Question: C++ Part 1 Method 1 - Linear 1-1. Create one array arr 1 of size 1000. Populate it with random numbers in the range from
C++
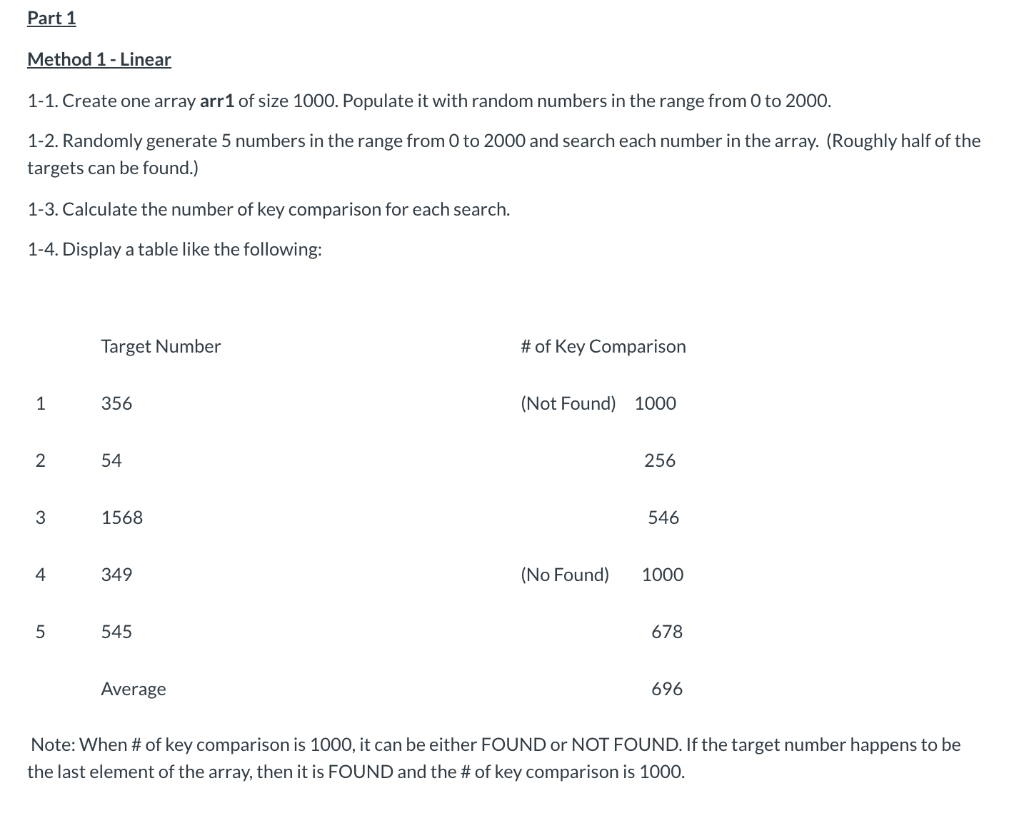


Part 1 Method 1 - Linear 1-1. Create one array arr 1 of size 1000. Populate it with random numbers in the range from 0 to 2000. 1-2. Randomly generate 5 numbers in the range from 0 to 2000 and search each number in the array. (Roughly half of the targets can be found.) 1-3. Calculate the number of key comparison for each search. 1-4. Display a table like the following: Target Number # of Key Comparison 1 356 (Not Found) 1000 256 - 2 3 4 54 1568 349 546 (No Found) 1000 545 678 Average 696 Note: When # of key comparison is 1000, it can be either FOUND or NOT FOUND. If the target number happens to be the last element of the array, then it is FOUND and the # of key comparison is 1000. Method 2 - Binary 2-1. Use the same array which was generated above. Sort the array. 2-2. Use binary search to do the search for the same 5 random numbers in Part 1. 2-3. Display the report like the one above. Compare the differences between the two tables. With this method, the numbers of key comparison should be fewer than 10, which is roughly 70 times faster than that of the Method 1. Hints - The steps to complete the program In general the coding cannot be easily done if we try to "directly solve the problem. This is mainly because the size of the array is 1000 and the numbers are random, and the complexity and time needed for tracing a big array like this can easily exhaust us. Instead of solving a large complicated problem all at a time, we should apply the technique of Divide N. Conquer to solve a few sub-problems one at a time. For example, we can divide the Part 2 problem into the following few sub-problems. (1) Start with two small arrays, such as 9 or 10. We can hard-code the integers in the array. (2) Ensure that the program works for both the cases which the array sizes are either even or odd. (3) Test the program with random numbers and bigger array sizes. (4) Finally, you can use the size of 1000. We can verify the answers generated from these methods. If they are the same, we know that very likely the code for these methods is all correct. Output example - The two sets of target number are exactly the same (Part 1) LINEAR SEARCH ======================= Target Number Key Comparisons 594 1000 1332 1000 (Not Found) 1939 131 410 1000 (Not Found) 374 1751 ======================== Average 701 (Part 1) BINARY SEARCH ======================= Target Number Key Comparisons 594 10 1332 10 (Not Found) 1939 410 10 (Not Found) 1751 10 ========================= Average
Step by Step Solution
There are 3 Steps involved in it

Get step-by-step solutions from verified subject matter experts


