Question: c++ The code you need to use company.cpp: #include #include #include #include #include using namespace std; class Company { public: Company(string name, int size); //Initializes
c++





The code you need to use
company.cpp:
#include
#include
#include
#include
#include
using namespace std;
class Company
{
public:
Company(string name, int size);
//Initializes the company object so it can accept "size" employee ids.
// Sets the name of the company object to name.
Company( );
//Initializes the company object so it can accept up to 15 employee id's of
//type int, and sets the name of the course to the empty string.
Company(const Company &acompany);
//Copy Constructor - you define this
~Company( );
//Destructor - you define this
//Returns all the dynamic memory used by the company object to the freestore.
void operator =(const Company& rightSide);
//Overloads the == operator, you define this
friend bool operator > (Company& cone, Company& ctwo);
//the overloaded > operator as a friend function, you define this
// methods to set and get the company name, and to set and get employee id numbers and salaries
void setName(string aname);
string getName();
void setEid(int location, int idValue);
int getEid(int location);
float getSalary(int id);
void setSalary (int id, float salary);
int CompanySize; //Number of employees that work for the company
private:
string Cname; // Name of the Company
int *Eid; //pointer to dynamic array that holds the values of the Employee ids
float *Esalary; // dynamic array that holds the salaries for each employess
float getPayroll(); // returns the company payroll (sum of the salaries in the Esalary array).
// Useful for implementing the > operator
}; // end definition of Company interface
// function to print out company information - note, you can redeclare this as a friend function,
// but its parameter acompany must remain pass by value- the same type as declared below
// you define this
void pCompanyInfo(Company acompany);
// function to sort companies into ascending order based on the total company payroll
// it must use the overloaded > operator for the Company class, and the overloaded assignment operator
// you define this. The parameters must remain the same type as declared below
void sortCompanies(Company CompanyList[], int num);
//Program to demonstrate (and test) the use of the class Company.
int main( ) {
Company *Clist[10]; // Array of pointers to Company Objects
ifstream infile; // The file pointer to the data file
char filename[30]; // Name of the file with the Company Data
string cname; // read the name of the company into cname
int csize; //read the number of employees into csize
int eid; // read an employee id into eid
float esalary; // read a salary into esalary
cout
cin >> filename;
infile.open(filename);
if (infile.fail()) {
cout
exit(1);
}
int companyCnt;
infile >> companyCnt; // get the number of companies stored in the file
for (int i = 0; i
// read in a company name
infile >> cname;
// read in a company size
infile >> csize;
Clist[i] = new Company(cname, csize); // instantiate a company and put it on the list of companies
for (int j=0; j
infile >> eid;
Clist[i]->setEid(j, eid);
}
for (int k=0; k
infile >> esalary;
Clist[i]->setSalary(Clist[i]->getEid(k), esalary);
}
} // end reading data from input file
cout
//Print out the information the program just obtained from the file
//The copy constructor you wrote will be tested here, as will
//The destructor you wrote
for (int i = 0; i
pCompanyInfo(*Clist[i]);
cout
//Create an array of Company Objects
Company CompObjects[10];
//Copy the objects pointed to by the Clist array to the array of
//objects CompObjects - your overloaded assignment operator
//will be tested here (and in the sortCompanies function)
for (int i = 0; i
CompObjects[i] = *Clist[i];
// now, sort the company objects into ascending order
// - the overloaded assignment operator
// and the overloaded > operator should be
// tested with the sort you write
sortCompanies(CompObjects, companyCnt);
cout
for (int i = 0; i
pCompanyInfo(CompObjects[i]);
return 0;
} // end main
// Implement the functions to print and sort as well as
// The methods and overloaded operators for the Company class
// function to print out company information - you define this
void pCompanyInfo(Company acompany) {
}
//function to sort the companies stored in the CompanyList into
//order of total payroll (that is, lowest total payroll to highest)
//you define this
void sortCompanies(Company CompanyList[], int num){
}
//Method Definitons for Company
Company::Company()
{
CompanySize = 15;
Cname="";
Eid = new int [CompanySize];
Esalary = new float [CompanySize];
}
Company::Company(string name, int size)
{
CompanySize = size;
Cname = name;
Eid = new int [CompanySize];
Esalary = new float [CompanySize];
}
//Copy Constructor - you define this
Company:: Company(const Company & acompany)
{
}
// destructor - you implement this
Company::~Company()
{
}
void Company::setName(string aname)
{
Cname = aname;
}
string Company::getName()
{
return Cname;
}
void Company::setEid(int location, int idValue)
{
if (location >= 0 && location
Eid[location] = idValue;
else
cout
}
int Company::getEid(int location)
{
return Eid[location];
}
void Company::setSalary(int id, float Value)
{
bool found = false;
for (int i = 0; i
if (Eid[i] == id) {
Esalary[i] = Value;
found = true;
break;
}
if (!found)
cout
return;
}
float Company::getSalary(int id) {
for (int i = 0; i
if (Eid[i] == id)
return (Esalary[i]);
cout
return 0.0;
}
//Overloaded assignment operator - you implement this
void Company::operator =(const Company& right_side)
{
}
// This might be useful for overloading the > operator for the Company Class
float Company::getPayroll() {
float total = 0;
for (int i = 0; i
total += Esalary[i];
return total;
}
// The overloaded > operator for the course class, you are to implement this.
