Question: C# - In this assignment, you will develop and implement a discrete simulator (single-threaded) that implements a five-level multilevel feedback queue. A feedback queue is
C# - In this assignment, you will develop and implement a discrete simulator (single-threaded) that implements a five-level multilevel feedback queue. A feedback queue is a technique used in operating systems to schedule processes for execution with the goal of optimizing turnaround time and minimizing response time. The structure of the scheduler is given in Figure 1. Each of the five levels of queues and the associated time quantum are as follows:
Ready queue, 0 units, FCFS input
Level one (entry level), 1 units, preemptive FCFS
Level two, 2 units, preemptive FCFS
Level three, 4 units, preemptive FCFS
Level four, 6 units, preemptive FCFS
Level five (bottom level), 8 units, round-robin
FCFS = First Come First Served
The program must accept input from a text file which contains the process number (one byte, arbitrary), arrival time (integer, in units), and execution duration (integer, in units). For example, 7~15~6 denotes process number 7, which arrives at time 15 and will execute for 6 time units. It is assumed that each file will contain jobs in arrival time order; however, if the input file is not in the correct sequence, then your program must ensure that the jobs are placed in the ready queue in the proper sequence.
The default name of the input file is, jobs.txt, but the name and path to the file must be able to be overridden from the command line. The default output file is named, traceout.txt, but the name and path to the file must also be able to be specified from the command line. A sample command line is provided below. The first command line parameter is assumed to be the input file name and path. The default files should be placed in the current working directory.
Simulator inputFile outputFile
Jobs can only be removed from a queue (preempted) if it has completed processing or when its quantum has expired. Processes cannot be preempted (interrupted) during its scheduled quantum. See
Figure 1 for an overview of the queue structure used in the process below.
1. N = 1, has_run = false
2. Check the ready queue: Is the first process available (arrival time is
a. Dequeue the process from the ready queue and enqueue in the first queue (queue
N). (repeat for all processes that are ready)
3. Check queue N: are there elements available to run?
a. Dequeue the process from the current queue (N)
b. Run one process from the queue for at most the quantum time units assigned to the queue.
c. Update time by the smaller of two: the quantum or the process's execution time. d. Has_run = true;
e. Does the process still require running time (process remaining run time != 0)?
i. Is N == 5?
1. Enqueue the process into queue N
ii. else
1. Enqueue the process into queue N + 1
4. Else
a. If N is less than 5 i. N = N + 1 ii. Goto 3
5. If has_run == false
a. Time = time + 1 b. Goto 1
6. Else
a. Are there any processes left to run in any of the queues?
i. Goto 1
7. Write output trace
8. Exit
The simulator should output an execution trace, which shows the arrival and execution of all processes in the following format:
Given the input: A, 0, 3
B, 0, 3
The output would look as follows:
Time: 00000000001
01234567890
Proc: ABAABB
Note: The above trace was limited to 10 time units. Traces must be as large as they need to be to complete the simulation, but simulations are not expected to exceed 99 time units.
The simulator ends when all processes have been fully executed to completion.
Figure 1 A five-level multi-level feedback queue
NOTE: Use the quantum values indicated in the assignment, not depicted on this figure.
Figure 1
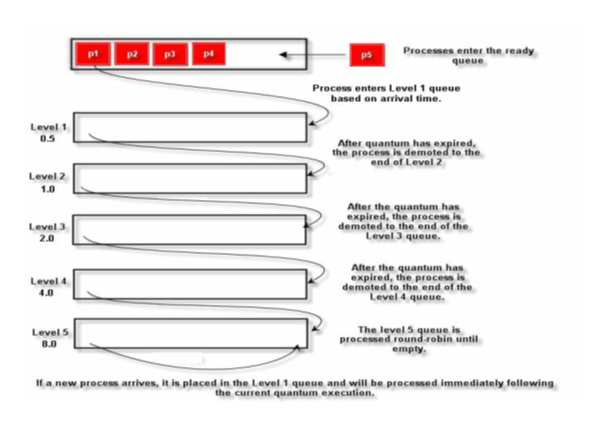
pt Processes enter the ready ps Process enters Level 1 queue based on arrival time. Level 1 0.5 After quantum has expired, the process is demoted to the end of Level 2 Level 2 1.0 After the quantum has expired, the proc es is Level 3 2.0 demoted to the end of the Level 3 queue. Level 4 4.0 After the quantum has expired, the process is demoted to the end of the Level 4 quese. The level 5 queue is Level 5 8.0 processed ro d-robin until empty If a new process arrives, it is placed in the Level 1 queue and will be processed immediately following the current quantum execution. pt Processes enter the ready ps Process enters Level 1 queue based on arrival time. Level 1 0.5 After quantum has expired, the process is demoted to the end of Level 2 Level 2 1.0 After the quantum has expired, the proc es is Level 3 2.0 demoted to the end of the Level 3 queue. Level 4 4.0 After the quantum has expired, the process is demoted to the end of the Level 4 quese. The level 5 queue is Level 5 8.0 processed ro d-robin until empty If a new process arrives, it is placed in the Level 1 queue and will be processed immediately following the current quantum execution
Step by Step Solution
There are 3 Steps involved in it

Get step-by-step solutions from verified subject matter experts


