Question: C++ there must be a main.cpp,RSA.cpp and RSA.h please help me Functions Define the functions specified below in RSA.cpp . We will put them together
C++


there must be a main.cpp,RSA.cpp and RSA.h please help me
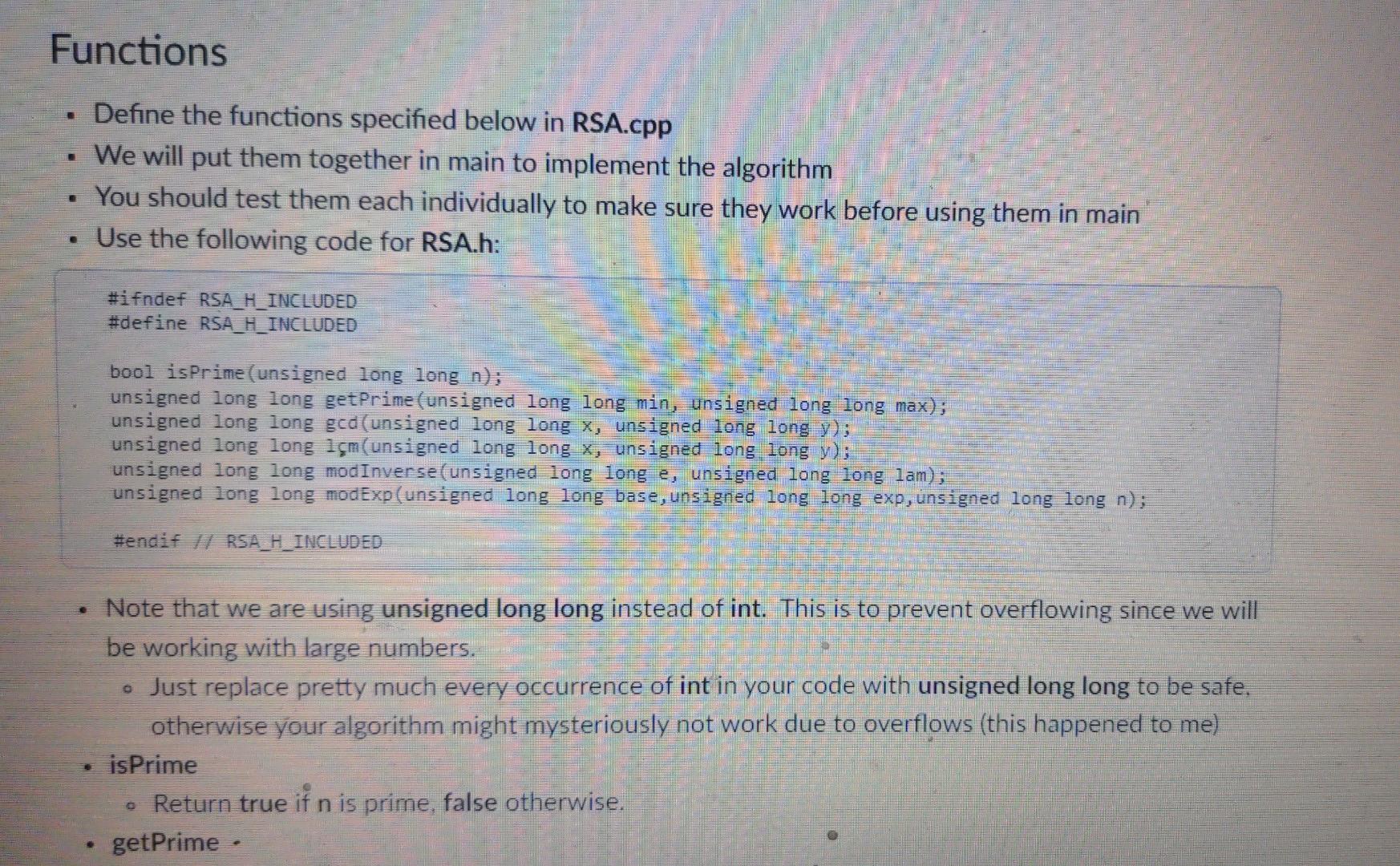
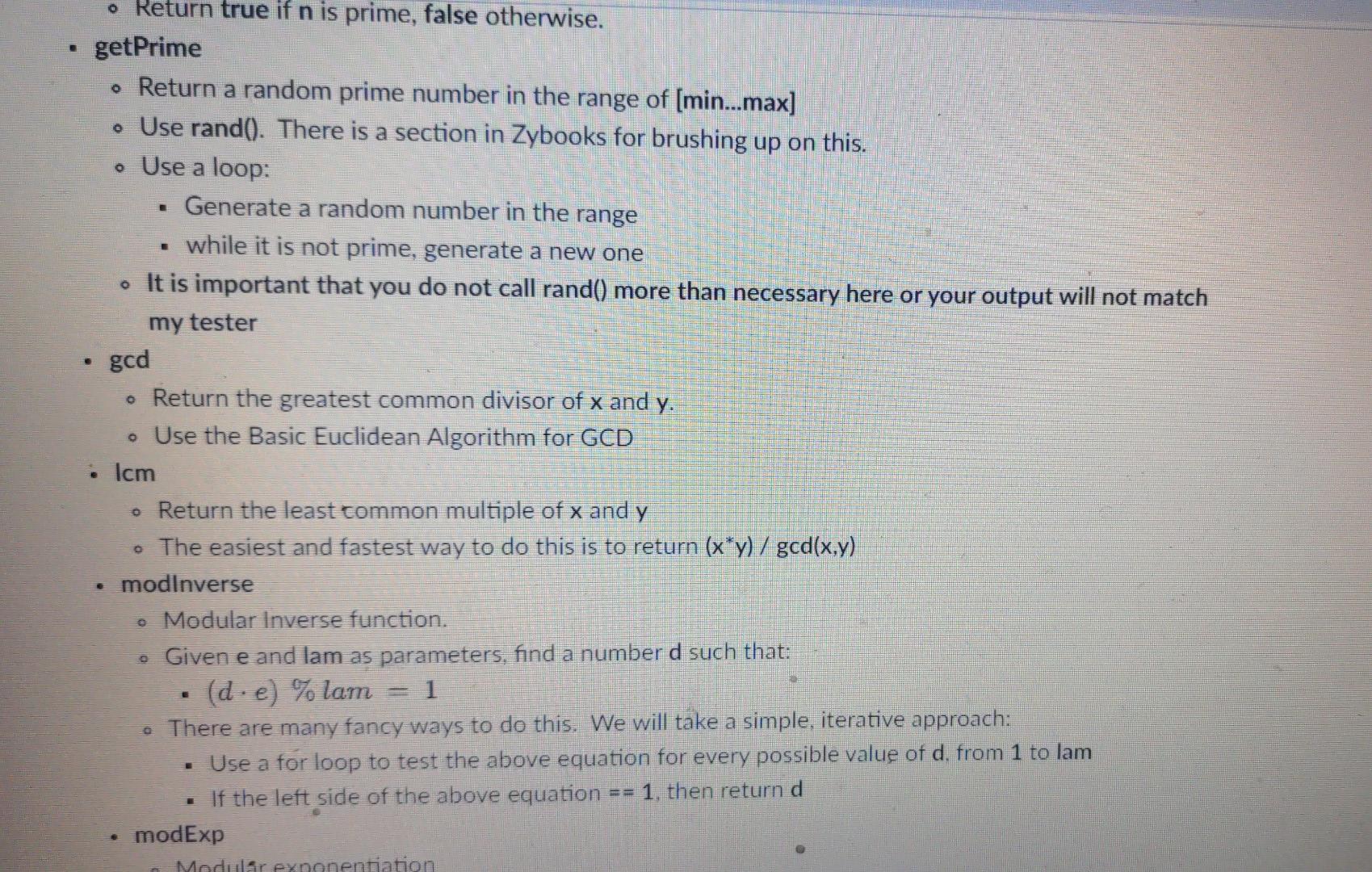
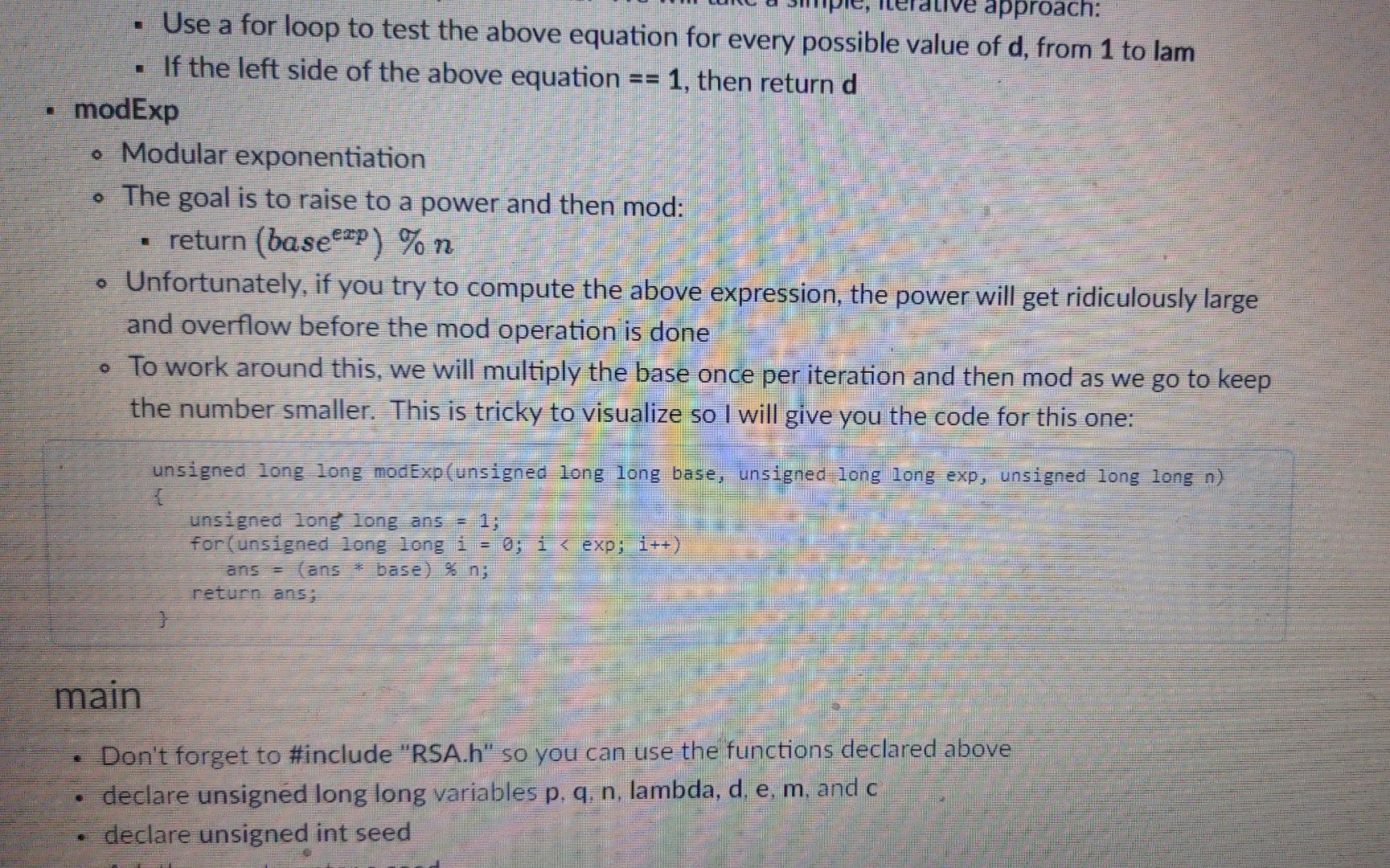
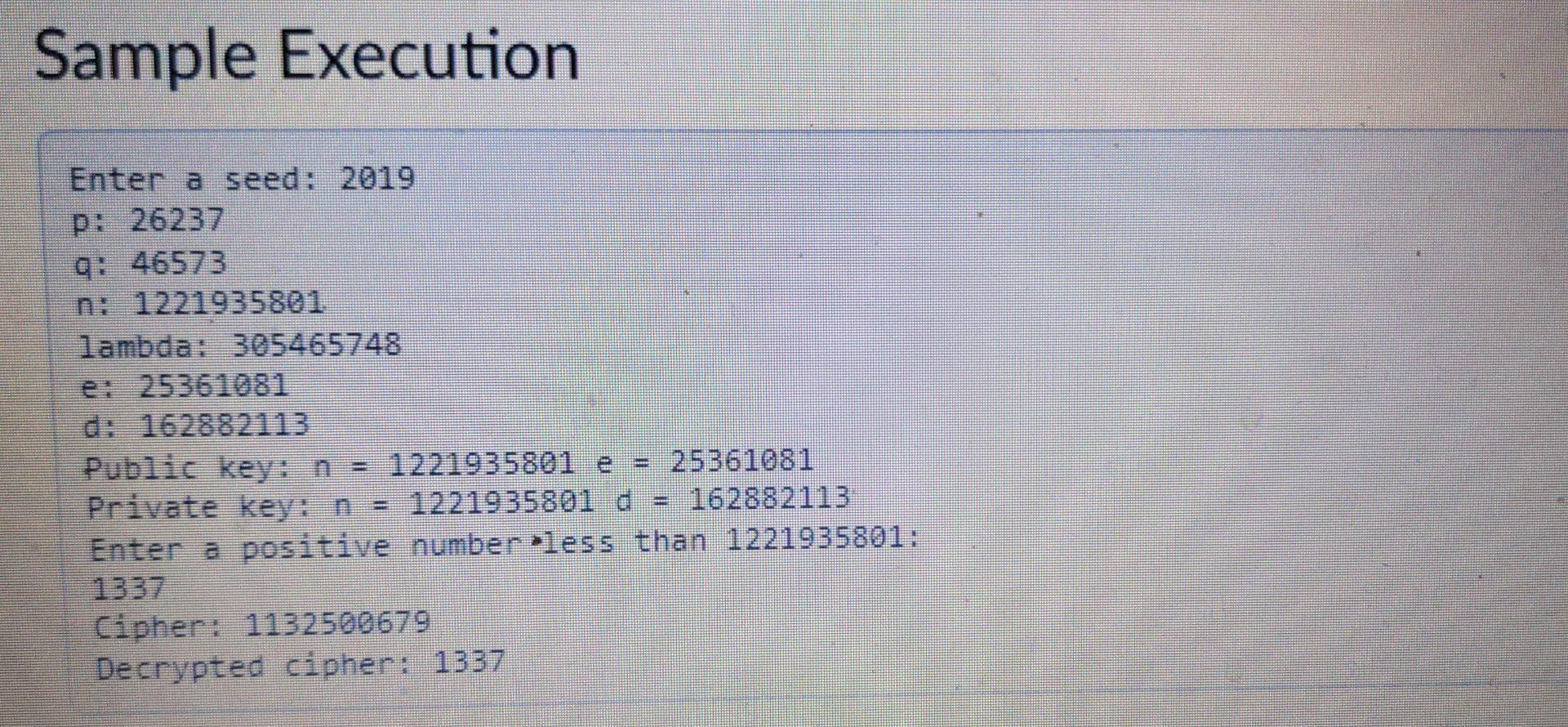
Functions Define the functions specified below in RSA.cpp . We will put them together in main to implement the algorithm You should test them each individually to make sure they work before using them in main Use the following code for RSA.h: #ifndef RSA_H_INCLUDED #define RSA_H_INCLUDED bool isPrime(unsigned long long n): unsigned long long getPrime (unsigned long long min, unsigned long long max): unsigned long long ged(unsigned long long x, unsigned long long y); unsigned long long lm(unsigned long long x, unsigned long long y); unsigned long long modInverse (unsigned long long e, unsigned long long lam); unsigned long long modExp(unsigned long long base, unsigned long long exp, unsigned long long n); #endif // RSA_H_INCLUDED