Question: C language 2.1 Implement a program in screenExample.c that reads in a names as a string, age as an integer, and weight as a float.
C language
2.1 Implement a program in screenExample.c that reads in a names as a string, age as an integer, and weight as a float. Then print out what was read.
2.2 Implement a program in fileExample.c that extends your program from exercise 2.1. Your new program should prompt the user to enter a name as a string, age as an integer, and weight as a float. Instead of printing the results to the screen, it should *append* them to a file named patients.txt. After the user enters this information, the program should ask if they want to enter data for another patient; if the user enters a "y", then they should be prompted for the same information again, otherwise the program should exit.
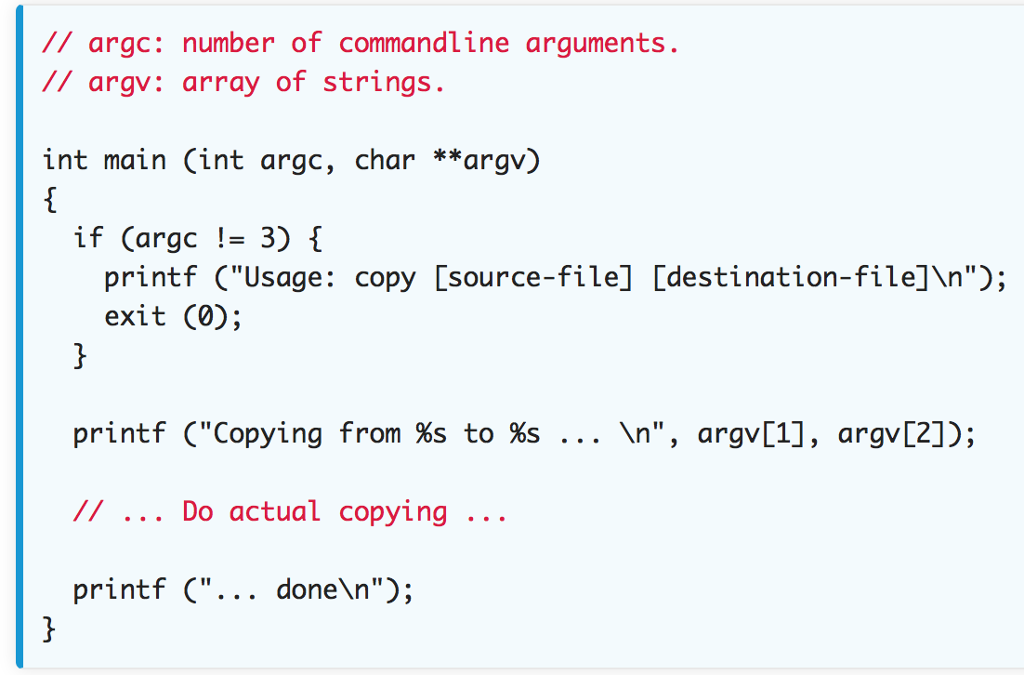
2.3 In copy.c use the template below and add in the code to perform data copying between the two files named as arguments when running the program. You've already seen how getc() reads a char at a time from a file. You can similarly write a char at a time using the function putc (char, FILE). You do not need to write EOF to the destination file, but you do need to close the file when you reach the end.
template for 2.3
// argc: number of commandline arguments // argv: array of strings. int main (int argc, char **argv) if Cargc 3) E printf C"Usage: copy [source-file] [destination-file] "); exit (); printf ("Copying from %s to %s /I Do actual copying printf C"... done "; Nn", argv[1], argv[2])
Step by Step Solution
There are 3 Steps involved in it

Get step-by-step solutions from verified subject matter experts