Question: Can anyone please explain how to work this out? Qualitative Analysis: PO43;CO32,S2,I;Cl, and NO3 How will you collect data for this experiment? virtuall Unknown Assignment



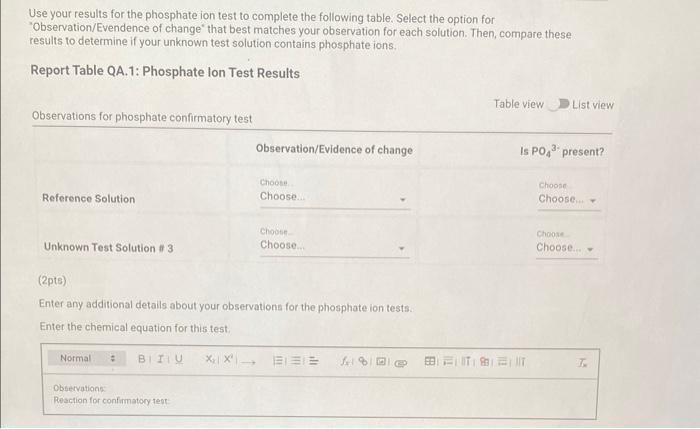
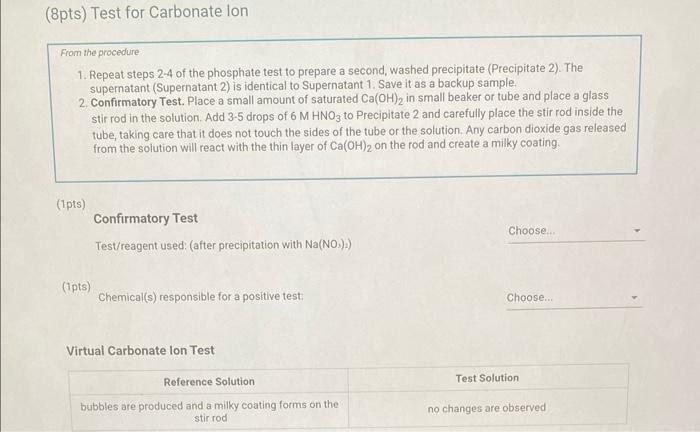
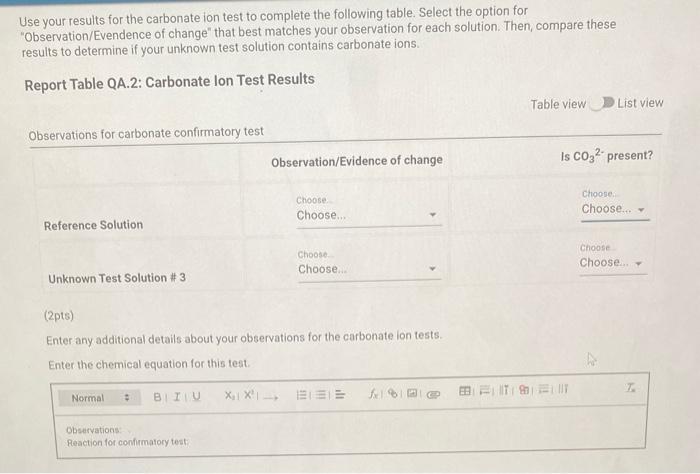
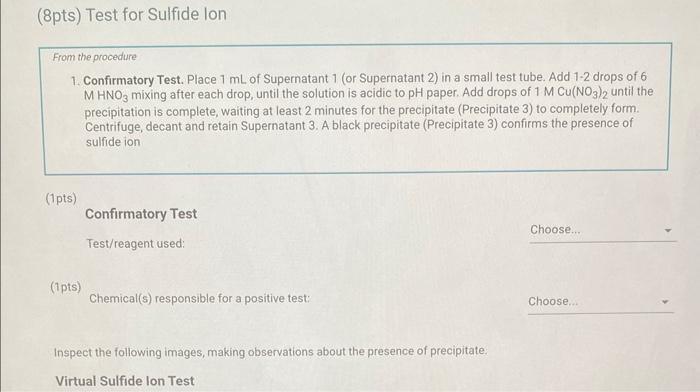

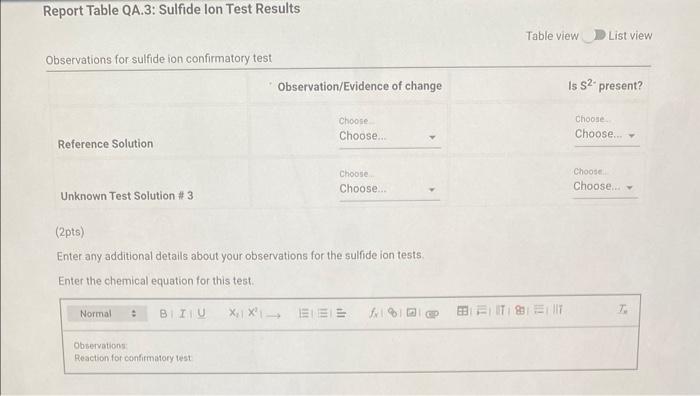
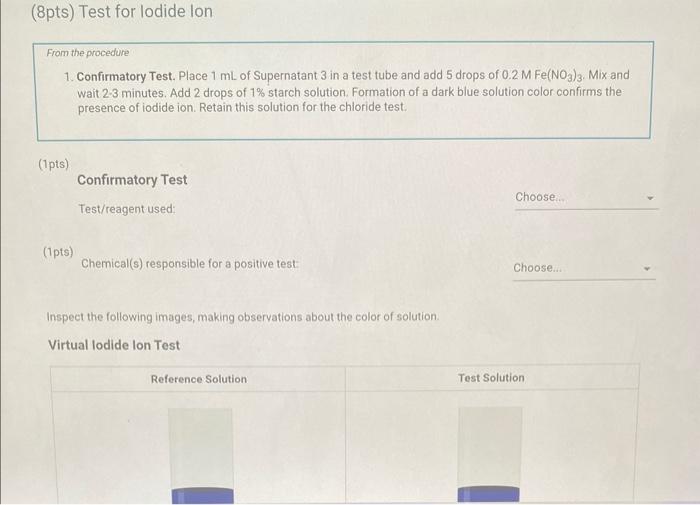
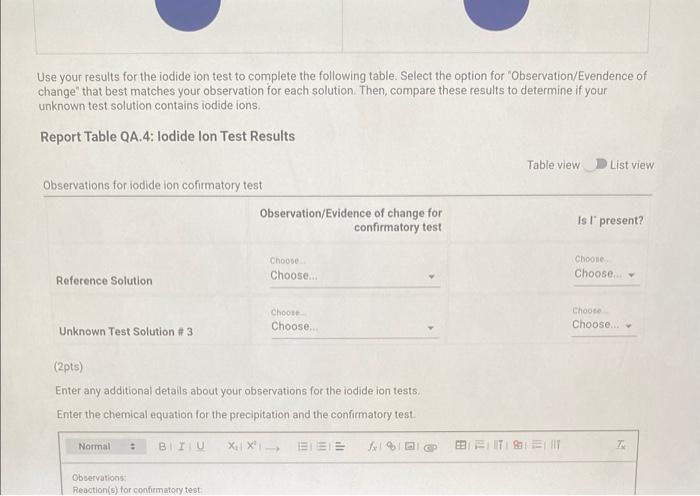
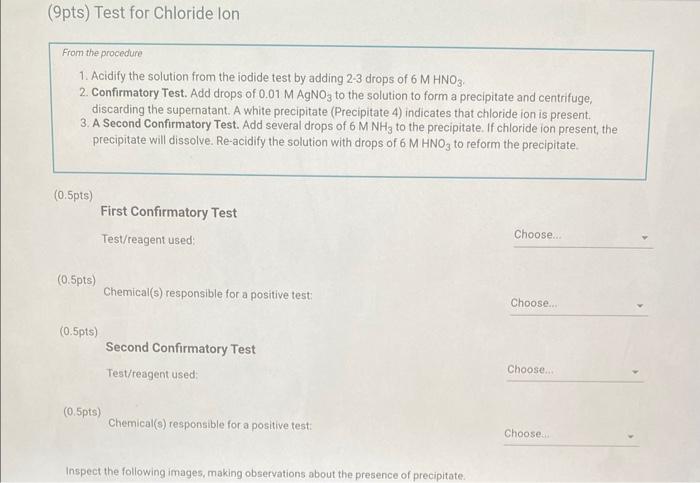
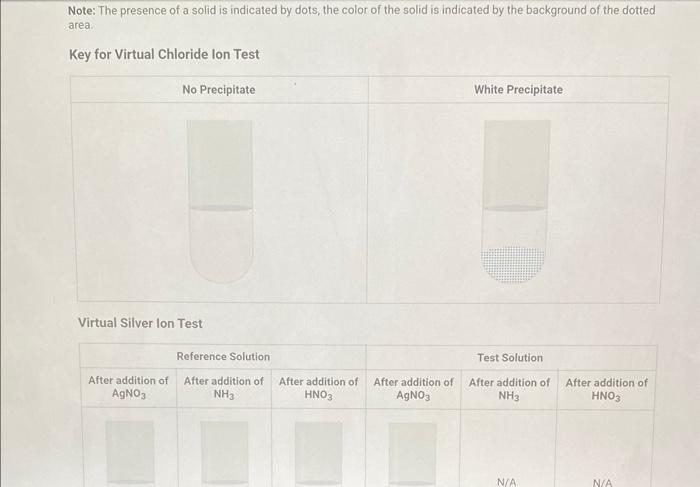
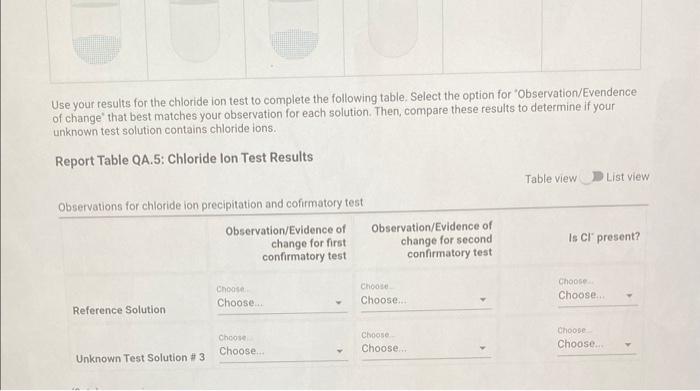
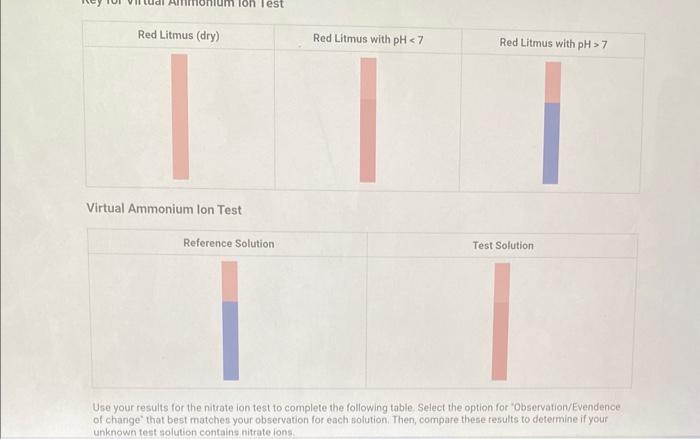
Qualitative Analysis: PO43;CO32,S2,I;Cl, and NO3 How will you collect data for this experiment? virtuall Unknown Assignment Procedure Overview - Two solutions are tested with various reagents in this analysis: (1) a reference solution containing all six of the anions and (2) an unknown test solution containing three of the anions. By comparing your observations during the testing of the two solutions, you will be able to identify the three. anions in the test solution. All tests are qualitative; only identification of the anion(s) is required. - You will start with a sample that contains the six anions (reference solution) and analyze it according to the Experimental Procedure. - As you carry out each test, stop and record your observations on the Report Sheet. After the presence of a anion is confirmed, save each test tube (labeled) that contains the characteristic appearance of a anion. Compare these saved tubes with the tubes from your analysis of the test solution (unknowns). - To analyze for anions in your test solution, place the test solution alongside the reference solution during the analysis. As you progress through the procedure, perform the same tests on the test solution that you performed on the reference solution. Record your comparative observations on the report sheet and use these to determine which anions are present. Label all solutions and retain all tubes until untill the experiment is complete. From the procedure 1. Prepare a warm water bath (60C) in a beaker on a hot plate or using a ring stand and Bunsen burner. 