Question: Brute Force and Exclude & Conquer Recursive Algorithms In the following problems, use the General Solution of 1st Order Linear Recurrence T(n)= a, T(n-1)+ bn,

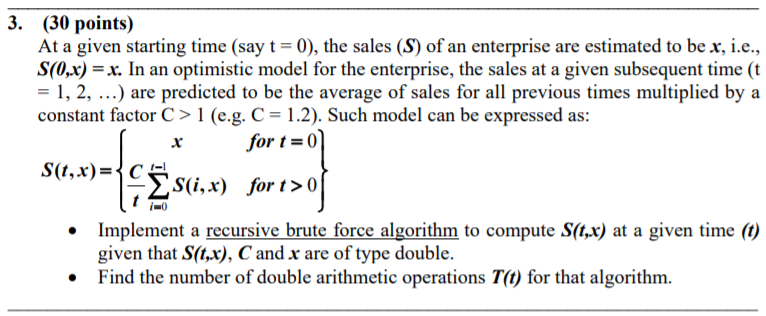
Brute Force and Exclude & Conquer Recursive Algorithms In the following problems, use the General Solution of 1st Order Linear Recurrence T(n)= a, T(n-1)+ bn, given T(0) or T(1) with the following solutions: Successive substitution gives for the cases of T(0) given and T(1) given: T(n)=T(0) la; + Eb; II a;+b. T(n)=T(1) IIa, + Eb II a;+by i=/ i=1 j=i+1 i=2 i=2 j=i+1 3. (30 points) At a given starting time (say t = 0), the sales (S) of an enterprise are estimated to be x, i.e., S(0,x) = x. In an optimistic model for the enterprise, the sales at a given subsequent time (t = 1, 2, ...) are predicted to be the average of sales for all previous times multiplied by a constant factor C> 1 (e.g. C = 1.2). Such model can be expressed as: for t=0 S(t, x)={C S(i,x) for t > 0 ort>01 Implement a recursive brute force algorithm to compute S(t,x) at a given time (t) given that S(t,x), C and x are of type double. Find the number of double arithmetic operations T(t) for that algorithm. $ix . Brute Force and Exclude & Conquer Recursive Algorithms In the following problems, use the General Solution of 1st Order Linear Recurrence T(n)= a, T(n-1)+ bn, given T(0) or T(1) with the following solutions: Successive substitution gives for the cases of T(0) given and T(1) given: T(n)=T(0) la; + Eb; II a;+b. T(n)=T(1) IIa, + Eb II a;+by i=/ i=1 j=i+1 i=2 i=2 j=i+1 3. (30 points) At a given starting time (say t = 0), the sales (S) of an enterprise are estimated to be x, i.e., S(0,x) = x. In an optimistic model for the enterprise, the sales at a given subsequent time (t = 1, 2, ...) are predicted to be the average of sales for all previous times multiplied by a constant factor C> 1 (e.g. C = 1.2). Such model can be expressed as: for t=0 S(t, x)={C S(i,x) for t > 0 ort>01 Implement a recursive brute force algorithm to compute S(t,x) at a given time (t) given that S(t,x), C and x are of type double. Find the number of double arithmetic operations T(t) for that algorithm. $ix
Step by Step Solution
There are 3 Steps involved in it

Get step-by-step solutions from verified subject matter experts


