Question: C program - Document every line. Write in C a program to do the discrete-event simulation of a distributed computer system. We assume that the
C program - Document every line.
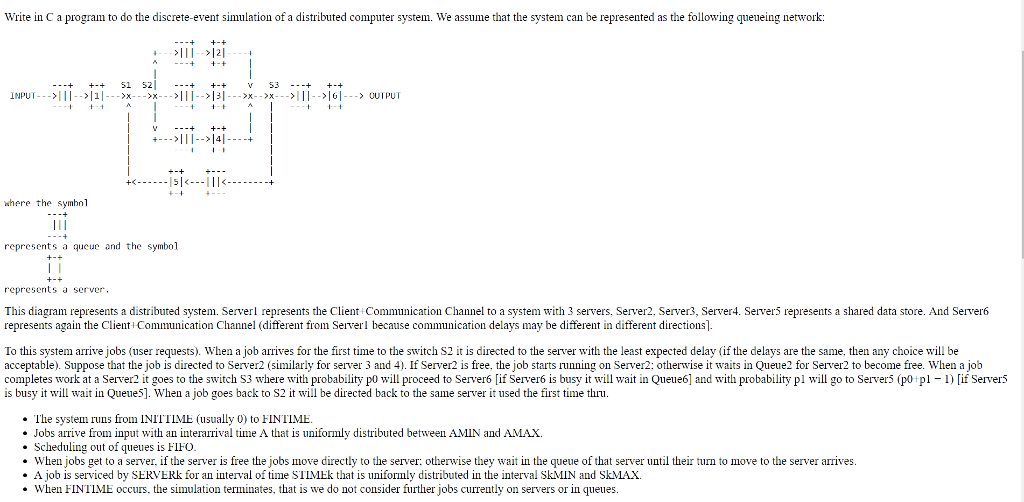

Write in C a program to do the discrete-event simulation of a distributed computer system. We assume that the system can be represented as the following queueing network >111>121 ' -+ +-+ SI 52| --+ +-+ v 53 --+ +-+ >>141 + where the symbol represents a queue and the symbol represents a server This diagram represents a distributed system. Sere represents the Client Communication Channel to a system with 3 servers, Server2, Server3, Server4. Server5 represents a shared data store. And Server6 represents again the Client Communication Channel (different from Serverl because communication delays may be different in different directions] To this system arrive jobs (user requests). When a job arrives for the first time to the switch S2 it is directed to the server with the least expected delay (if the delays are the same, then any choice wil be acceptable). Suppose that the job is directed to Server2 (similarly for server 3 and 4). If Server2 is free, the job starts running on Server2; otherwise it waits in Queue2 for Server2 to become free. When a job completes work at a Server2 it goes to the switch S3 where with probability po will proceed to Server6 [if Server6 is busy it will wait in Queue6] and with probability pl will go to Servers (po pl-I) [if Server5 is busy it will wait in QueueS]. When a job goes back to S2 it will be directed back to the same server it used the first time thru. The system runs from INIITIME (usually 0) to FINTIME Jobs arrive from input with an interarrival time A that is uniformly distributed between AMIN and AMAX. . Scheduling out of queues is FIFO When jobs get to a server, if the server is free the jobs move directly to the server: otherwise they wait in the queue of that server until their turn to move to the server arrives - A job is serviced by SERVERk for an interval of time STIMEk that is uniformly distributed in the interval SkMIN and SkMAX. When FINTIME occurs, the simulation terminates, that is we do not consider further jobs currently on servers or in queues. Write in C a program to do the discrete-event simulation of a distributed computer system. We assume that the system can be represented as the following queueing network >111>121 ' -+ +-+ SI 52| --+ +-+ v 53 --+ +-+ >>141 + where the symbol represents a queue and the symbol represents a server This diagram represents a distributed system. Sere represents the Client Communication Channel to a system with 3 servers, Server2, Server3, Server4. Server5 represents a shared data store. And Server6 represents again the Client Communication Channel (different from Serverl because communication delays may be different in different directions] To this system arrive jobs (user requests). When a job arrives for the first time to the switch S2 it is directed to the server with the least expected delay (if the delays are the same, then any choice wil be acceptable). Suppose that the job is directed to Server2 (similarly for server 3 and 4). If Server2 is free, the job starts running on Server2; otherwise it waits in Queue2 for Server2 to become free. When a job completes work at a Server2 it goes to the switch S3 where with probability po will proceed to Server6 [if Server6 is busy it will wait in Queue6] and with probability pl will go to Servers (po pl-I) [if Server5 is busy it will wait in QueueS]. When a job goes back to S2 it will be directed back to the same server it used the first time thru. The system runs from INIITIME (usually 0) to FINTIME Jobs arrive from input with an interarrival time A that is uniformly distributed between AMIN and AMAX. . Scheduling out of queues is FIFO When jobs get to a server, if the server is free the jobs move directly to the server: otherwise they wait in the queue of that server until their turn to move to the server arrives - A job is serviced by SERVERk for an interval of time STIMEk that is uniformly distributed in the interval SkMIN and SkMAX. When FINTIME occurs, the simulation terminates, that is we do not consider further jobs currently on servers or in queues
Step by Step Solution
There are 3 Steps involved in it

Get step-by-step solutions from verified subject matter experts


