Question: C++ The class dateType defined in the previous project prints the date in numerical form. Some applications might require the date to be printed in
C++
The class dateType defined in the previous project prints the date in numerical form. Some applications might require the date to be printed in another form, such as March 24, 2017. Derive the class extDateType and add member functions so that the date can be printed these forms:
March 24, 2017
March, 2017
Copy over dateType.h and dateType.cpp. Create a static array to hold the month names and static functions to access and modify the defaults. Write an appropriate constructor for the derived class. Write a program to test the extDateType class.
Here is the UML diagram for this class:
Turn in extDateClass.h, extDateClass.cpp, and your test program. Also turn in one or more screen shots showing the results of your testing.
**********************************************************
***********************************************************
Please make it match my code from last question here your go
#include
using namespace std;
class Date{
private:
int day, month, year;
static Date defaultDate;
public:
void setDefaultDate(int aDay,int aMonth, int aYear);
void setDay(int aDay);
int getDay() const;
void addDay(int x);
void setMonth(int aMonth);
int getMonth() const;
void addMonth(int x);
void setYear(int aYear);
int getYear() const;
void addYear(int x);
int day_of_remain();
int day_of_passed();
bool leapYear(int x)const;
Date(int aDay , int aMonth, int aYear);
void setDate(int aDay , int aMonth, int aYear);
~Date(); //Destructor
};
Date Date::defaultDate(1,1,1500);
Date::Date(int aDay, int aMonth, int aYear)
{
if(aDay==0)
{
this->day = defaultDate.day;
}
else
{
setDay(aDay);
}
if(aMonth==0)
{
this->month = defaultDate.month;
}
else
{
setMonth(aMonth);
}
if(aYear==0)
{
this->year = defaultDate.year;
}
else
{
setYear(aYear);
}
}
int Date:: day_of_remain()
{
if(leapYear(year))
return (366 - day_of_passed());
else
return (365 - day_of_passed());
}
int Date:: day_of_passed()
{
int count[]={0,31, 59, 90, 120, 151, 181, 212, 243, 273, 304, 334, 365};
if ((year % 4==0) && (year % 100 != 0) && (year % 400 == 0 )&& (month>=2)) ((count[month]+day)+1);
return (count[month-1]+day);
}
void Date::setMonth(int a) {
if(a > 0 && a
{
month = a;
}
}
int Date:: getMonth() const {
return month;
}
void Date::addYear(int x)
{
year += x;
if(day == 29 && month == 2 && !leapYear(year))
{
day = 1;
month = 3;
}
}
bool Date::leapYear(int x) const {
if((x%4 == 0 && x%100 != 0) || (x%400==0))
{
return true;
}
else
{
return false;
}
}
void Date::setYear(int aYear){
year=aYear;
}
void Date::setDay(int aDay){
day=aDay;
}
void Date::setDate(int aDay , int aMonth, int aYear){
setDay(aDay);
setMonth(aMonth);
setYear(aYear);
cout
}
Date::~Date(){
cout
}
is the header fileDateType.h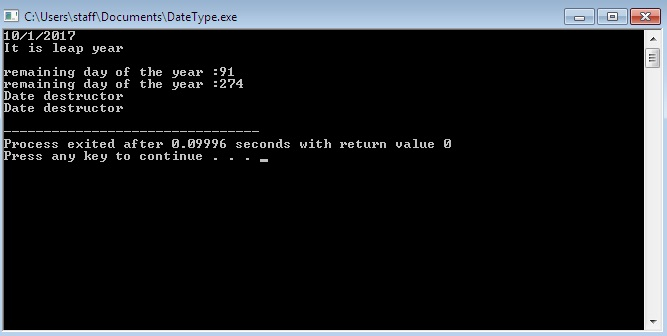
#include "DateType.h"
using namespace std;
int main()
{
Date MyDate(0,0,0);
MyDate.setDate(1,10,2017);
if(MyDate.leapYear(2017))
cout
else
cout
cout
cout
}
is main file
Step by Step Solution
There are 3 Steps involved in it

Get step-by-step solutions from verified subject matter experts