2. Place 1.5mL of the reference solution in a small test tube. Test pH with test paper and, if acidic, add no more than 3-4 drops of 3MNH3, stirring after each drop, until the solution is basic. 3. Add 10-12 drops of 0.1MCa(NO3)2 with mixing, until the precipitation is complete. 4. Centrifuge. Decant the supernatant (Supernatant 1) into a small test tube and retain for further testing. 5. Wash the precipitate (Precipitate 1) by mixing with 1mL of water and recentrifuging. Discard the washing. Repeat for a second wash. 6. Confirmatory Test. Dissolve Precipitate 1 in a few drops of 6MHNO3 and then add 1mL of 0.5M (NH4)2MOO4. Mix, then place in a warm water bath (60C) for a minute. Let stand at room temperature for 10-15 minutes. The slow formation of a yellow precipitate confirms the presence of phosphate ion. Virtual Phosphate lon Test Use your results for the phosphate ion test to complete the following table. Select the option for "Observation/Evendence of change' that best matches your observation for each solution. Then, compare these results to determine if your unknown test solution contains phosphate ions. Report Table QA.1: Phosphate lon Test Results (2ptB) Enter any additional details about your observations for the phosphate ion tests. Enter the chemical equation for this test. From the procedure 1. Repeat steps 24 of the phosphate test to prepare a second, washed precipitate (Precipitate 2). The supernatant (Supernatant 2) is identical to Supernatant 1. Save it as a backup sample. 2. Confirmatory Test. Place a small amount of saturated Ca(OH)2 in small beaker or tube and place a glass stir rod in the solution. Add 3.5 drops of 6MHNO3 to Precipitate 2 and carefully place the stir rod inside the tube, taking care that it does not touch the sides of the tube or the solution. Any carbon dioxide gas released from the solution will react with the thin layer of Ca(OH)2 on the rod and create a milky coating. Use your results for the carbonate ion test to complete the following table. Select the option for "Observation/Evendence of change" that best matches your observation for each solution. Then, compare these results to determine if your unknown test solution contains carbonate