Question: Black-Scholes model for pricing a call option and a put option a below: C = [s*edt-N(d 1) - [X*e*rt*N(D2)] : where d1 = [In(Se dt/X)
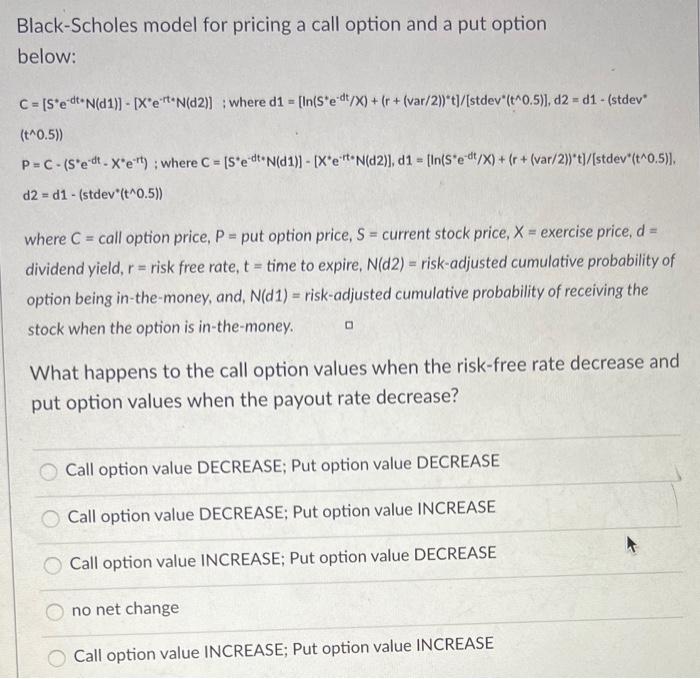
Black-Scholes model for pricing a call option and a put option a below: C = [s*edt-N(d 1) - [X*e*rt*N(D2)] : where d1 = [In(Se dt/X) + (r + (var/2)*t)/(stdev"(t^0.5)), d2 = 01. (stdev (t^0.5)) P=C-(s'e dt.X'e't): where C = [s*edN(01)) - [X*e "N(D2)], 01 = [In(Se dt/X) + (r + (var/2))"t)/(stdev"(t^0.5)). d2=d1- (stdev"(t^0.5)) where C = call option price, P = put option price, S = current stock price, X = exercise price, d = dividend yield, r = risk free rate, t = time to expire, N(d2) = risk-adjusted cumulative probability of option being in the money, and, N(D1) = risk-adjusted cumulative probability of receiving the stock when the option is in-the-money. What happens to the call option values when the risk-free rate decrease and put option values when the payout rate decrease? Call option value DECREASE; Put option value DECREASE Call option value DECREASE; Put option value INCREASE Call option value INCREASE; Put option value DECREASE no net change Call option value INCREASE; Put option value INCREASE
Step by Step Solution
There are 3 Steps involved in it

Get step-by-step solutions from verified subject matter experts


