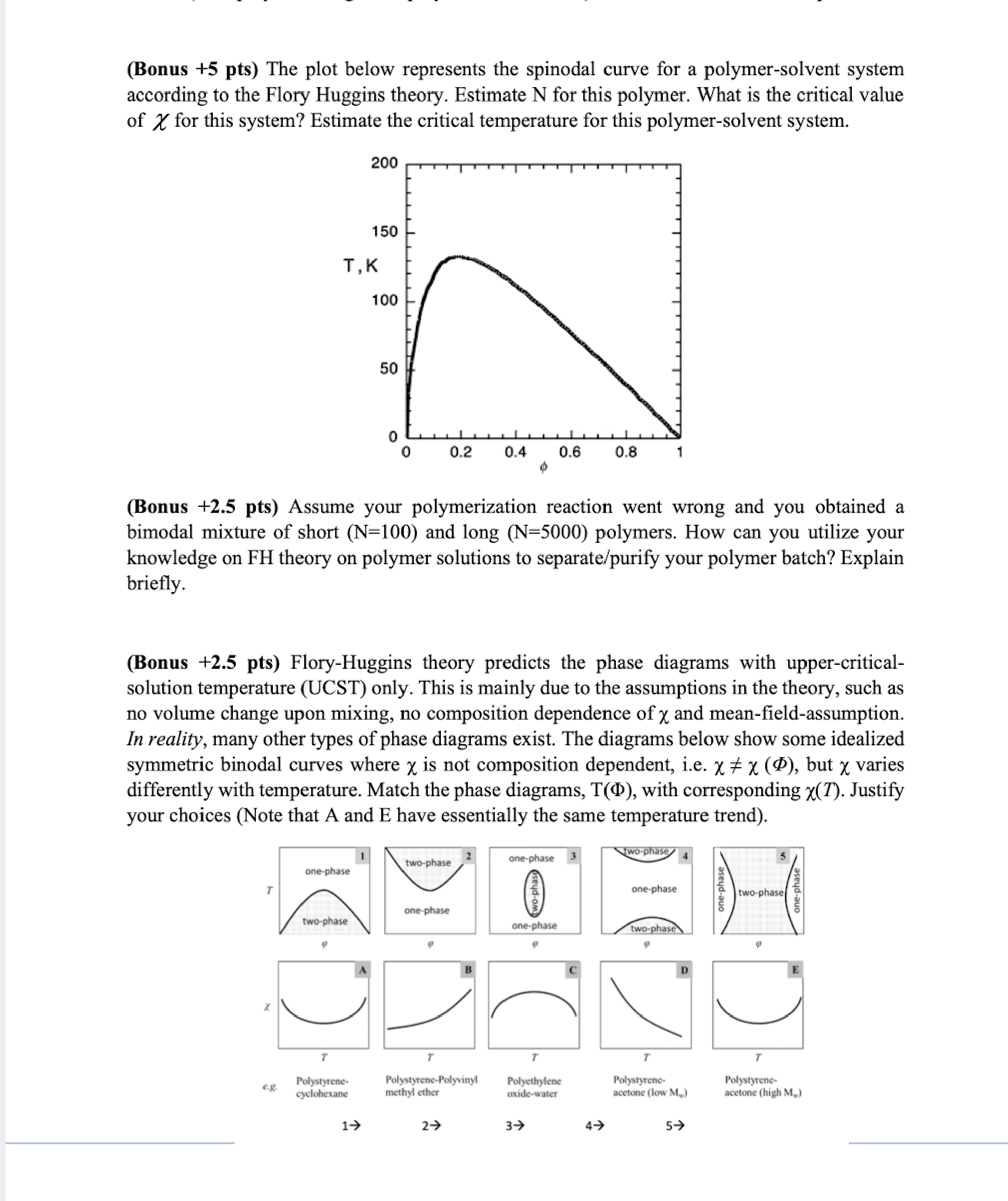
Question: ( Bonus + 5 pts ) The plot below represents the spinodal curve for a polymer - solvent system according to the Flory Huggins theory.
Bonus pts The plot below represents the spinodal curve for a polymersolvent system
according to the Flory Huggins theory. Estimate for this polymer. What is the critical value
of for this system? Estimate the critical temperature for this polymersolvent system.
Bonus pts Assume your polymerization reaction went wrong and you obtained a
bimodal mixture of short and long polymers. How can you utilize your
knowledge on FH theory on polymer solutions to separatepurify your polymer batch? Explain
briefly.
Bonus pts FloryHuggins theory predicts the phase diagrams with uppercritical
solution temperature UCST only. This is mainly due to the assumptions in the theory, such as
no volume change upon mixing, no composition dependence of and meanfieldassumption.
In reality, many other types of phase diagrams exist. The diagrams below show some idealized
symmetric binodal curves where is not composition dependent, ie but varies
differently with temperature. Match the phase diagrams, with corresponding Justify
your choices Note that A and E have essentially the same temperature trendFloryHuggins theory considers only the attractive interactions between the
molecules, therefore the interaction parameter has only the enthaplic part. Due to
volume change upon mixing, there is also entropy contribution to chi Experimentally it
was shown that
v where vo is the volume of the molecules ~
o
kT
nm What is the largest solubility parameter difference that allows polymer solutions
with polymers degree of polymerization to be miscible at room temperature?
Bonus pts The plot below represents the spinodal curve for a polymersolvent system according to the Flory Huggins theory. Estimate N for this polymer. What is the critical value of for this system? Estimate the critical temperature for this polymersolvent system.
Bonus pts Assume your polymerization reaction went wrong and you obtained a bimodal mixture of short N and long N polymers. How can you utilize your knowledge on FH theory on polymer solutions to separatepurify your polymer batch? Explain briefly.
Bonus pts FloryHuggins theory predicts the phase diagrams with uppercritical solution temperature UCST only. This is mainly due to the assumptions in the theory, such as no volume change upon mixing, no composition dependence of chi and meanfieldassumption. In reality, many other types of phase diagrams exist. The diagrams below show some idealized symmetric binodal curves where chi is not composition dependent, iechi chi Phi but chi varies differently with temperature. Match the phase diagrams, TPhi with corresponding chi T Justify your choices Note that A and E have essentially the same temperature trend
Step by Step Solution
There are 3 Steps involved in it
1 Expert Approved Answer
Step: 1 Unlock


Question Has Been Solved by an Expert!
Get step-by-step solutions from verified subject matter experts
Step: 2 Unlock
Step: 3 Unlock


