Question: calculating an installment loan payment using simple interest(please make sure to check on all) Assignment: Chapter 07 Using Consumer Loans Attempts Keep the Highest/6 8.
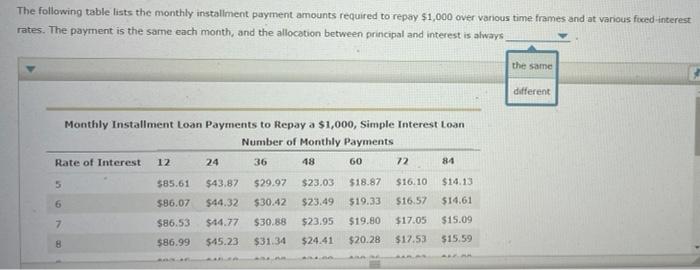
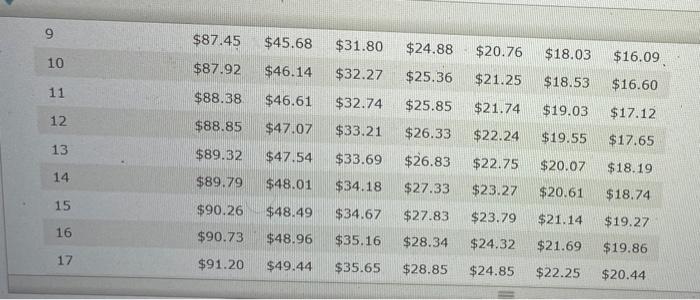
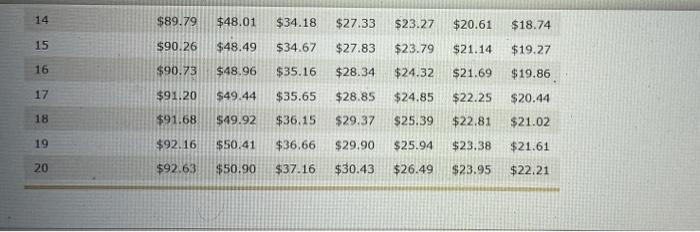
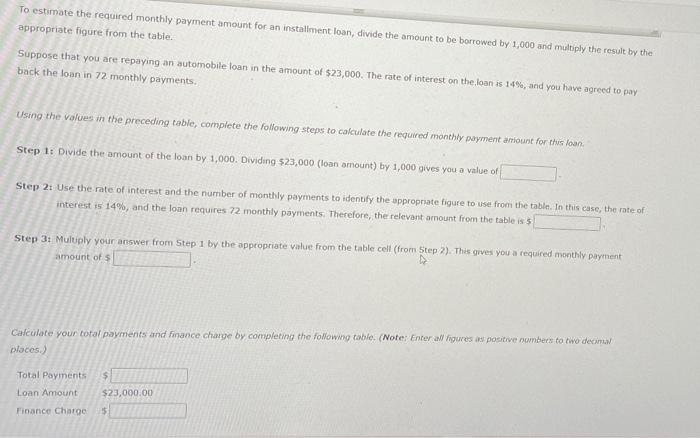
Assignment: Chapter 07 Using Consumer Loans Attempts Keep the Highest/6 8. Calculating an installment loan payment using simple interest Calculating the Loan Payment on a Simple Interest Installment Loan Installment loans allow borrowers to repay the loan with periodic payments over time. They are more common than single-payment loans because it is easier for most people to pay a fixed amount periodically (usually monthly) than budget for paying one big amount in the future. Interest on installment loans may be computed using the simple interest method or the add-on method, For an installment loan using simple interest and equal payments throughout the life of the lom, a portion of each repayment is dedicated to the principal and a portion to the interest. Remember that interest is charged only on the outstanding balance. This means that we each payment is made more of it is allocated to the finance charge The following table lists Jayment amounts required to repay $1,000 over various time frames and at various foed interest rates. The payment is the reducing the principal the allocation between principal and interest is always The following table lists the monthly installment payment amounts required to repay $1,000 over various time frames and at various fooed interest rates. The payment is the same each month, and the allocation between principal and interest is always the same different Monthly Installment Loan Payments to Repay a $1,000, Simple Interest Loan Number of Monthly Payments Rate of Interest 12 24 36 48 60 72 86 5 585.61 $43.87 $29.97 $23.03 $18.87 $16.10 $14.13 6 $86.07 $44.32 $30.42 $23.49 $19.33 $16.57 $14.61 7 $86.53 $44.77 $30.88 $23.95 $19.80 $17.05 $15.09 B 586.99 $45.23 $31.34 $24.41 $20.28 $17.53 $15.59 9 $87.45 $45.68 $31.80 $24.88 $20.76 $18.03 10 $87.92 $46.14 $32.27 $25.36 $21.25 $18.53 11 $88.38 $32.74 $16.09 $16.60 $17.12 $17.65 $25.85 $46.61 $47.07 $21.74 $19.03 12 $88.85 $33.21 $26.33 $22.24 $19.55 13 $89.32 $47.54 $33.69 $26.83 $22.75 $20.07 $18.19 14 $89.79 $48.01 $34.18 $27.33 $23.27 $20.61 $18.74 15 $48.49 $34.67 $27.83 $90.26 $90.73 $23.79 $21.14 $19.27 16 $48.96 $35.16 $28.34 $24.32 $21.69 $19.86 17 $91.20 $49.44 $35.65 $28.85 $24.85 $22.25 $20.44 14 $89.79 $48.01 $34.18 $27.33 $23.27 $20.61 $18.74 15 $90.26 $48.49 $34.67 $23.79 $21.14 $19.27 $27.83 $28.34 16 $90.73 $48.96 $35.16 $24.32 $21.69 $19.86 17 $91.20 $24.85 $20.44 $49.44 $49.92 $35.65 $36.15 $28.85 $29.37 $22.25 $22.81 18 $91.68 $25.39 $21.02 19 $92.16 $50.41 $36.66 $29,90 $25.94 $23,38 $21.61 20 $92.63 $50.90 $37.16 $30.43 $26.49 $23.95 $22.21 To estimate the required monthly payment amount for an installment loan, divide the amount to be borrowed by 1,000 and multiply the result by the appropriate figure from the table. Suppose that you are repaying an automobile loan in the amount of $23,000. The rate of interest on the loan is 14%, and you have agreed to pay back the loan in 72 monthly payments. Using the values in the preceding table, complete the following steps to calculate the required monthly payment amount for this loan Step 1: Divide the amount of the loan by 1,000. Dividing $23,000 (loan amount) by 1,000 gives you a value of Step 2: Use the rate of interest and the number of monthly payments to identify the appropriate figure to use from the table. In this case, the rate of interest is 14%, and the loan requires 72 monthly payments. Therefore, the relevant amount from the table is 5 Step 3: Multiply your answer from Step 1 by the appropriate value from the table cell (from Step 2). This gives you a required monthly payment amount of s Calculate your total payments and finance charge by completing the following table. (Note: Enter all figures a positive numbers to two decin places. Total Payments $ Loan Amount $23,000.00 Finance Charge 5
Step by Step Solution
There are 3 Steps involved in it

Get step-by-step solutions from verified subject matter experts