Note that we are using unsigned long long instead of int. This is to prevent overflowing since we will be working with large numbers. Just replace pretty much every occurrence of int in your code with unsigned long long to be safe. otherwise your algorithm might mysteriously not work due to overflows (this happened to me) isPrime Return true if n is prime, false otherwise. getPrime o keturn true if n is prime, false otherwise. getPrime . Return a random prime number in the range of [min...max] a . Use rand(). There is a section in Zybooks for brushing up on this. Use a loop: Generate a random number in the range while it is not prime, generate a new one . It is important that you do not call rand() more than necessary here or your output will not match my tester god . Return the greatest common divisor of x and y. . Use the Basic Euclidean Algorithm for GCD Icm Return the least common multiple of x and y The easiest and fastest way to do this is to return (x*y) / gcd(x,y) modlnverse Modular Inverse function. . Given e and lam as parameters, find a number d such that: (de) % lam = 1 . There are many fancy ways to do this. We will take a simple, iterative approach: Use a for loop to test the above equation for every possible value of d. from 1 to lam If the left side of the above equation == 1, then return d modExp Modulr pynonentiation E approach: Use a for loop to test the above equation for every possible value of d, from 1 to lam If the left side of the above equation 1, then return d modExp . Modular exponentiation The goal is to raise to a power and then mod: return (baseexP) %n . Unfortunately, if you try to compute the above expression, the power will get ridiculously large and overflow before the mod operation is done To work around this, we will multiply the base once per iteration and then mod as we go to keep the number smaller. This is tricky to visualize so I will give you the code for this one: unsigned long long modExp(unsigned long long base, unsigned long long exp, unsigned long long n) unsigned long long ans = 1; for(unsigned long long i = 0; i . This means that p is between 8 and 16 bits in length Do the same for a Output the values of p and a The modulus n is obtained by multiplying the two large