Question: Binary Tree Inorder Traversal (Java) Java Solution - Iterative Solution The key to solve inorder traversal of binary tree includes the following: 1. The order
Binary Tree Inorder Traversal (Java)
Java Solution - Iterative Solution
The key to solve inorder traversal of binary tree includes the following:
1. The order of "inorder" is: left child -> parent -> right child
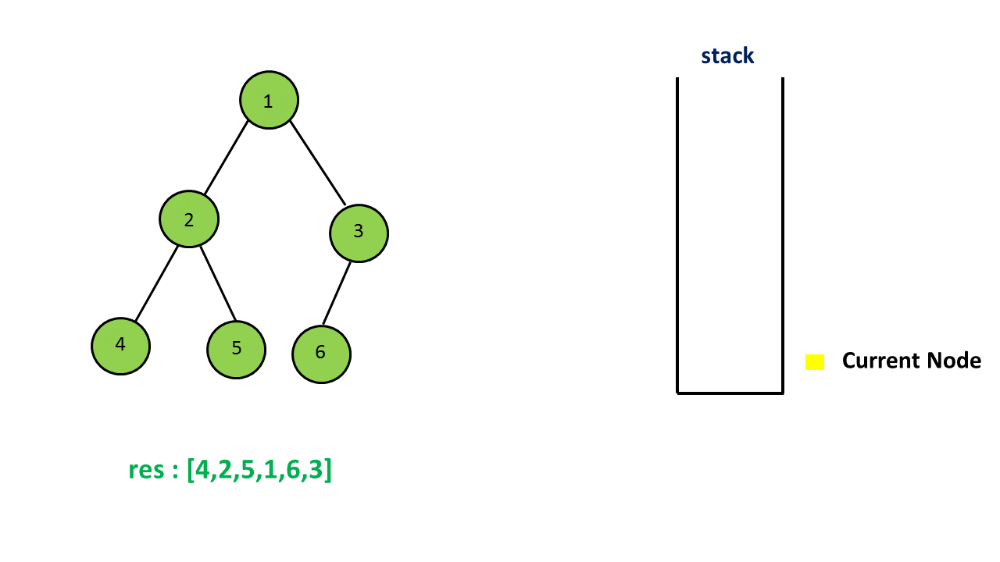
2. Use a stack to track nodes
3. Understand when to push node into the stack and when to pop node out of the stack
For this problem, I have worked towards understanding the solution on my own and I have come up with the following source code comments to explain the iterative solution of the Binary Tree Inorder Traversal problem. Please let me know what else would you add to my explanations or if you see if something is wrong on my explanation.
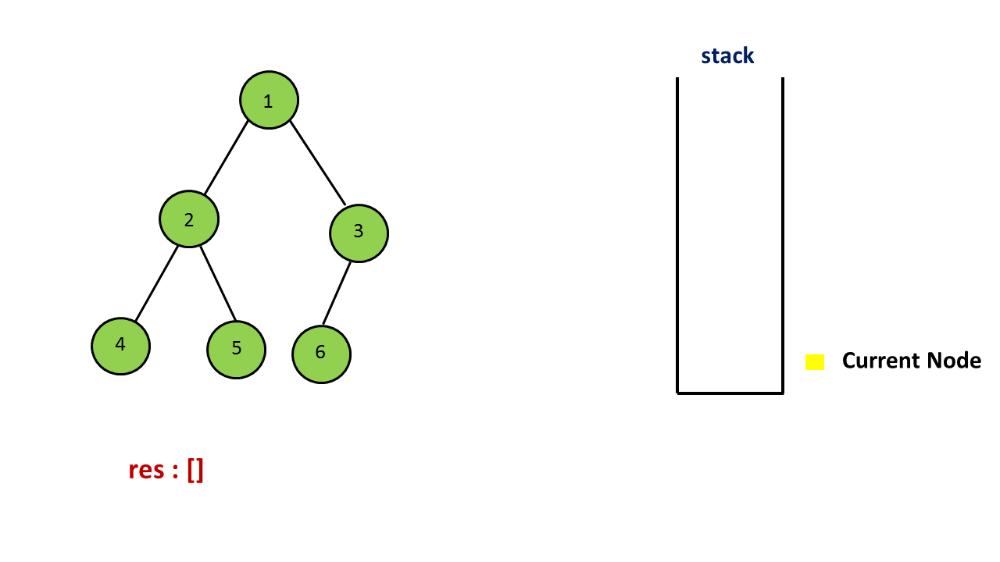
Here is a different BST diagram. Step 1
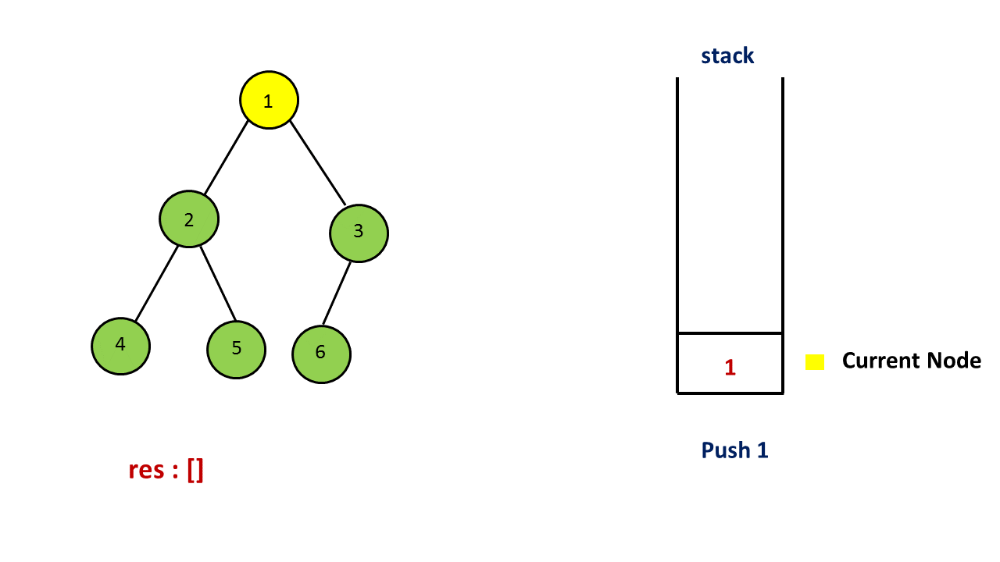
Step 2:
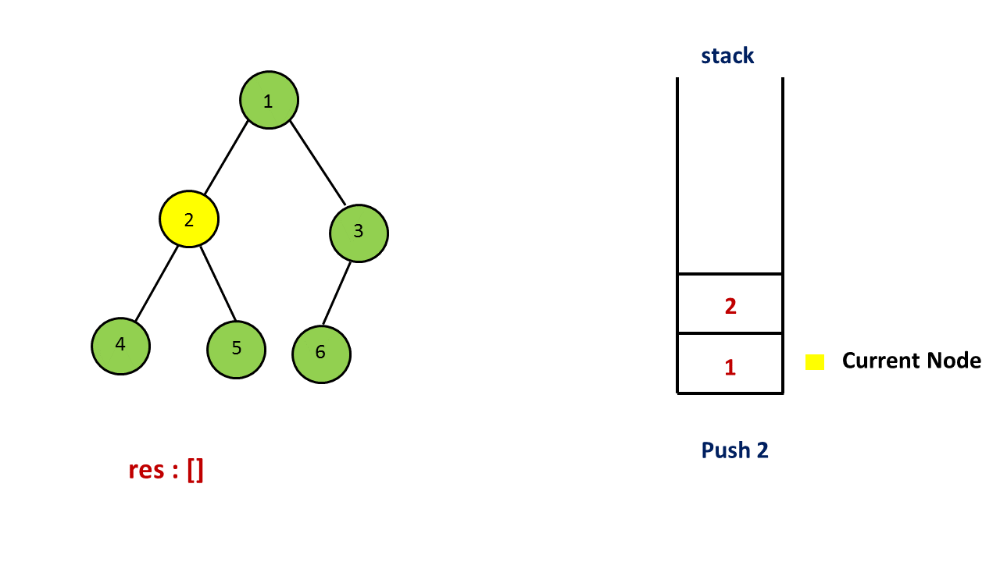
Step 3:
//Definition for binary tree public class TreeNode { int val; TreeNode left; TreeNode right; TreeNode(int x) { val = x; } } public class Solution { public ArrayList inorderTraversal(TreeNode root) { // IMPORTANT: Please reset any member data you declared, as // the same Solution instance will be reused for each test case. ArrayList lst = new ArrayList(); if(root == null) return lst; Stack stack = new Stack(); //define a pointer to track nodes TreeNode p = root; while(!stack.empty() || p != null){ // if it is not null, push to stack //and go down the tree to left if(p != null){ stack.push(p); p = p.left; // if