Question: Briefly explain this (Table 3 in point 3.2 and Table 4 in point 4 from image) below, and explain it in a detail and
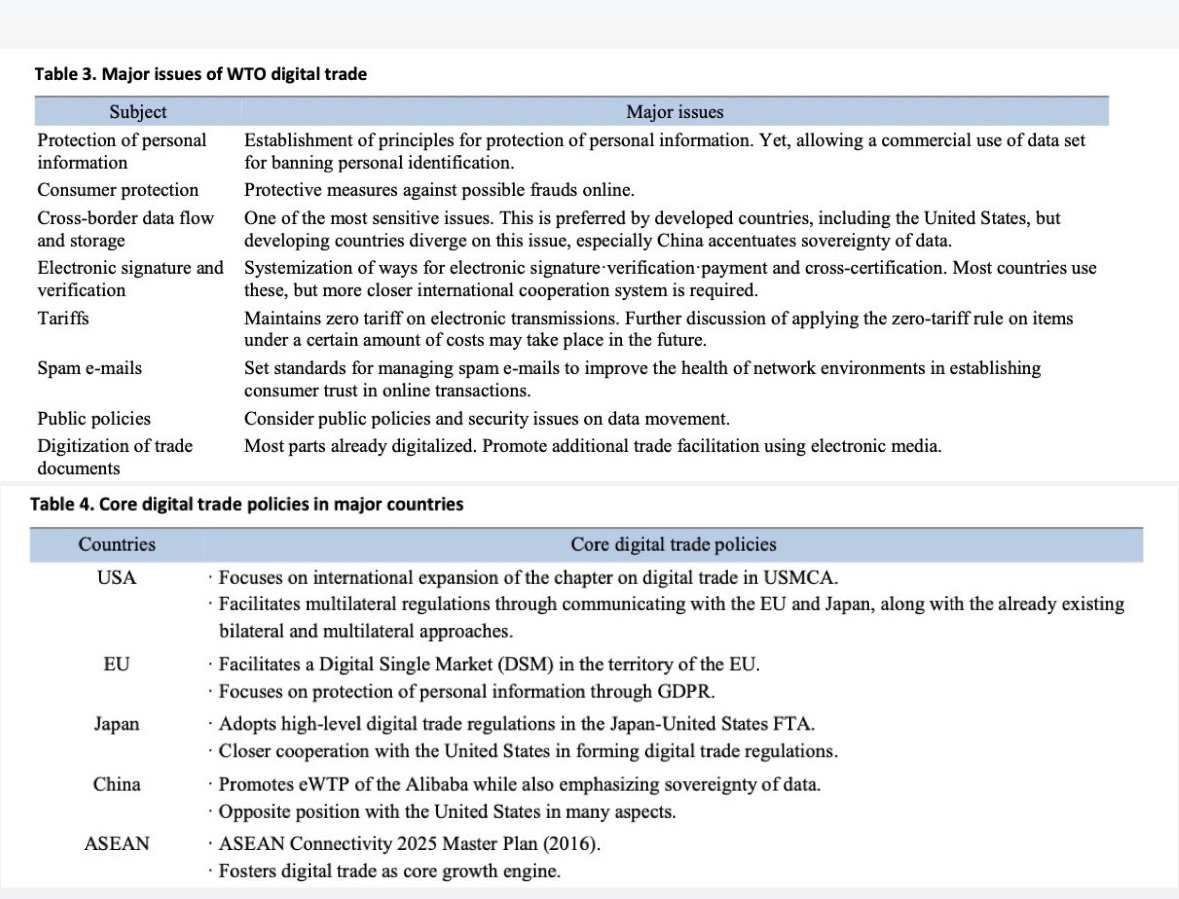
" Briefly explain this (Table 3 in point 3.2 and Table 4 in point 4 from image) below, and explain it in a detail" and give an example as well. 3.2 Controversial issues of digital trade regulationsNot only the WTO, but also bilateral trade agreements recently show interests in international regulations on digital trade, In order to establish efficient digital trade regulations, there needs a review on the major issues across countries. Some of the major issues can include tariff policies, localization requirements, cross-border data flow restrictions, level of protection in personal information, approach of source codes, and standardization of technologies such as electronic payments and accounts.As the future negotiations begin, there could be some controversy about the definition of digital items, the coverage of applying new rules, zero-tariff for digital transmissions, non-discrimination for digital items, electronic signature and verification, protection of online consumers, use of administrative documents of e-commerce, regulations of net neutrality and more. The application coverage of e-commerce/digital chapter varies across agreements. While the Japan-Switzerland FTA regulates the e-commerce market that applies all goods and services, the PA does not apply on service and investment but only regulates within e-commerce of goods including digital items. And, the Mexico-Panama FTA adopts a chapter similar with that of PA.3.3 Positions of major countries on digital trade regulationsThe Table 4 summarizes core policies on digital trade by major country/region. The most important issues in digital trade rules are the ban on localization of data centers, cross-border transmission of data, and the ban on access to source code, which were also reflected in the Comprehensive and Progressive TransPacific Partnership Agreement (CPTPP). In addition to these norms, the United States-Mexico-Canada Agreement (USMCA) also allowed indemnification for platform operators. From the current trade agreements and government policies, Korea agrees to ban access to the source code, but has a negative position on the rest. Korea's refusal to Google's maps implies localization of data centers and restrictions on the movement of data across borders. The United States fundamentally pursues the Open Internet. Owing to the tech giants, GAFA (Google, Apple, Facebook and Amazon), the United States has introduced exemption provisions on the United States e-commerce companies and abrogated access restriction of the Internet in order to facilitate establishing international regulations for digital trade in creating an environment viable for the United States companies to go overseas. Minimizing foreign regulations on the Internet and e-commerce, including prohibition of server localization and permission of cross-border data movement, the United States seeks to internationally standardize protection of intellectual property rights and security of technology for the United States companies that dominate the ICT technology in the world. These regulations have been included in the USMCA, which was signed with the United States in lead. Japan's digital trade policies share great similarity with those of the United States. The United States and Japan already includes such rules in their bilateral FTA.EU has begun building the Digital Single Market toward all the EU member countries in 2015 as a strategy to cope with the US' GAFA. While cooperating with the US, it protects its citizens' personal information through the general data protection regulation (GDPR) which became effective in May 2019 and permits the movement of information within the EU member countries, promoting a strategy to realize digital economy within Europe by expanding e-commerce platforms from its own perspective.
Step by Step Solution
There are 3 Steps involved in it

Get step-by-step solutions from verified subject matter experts


