Question: Born series: code We will assume computational units, m= h = 1. First, we import the Scipy libraries, and the Matplotib library for plotting. Then,
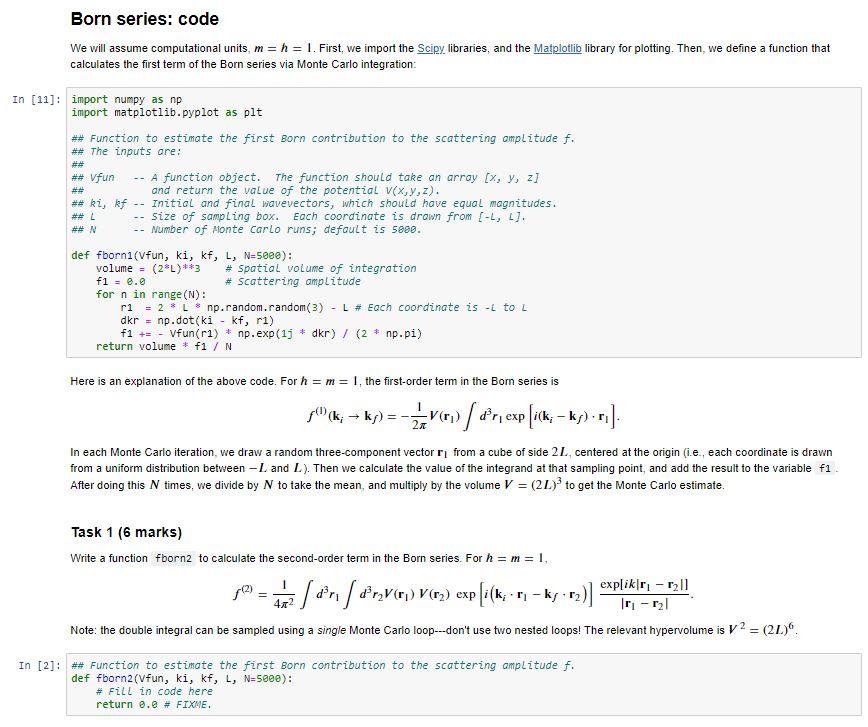
Born series: code We will assume computational units, m= h = 1. First, we import the Scipy libraries, and the Matplotib library for plotting. Then, we define a function that calculates the first term of the Born series via Monte Carlo integration: In [11]: import numpy as np import matplotlib.pyplot as plt ## Function to estimate the first Born contribution to the scattering omplitude f. ** The inputs are: ## Vfun -- A function object. The function should take an array (x, y, z] and return the value of the potential V(x, y, z). ** ki, kf -- Initial and final wavevectors, which should have equal magnitudes. ## 2 size of sampling box. Eoch coordinate is drawn from [-L, L). Number of Monte Carlo runs; default is 5880. ## N def fborn1(Vfun, ki, kf, L, N=5680): volume = (2L)**3 # Spatial volume of integration fi = 0.0 # scattering amplitude for n in range(N): ri = 2 * L * np.random.random(3) - L# Each coordinate is - to L dkr = np.dot(ki - kf, ri) f1 += - Vfun(r1) np.exp(13 * dkr) / (2 * np.pi) return volume * f1/N Here is an explanation of the above code. For h = m = 1, the first-order term in the Born series is 30(ks ks) = v) d'r, exp[icks kj) -ri]. In each Monte Carlo iteration, we draw a random three-component vector r from a cube of side 2L, centered at the origin (i.e., each coordinate is drawn from a uniform distribution between -L and L). Then we calculate the value of the integrand at that sampling point, and add the result to the variable fi After doing this N times, we divide by N to take the mean, and multiply by the volume V = (2L) to get the Monte Carlo estimate. Task 1 (6 marks) Write a function fborn2 to calculate the second-order term in the Born series. For h = m = 1, I din / drV(r) V() exp explikir-r21 exp [i(k: - ks r) Iri - r21 Note: the double integral can be sampled using a single Monte Carlo loop-don't use two nested loops! The relevant hypervolume is V2 = (21)". 4x2 In [21: ## Function to estimate the first Born contribution to the scattering amplitude f. def fborn2(Vfun, ki, kf, L, N=5800): # Fill in code here return 0.2 # FIXME. Born series: code We will assume computational units, m= h = 1. First, we import the Scipy libraries, and the Matplotib library for plotting. Then, we define a function that calculates the first term of the Born series via Monte Carlo integration: In [11]: import numpy as np import matplotlib.pyplot as plt ## Function to estimate the first Born contribution to the scattering omplitude f. ** The inputs are: ## Vfun -- A function object. The function should take an array (x, y, z] and return the value of the potential V(x, y, z). ** ki, kf -- Initial and final wavevectors, which should have equal magnitudes. ## 2 size of sampling box. Eoch coordinate is drawn from [-L, L). Number of Monte Carlo runs; default is 5880. ## N def fborn1(Vfun, ki, kf, L, N=5680): volume = (2L)**3 # Spatial volume of integration fi = 0.0 # scattering amplitude for n in range(N): ri = 2 * L * np.random.random(3) - L# Each coordinate is - to L dkr = np.dot(ki - kf, ri) f1 += - Vfun(r1) np.exp(13 * dkr) / (2 * np.pi) return volume * f1/N Here is an explanation of the above code. For h = m = 1, the first-order term in the Born series is 30(ks ks) = v) d'r, exp[icks kj) -ri]. In each Monte Carlo iteration, we draw a random three-component vector r from a cube of side 2L, centered at the origin (i.e., each coordinate is drawn from a uniform distribution between -L and L). Then we calculate the value of the integrand at that sampling point, and add the result to the variable fi After doing this N times, we divide by N to take the mean, and multiply by the volume V = (2L) to get the Monte Carlo estimate. Task 1 (6 marks) Write a function fborn2 to calculate the second-order term in the Born series. For h = m = 1, I din / drV(r) V() exp explikir-r21 exp [i(k: - ks r) Iri - r21 Note: the double integral can be sampled using a single Monte Carlo loop-don't use two nested loops! The relevant hypervolume is V2 = (21)". 4x2 In [21: ## Function to estimate the first Born contribution to the scattering amplitude f. def fborn2(Vfun, ki, kf, L, N=5800): # Fill in code here return 0.2 # FIXME
Step by Step Solution
There are 3 Steps involved in it

Get step-by-step solutions from verified subject matter experts