prime numbers, p and q: Assign n = p *a Output the value of n The next steps use modular arithmetic number theory to generate the variables. We will implement the steps, but fully understanding the theory behind them is not required. Assign lambda to the lcm of p - 1 and q - 1 Output the value of lambda Lambda is a value that we will use to generate e and d In the next step we will generate e e must be a prime smaller than lambda that does not divide evenly into lambda Call getPrime to assign toe a random prime in the range [2...lambda - 1] a - use lo genelde e aha a . In the next step we will generate e e must be a prime smaller than lambda that does not divide evenly into lambda Call getPrime to assign to e a random prime in the range [2...lambda - 1] Use a loop to ensure that lambda is not divisible by e: while lambda is divisible by e, assign to e a new random prime in the range [2...lambda - 1] Output the value of e o assign to d the modlnverse of e and lambda Output the value of d Output the public key, which is the values of n and e Output the private key, which is the values of n and d Prompt the user to enter the plain message m, which must be a positive number less than the value of o input m Use modExp to assign to cipher c the modular exponent (m) % n This is your encrypted value, which is what a client would send to a server Output the value of the cipher Decrypt and output the cipher c by calculating the modular exponent (cm) % n . You should get the original message m This is what the server, having the private key d and n, would do to decrypt the client's message Sample Execution Sample Execution Enter a seed: 2019 p: 26237 Q: 46573 n: 1221935801 lambda: 305465748 e: 25361081 do 162882113 Public key: n = 1221935801 e = 25361081 Private key: n = 1221935801 d 162882113 Enter a positive numberless than 1221935801: Cipher: 1132500679 Decrypted cipher: 1337 If your encryption / decryption is working but your random numbers are different, make sure your calls to rand() in getPrime are using the correct ranges and that you are not calling rand() or srand() more often than necessary
Step by Step Solution
There are 3 Steps involved in it

Get step-by-step solutions from verified subject matter experts


