Question: Biochemical engineering is all about extending chemical engineering principles to systems that typically use a biological catalyst (enzyme) in place of a chemical one. The
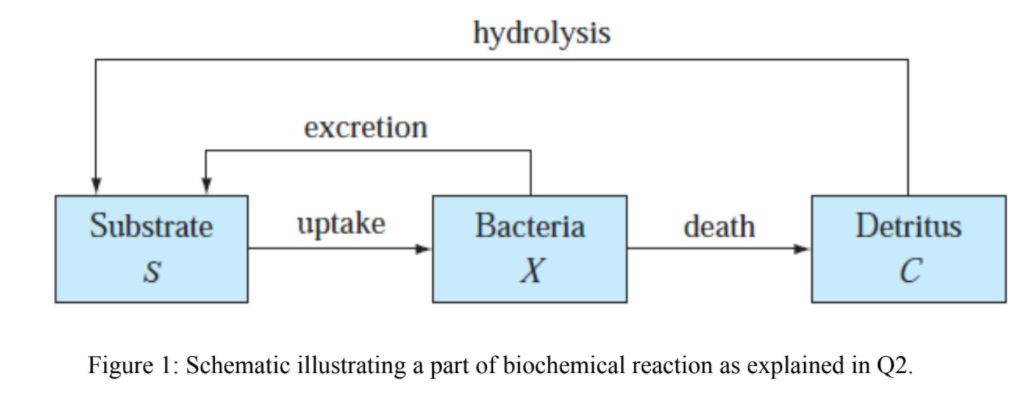
Biochemical engineering is all about extending chemical engineering principles to systems that typically use a biological catalyst (enzyme) in place of a chemical one. The heart of a biochemical process is a bioreactor where chemical transformation of a substrate (similar to a reactant) into product takes place in presence of enzyme. Often, this enzyme is produced by microorganisms that are also grown in the bioreactor itself. In one scenario, bacteria (at a concentration X mg/L) growing in a batch reactor utilizes a soluble substrate (S mg/mL), and produces a dead organic material called detritus (C mg/mL) upon dying, as depicted in Figure 1 below. The detritus is subsequently converted back to substrate upon hydrolysis. In addition, bacteria also secrete some substrate directly. The uptake of the substrate by the bacteria is represented by a logistic model with a Michaelis-Menten limitation (a model describing enzyme kinetics). Death, hydrolysis and excretion are all simulated as first-order reactions.
Figure 1: Schematic illustrating a part of biochemical reaction as explained in Q2.
2
Mass balance for the above system is represented by the following system of three ODES. dX/dt = Max (1 X/K) (S/(Ks + S)) (X kdX keX)
dC/dt = kdX khC dS/dt = keX + khC Max (1 X/K) (S/(Ks + S)) X
where X, C, & S denotes the concentrations [mg/L] of bacteria, detritus, and substrate, respectively; Max= maximum growth rate [/d], K = the logistic carrying capacity [mg/L]; Ks = the Michaelis-Menten half-saturation constant [mg/L], kd = death rate [/d]; ke = excretion rate [/d]; and kh = hydrolysis rate [/d]. Employ the following parameters in your calculation: Max= 10/d, K = 10 mg/L, Ks = 10 mg/L, kd = 0.1/d, ke = 0.1/d, and kh = 0.1/d. The initial conditions are given as: X (0) = 1 mg/L, S (0) = 100 mg/L & C (0) = 0 mg/L. Develop a code for Runge-Kutta (RK) 4th order method in MATLAB to solve the given system of ODEs and obtain the profile for X, C, & S over time using a step-size of 1 hour. Report the values of concentrations
hydrolysis excretion uptake death Substrate S Bacteria X Detritus Figure 1: Schematic illustrating a part of biochemical reaction as explained in Q2
Step by Step Solution
There are 3 Steps involved in it

Get step-by-step solutions from verified subject matter experts