ions. Report Table QA.2: Carbonate lon Test Results Table view List view (2pts) Enter any additional details about your observations for the carbonate ion tests. Enter the chemical equation for this test. (8pts) Test for Sulfide lon From the procedure 1. Confirmatory Test. Place 1mL of Supernatant 1 (or Supernatant 2) in a small test tube. Add 1-2 drops of 6 MHNO3 mixing after each drop, until the solution is acidic to pH paper. Add drops of 1MCu(NO3)2 until the precipitation is complete, waiting at least 2 minutes for the precipitate (Precipitate 3) to completely form. Centrifuge, decant and retain Supernatant 3. A black precipitate (Precipitate 3 ) confirms the presence of sulfide ion Inspect the following images, making observations about the presence of precipitate. Virtual Sulfide Ion Test Use your results for the sulfide ion test to complete the following table. Select the option for "Observation/Evendence of change" that best matches your observation for each solution. Then, compare these results to determine if your unknown test solution contains sulfide ions. Report Table QA.3: Sulfide Ion Test Results Table view List view (2pts) Enter any additional details about your observations for the sulfide ion tests. Enter the chemical equation for this test. From the procedure 1. Confirmatory Test. Place 1mL of Supernatant 3 in a test tube and add 5 drops of 0.2MFe(NO3)3. Mix and wait 2.3 minutes. Add 2 drops of 1% starch solution. Formation of a dark blue solution color confirms the presence of iodide ion. Retain this solution for the chloride test. Use your results for the iodide ion test to complete the following table. Select the option for "Observation/Evendence of change" that best matches your observation for each solution. Then, compare these results to determine if your unknown test solution contains iodide ions. Report Table QA.4: lodide lon Test Results Table view: List view (2pts) Enter any additional details about your observations for the iodide ion tests. Enter the chemical equation for the precipitation and the confirmatory test. From the procedure 1. Acidify the solution from the iodide test by adding 23 drops of 6MHNO. 2. Confirmatory Test. Add drops of 0.01MAgNO3 to the solution to form a precipitate and centrifuge, discarding the supernatant. A white precipitate (Precipitate 4) indicates that chloride ion is present. 