no left child // pop stack, process the node // then let p point to the right }else{ TreeNode t = stack.pop(); lst.add(t.val); p = t.right; } } return lst; } } I understand the first part of the source code shown above is the definition of a binary tree called TreeNode. I also get that we need to create a new array list of type Integer and we call this array list lst. ArrayList lst = new ArrayList(); If root is equal to NULL then why do we need to return list, especially if list is an empty array list? if(root == null) return lst; |
Then we create a new stack called simply stack using the TreeNode class.
Stack stack = new Stack();
Then we create a pointer to track nodes and set this pointer p equal to root.
TreeNode p = root;
If the stack is NOT empty OR if p is NOT EQUAL to null then we can start the while loop. while(!stack.empty() || p != null){...
}
If the TreeNode p is not null, then we push the node p to stack and then we go down the tree to its left side, it's left child. Right? if(p != null){ stack.push(p); p = p.left;}
If it turns out there is no left child then we pop the stack, and process the node and then let p point to the right child of the TreeNode t. Right? }else{ TreeNode t = stack.pop(); lst.add(t.val); p = t.right; } }Why are we adding the value of the node t to the list?
Finally, we return the list which returns a completed list of the inorder traversal of the BST.
This is the final step of the inorder traversal of the BST and the last step is where the source code returns the list lst.
1 3 4 5
Step by Step Solution
There are 3 Steps involved in it

Get step-by-step solutions from verified subject matter experts