bool operator > (Company& cone, Company& ctwo) {
}
company.dat:
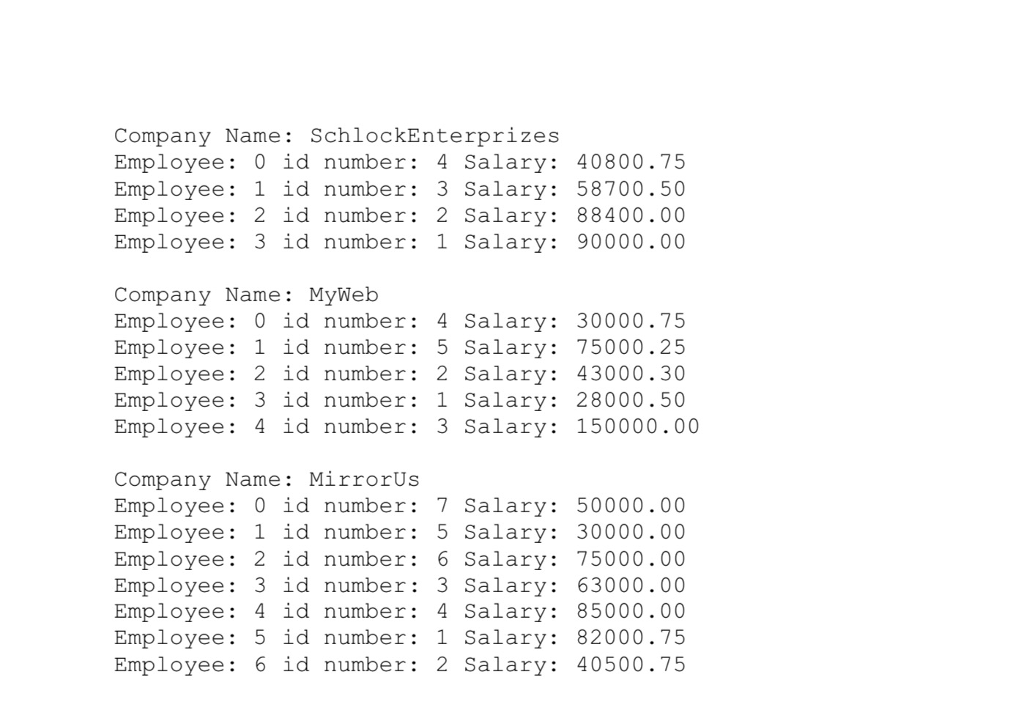
5 ACME 3 1 3 2 45000.00 49000.50 100000.75 MyWeb 5 4 5 2 1 3 30000.75 75000.25 43000.30 28000.50 150000.00 PiFun 2 1 2 50000.75 50000.50 MirrorUs 7 7 5 6 3 4 1 2 50000.00 30000.00 75000.00 63000.00 85000.00 82000.75 40500.75 SchlockEnterprizes 4 4 3 2 1 40800.75 58700.50 88400.00 90000.00
Problem A) Implementing the Big Three for the Company Class and using them (40 points) In lecture we will discuss the Course class to demonstrate the use of dynamic memory in classes, and the need for implementing the copy constructor, destructor, and an overloaded version of the assignment operator when dynamic memory is used in a class (The Course Class and an example of its use will be posted on the Moodle site for this after we go over it in lecture). In this assignment you will implement the big three in similar fashion as they are implemented in the Course class for a different class, the Company class NOTE, there are differences between the two classes (Course and Company). You will have to account for the differences in your implementation of the methods, operators, and functions for the Company class. Specifically, in this assignment you will augment the program (that is, add the necessary C++ code) to what we provide by defining and using following methods, operators, and functions for the Company class: 1) A Copy Constructor - creates a copy of an object of type Company when it is passed "by value" to a function, or when a programmer want to make a copy of an existing company object by calling it. A Destructor - which deallocates the memory dynamically that was dynamically allocated when an instance of the class Company was created (e.g., the destructor is called when an object is deleted, when returning from a function that has a call-by-value parameter that is an object, and in other cases)) 2) 3) An overloaded assignment operator, used when assigning one object of type Company to another object of type Company. 4) An overloaded > (greater than) relational operator 5) A function that prints out the information stored in an object of class Company 6) A sort function that sorts an array of Company objects using the overloaded assignment operator () and overloaded > (greater-than) operator that you define for the class ompany. The C++ Code you are to augment for this assignment is in the file Company.cpp, and available on Moodle, with this assignment description. Overview of the Company Class - from the file Company. cpp in the HW 10 Assignment folder on Moodle. Note, the comments in the class definition for Company below describe what we have provided, and what we require you to implement
Step by Step Solution
There are 3 Steps involved in it

Get step-by-step solutions from verified subject matter experts


