Question: can i have some idea with my code? from hidden import (apply_move, is_duplicate_move, path_coordinate_is_valid) # Part 1 def generate_next_path(last_position, previous_position, possible_moves): #### STUDENTS TO IMPLEMENT
can i have some idea with my code? 

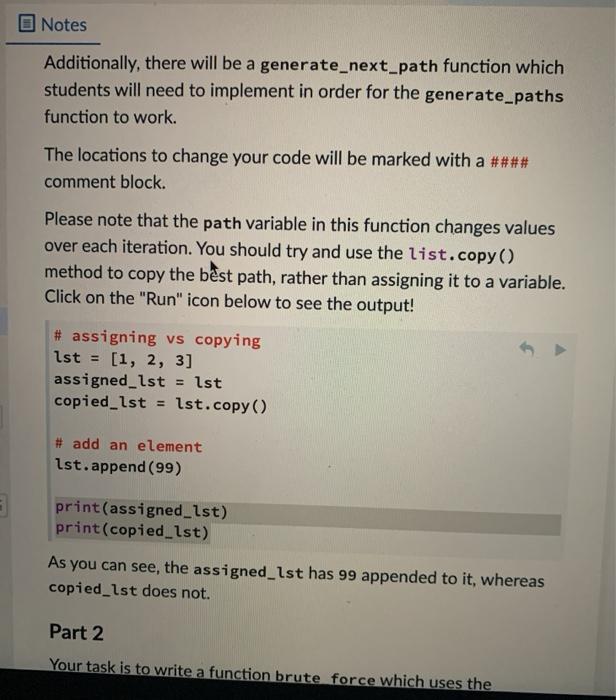

from hidden import (apply_move, is_duplicate_move, path_coordinate_is_valid)
# Part 1
def generate_next_path(last_position, previous_position, possible_moves):
#### STUDENTS TO IMPLEMENT THIS FUNCTION #####
# 1. Calculate the last move
# 2. Find the next available move in possible_moves list
# 3. Replace the last move by the next available move found
# 4. Return the resulting turtle position
for pm in possible_moves:
if (previous_position[0]+pm[0],previous_position[1]+pm[1]) == last_position:
continue
return pm
def generate_paths(grid):
N = len(grid)
# possible moves for the x, y coordinate (right, down, diagonal-right-down)
possible_moves = [(1, 0), (0, 1), (1, 1)]
# path is a sequence of visited cells
path = [(0, 0)]
#### STUDENTS TO FILL BELOW ########
# you can add your variables here if you are making any
vaildpath = []
####################################
while True:
# explore current path whilst the coordinate is valid (inside the cave)
while path_coordinate_is_valid(path[-1], N):
# add the next move
path.append(apply_move(path[-1], possible_moves[0]))
# if our current location is the goal location
if path[-1] == (N, N):
# then remove the last move which goes past the grid walls
path.pop()
#### STUDENTS TO FILL BELOW ########
# store your current path somewhere
# The placeholder code below just prints out all the paths:
# path.append(apply_move(path[-1], path[-2], possible_moves[0]))
print(path)
vaildpath = path.copy()
# return path
return vaildpath
####################################
# remove future moves that have already been explored
while len(path) > 1 and is_duplicate_move(path[-1], path[-2]):
path.pop()
# if we have finished the final path, then we are done!
if len(path)
#### STUDENTS TO CHANGE BELOW ######
# replace None with what you want to return
# (i.e your saved paths)
# path = generate_path(grid)
return path
####################################
else:
# otherwise, generate the next possible path
path[-1] = generate_next_path(path[-1], path[-2], possible_moves)
# Part 2
def brute_force(matrix):
maxv = 0
total = 0
best_path=[]
for path in generate_paths(matrix):
for pos in path:
total += matrix[pos[1],pos[0]]
if maxv
maxv = total
best_path = path.copy()
return best_path
brute_force([[0, 0, 0, 0], [0, 0, 0, 0], [0, 0, 0, 0], [0, 0, 0, -1000]])
Step by Step Solution
There are 3 Steps involved in it
1 Expert Approved Answer
Step: 1 Unlock


Question Has Been Solved by an Expert!
Get step-by-step solutions from verified subject matter experts
Step: 2 Unlock
Step: 3 Unlock


