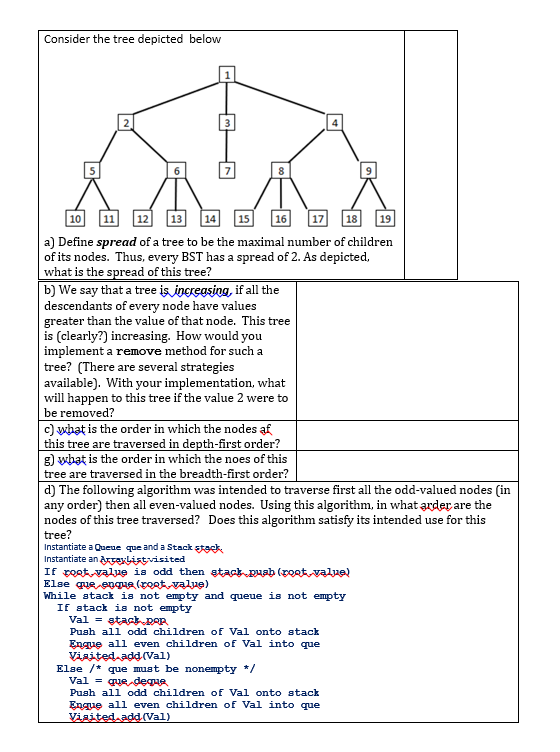
Question: Binary Tree Data Structure with Java Consider the tree depicted below 2 4 6 9 10 11 12 13 14 15 16 17 18 19
Binary Tree Data Structure with Java
Consider the tree depicted below 2 4 6 9 10 11 12 13 14 15 16 17 18 19 a) Define spread of a tree to be the maximal number of children of its nodes. Thus, every BST has a spread of 2. As depicted, what is the spread of this tree? b) We say that a tree is increasing, if all the descendants of every node have values greater than the value of that node. This tree is (clearly?) increasing. How would you implement a remove method for such a tree? (There are several strategies available). With your implementation, what will happen to this tree if the value 2 were to be removed? c) what is the order in which the nodes af this tree are traversed in depth-first order? g) what is the order in which the noes of this tree are traversed in the breadth-first order? d) The following algorithm was intended to traverse first all the odd-valued nodes (in any order) then all even-valued nodes. Using this algorithm, in what arder are the nodes of this tree traversed? Does this algorithm satisfy its intended use for this tree? Instantiate a Queue que and a Stack stock Instantiate andravlist visited If post-value is odd then stack puab (poet-value) Else que enque (poet-value) While stack is not empty and queue is not empty If atack is not empty Val = stack por Push all odd children of Val onto stack Enque all even children of Val into que Visited add. (Val) Else /* que must be nonempty */ Val = que deque Push all odd children of Val onto stack Enque all even children of Val into que Visited add (Val)
Step by Step Solution
There are 3 Steps involved in it

Get step-by-step solutions from verified subject matter experts