3. A Second Confirmatory Test. Add several drops of 6MNH3 to the precipitate. If chloride ion present, the precipitate will dissolve. Re-acidify the solution with drops of 6MHNO to reform the precipitate. Note: The presence of a solid is indicated by dots, the color of the solid is indicated by the background of the dotted area. Key for Virtual Chloride lon Test Virtual Silver lon Test Use your results for the chloride ion test to complete the following table. Select the option for "Observation/Evendence of change' that best matches your observation for each solution. Then, compare these results to determine if your unknown test solution contains chloride ions. Report Table QA.5: Chloride lon Test Results Enter the chemical equation for the precipitation and the confirmatory test (8pts) Test for Nitrate lon Froum the procedure 1. Prepare a hot water bath (90C) and obtain a piece of red litmus paper. 2. Place 1.5mL of the reference solution in a small test tube. Add 56 drops of 6MNaOH and mix. Add a few granules of aluminum metal and place the in the hot water bath. 3. Confirmatory Test. Hold the red litmus paper just inside the mouth of the test tube. Any NH3 vapors leaving the tube will turn the paper a uniform blue. Small blue spots that may appear are due to spray of the basic solution. Look for a uniform change in the color of the litmus paper. Virtual Ammonium lon Test Use your results for the nitrate ion test to complete the following table Select the option for 'Observation/Evendence of change' that best matches your observation for each solution. Then, compare these results to determine if your unknown test solution contains nitrate ions. Report Table QA.6: Nitrate lon Test Results Table view Dist view Observations for litmus paper after nitrate ion test ( 2pts) Enter any additional details about your observations for the nitrate ion tests. Enter the chemical equation for this test
Step by Step Solution
There are 3 Steps involved in it

Get step-by-step solutions from verified subject matter experts


